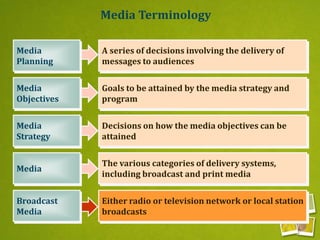
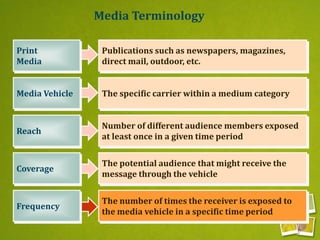
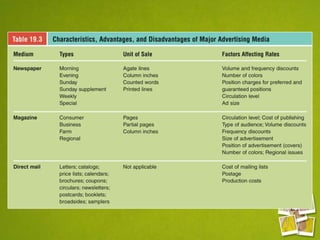
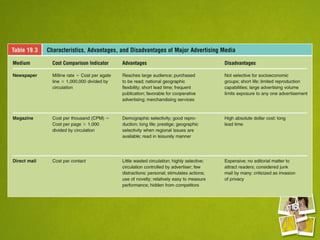
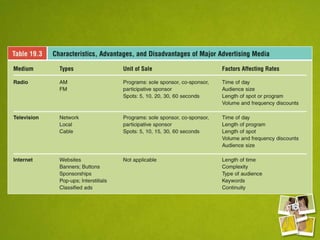
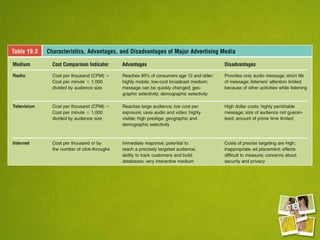
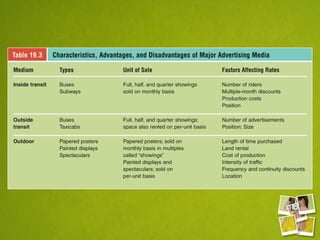
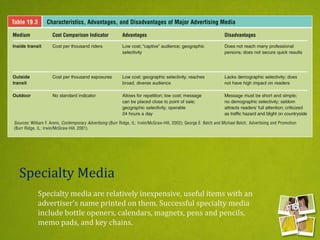
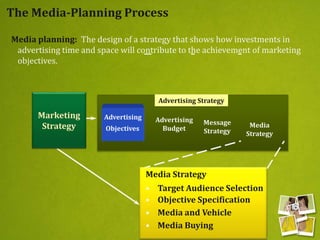
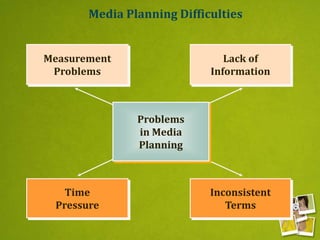
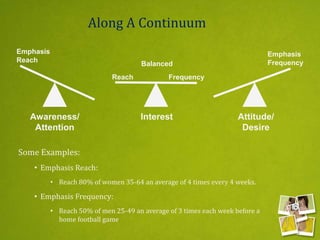
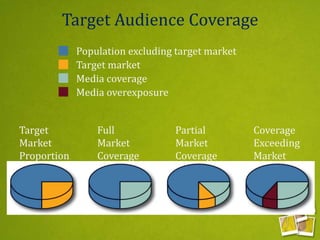
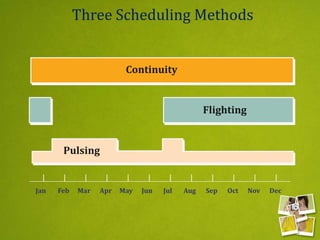
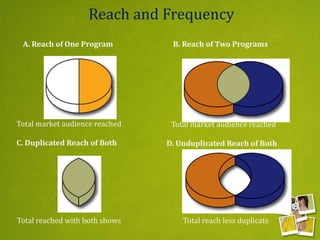
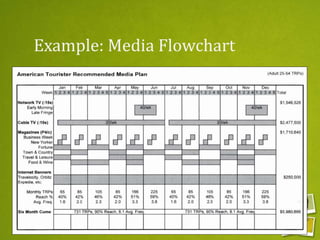
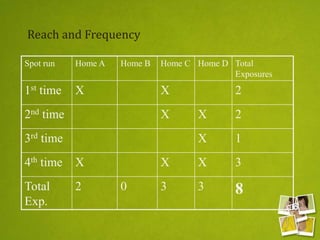
Media planning involves setting objectives for reach, frequency, and weight to deliver messages to target audiences. A media strategy is then developed considering the target, budget, scheduling, creative elements, and weight of delivery across different media. Media buying implements the strategy by selecting specific media vehicles, negotiating placements, and monitoring performance. Research is crucial to the planning and buying processes to understand audiences, costs, and media environment.