MedChem Assignments Histamine, H1, Proton Pump & Cancer (Rahul Pals)
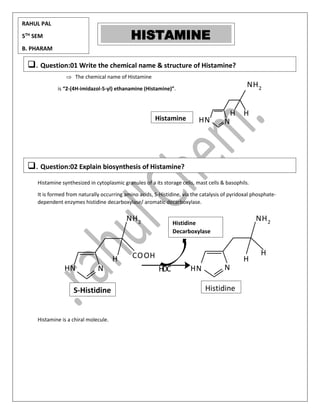
- 1. The chemical name of Histamine is “2-(4H-imidazol-5-yl) ethanamine (Histamine)”. Histamine synthesized in cytoplasmic granules of a its storage cells, mast cells & basophils. It is formed from naturally occurring amino acids, S-Histidine, via the catalysis of pyridoxal phosphate- dependent enzymes histidine decarboxylase/ aromatic decarboxylase. Histamine is a chiral molecule. HISTAMINE ❑. Question:01 Write the chemical name & structure of Histamine? ❑. Question:02 Explain biosynthesis of Histamine? NH2 N HN H H Histamine HDC COOH HN N HN N H NH2 NH2 H H S-Histidine Histidine Histidine Decarboxylase RAHUL PAL 5TH SEM B. PHARAM
- 2. Drugs the block the action of histamine of H1, H2, H4 & H4 receptors. The development of Antihistamines Began by the discovery of “Piperoxam”. A. Drugs that inhibits the histamine release. B. Drugs that inhibits the action of released histamine. ❑ H1 Antagonists (I, II, III generation Antagonists) ❑ H2 Antagonists. ❑ H3 Antagonists. C. Drugs having dual action. H1 Antagonists (1st Generation) The amine is substituted with the small alkyl group. Classification: The commonly used antihistamines may be classified on the basis of their chemical structures: . Amino Alkyl Ethers: Diphenhydramine, Doxylamine, Clemastine, medrylamine, Carbinoxmine, Bromodiphenhydramine. . Ethylenediamine: Tripelenamine, pyrilamine, methapyrilene, thonzalamine, Zolamine. . Propyl Amine Derivatives: Saturated drugs: pheniramine, chlorpheramine, Unsaturated Drugs: Pyrrobutamine, triprolidine. . Phenothiazine Derivatives. Promethazine, Trimeprazine. . Piperazine Derivative. Cyclazine, chlorcyclines, meclizine. H1 Antagonists (2nd Generation) Laratidine, Estemizole. H1 Antagonists (3rd Generation) Acrivestine. H2 Antagonists Cemetidine, famotidine, ranitidine, nizatidine. H3 Antagonist Omeprazole, Lansoprazole, Rabeprazole, Pantoprazole. ❑. Question: 03 Classification of Antihistamines?
- 3. Histamines receptors are belonging to the family of G-Protein Coupled receptors. These subtypes of histamine receptors: A. H1. B. H2. C. H3. D. H4. Receptors H1 H2 H3 H4 Locations Brain, GIT, CVS, Lymphocytes. Myocardial cells, parietal cells. CNS, Myentric plexus, gastric Mucosa. Spleen, thymus, T-cells, eosinophils. ❑. Question: 04 Name the different type of Histamine receptors & their Distribution?
- 4. 01. Amino Alkyl Ether: Diphenhydramine, Bromodiphenhydramine, Dimenhydrinate, Doxylamine succinate, Diphenylpyraline. 02. Ethylenediamine: Mepyramine, Tripelennamine, Thonzylamine, Zolamine. 03. Thiophene Derivatives: Methapyrilene, Methaphenilene, Thenyldiamine, Chlorothen Citrate. 04. Cyclic Basic Chain Analogues: A. Imidazoline: Antazoline. B. Piperazine: Cyclizine, Chlorcyclizine, Meclizine, Buclizine. C. Piperidine: Thenalidine Tartarate. 05. Phenothiazine: Promethazine, Promethazine Teolclate, Trimeprazine, Methdilazine. 06. Second-Generation Non-Sedating Antihistamines: Terfenadine, Astemizole, Loratadine, Acrivastine. 07. Miscellaneous Agents: Phenindamine, Triprolidine, Chlorpheniramine, Cyproheptadine. Sedative antihistamines: N-Dimethylthenamine.HCl & 1-Methyl Piperidine. Non-Sedative Antihistamine: Fexofenadine, Citrizine Levocetrazine, loratadine, Desloratadine, Acrivastine. Ar is Aryl: Phenyl, substituted phenyl, heteroaryl groups such as 2-pyridyl. Ar1: Second aryl or aryl methyl group. (CH2) n: Represents a carbon chain, usually ethyl. NRR1 = Basic, terminal amine functional group. X = Connecting atom of 0, C & N. ❑. Question:01 Give the classification of H1 Antagonists? ❑. Question:02 Explain SAR of Amino Alkyl Ethers? H1 ANTAGONISTS R R1
- 5. Mepyramine, Tripelennamine, Thonzylamine, Zolamine. ❑. Question:03 Give Chemical Structure of Amino Alkyl Ethers? ❑. Question:04 Give Chemical Structure of Ethylenediamine Derivatives? Mepyramine Tripelennamine Thonzylamine Zolamine
- 6. ANS: Structure Activity Relationship: ➢ Ethylenediamine derivatives are characterized by “Nitrogen” connecting atom. ➢ Phenbenzamine was first clinically useful member. ➢ Replacement of phenyl moiety of Phenbezamine with a 2-pyridyl system yielded “tripelennamine”. ➢ Replacements of benzyl group of tripelennamine with a 2-thienulmethyl group provided methapyrilene. ➢ Replacement of tripelennamine with 2pyridyl group with a pyrimidinyl moiety yields thonzylamine. ➢ The anticholinergic & antiemetics action of these compounds are low. #. Mode of Action: H1 Antagonists act by competitively inhibiting the effects of Histamine at H1 receptor. H1 receptor blockade results in decreased vascular permeability. Reduction of pruritus, relaxation of smooth muscle in the respiratory. GIT. #. USES: 01. Allergic Reactions. 02. Block the release of histamine. 03. Not effective in humoral & cell mediated allergies. ❑. Question:05 Explain SAR of Ethylenediamine Derivatives? ❑. Question:06 Gives Uses & Mode of Action of H1 Antagonists?
- 7. The second-generation drugs have little affinity for muscarinic, adrenergic receptors. The second-Generation have a relative low affinity for central H1 receptor & largely from sedation. Examples: Terfenadine, Fexofenadine, cetirizine. “Terfenadine” is a long acting H1 Antagonists. “Fexofenadine” is a primary oxidation metabolite of “Terfenadine” & does not cross the BBB. “Cetirizine” highly selective in its interaction with various neuronal binding sites & highly potent as well. Ar 1 X C C N Ar’ 3 In the above general structure, Ar is aryl group & Ar’ is aryl methyl group. In the general structure the X part determines the class of drug to which that belongs i.e. if X = O (amino alkyl analogue), X = N (Ethylene diamine derivatives). Some times two aromatic rings are bridges that constitutes the tricycle ring derivatives. ❑. Question:08 Explain SAR of H1 Antagonists? ❑. Question:07 Write the note on Second generation H1 Antagonists? Terfenadine Fexofenadine Cetirizine 4 2
- 8. Most of the H1 Antagonists have ethylene chain, extension of this chain or branching of this chain leads to reduce the activity of the compounds. Homologation played to improve the drug like tricyclic anti-depressants, neuroleptics. Due to the close resemblance of antihistamine structure to the cholinergic blocking agents, most of the antihistamines show the activity of anti-cholinergic activity. Diphenhydramine have maximum anti-cholinergic activity & maximum ability to cross the blood brain barrier & are thus most effective in motion sickness. #. Uses: I. It is recommended in various allergic conditions & to a lesser as an antitussive & Parkinsonism drugs. II. It is also used OTC sleep air products. III. Treatment of urticaria, seasonal rhinitis (hey fever) & some dermatoses. ❑. Question:09 Give Synthesis & Use of Diphenhydramine Chloride?
- 9. Promethazine hydrochloride is a white to faint yellow crystalline powder that Is very soluble in water, in hot absolute alcohol, in chloroform. #. USES: I. Treating allergic illness such as hives, serum disease & hay fever. II. Enhancing action of analgesics & local anesthetics. III. Also, treatment of rheumatism with allergic components. ❑. Question:10 Give Synthesis & Use of Promethazine?
- 10. It is SP2 alkylamine. It is available as an oral liquid or syrups & is administered every 6 hours. #. USES: I. It is used for allergy symptoms, rhinitis. ❑. Question:11 Give synthesis & uses of Triprolidine?
- 11. “Proton pump inhibitors (PPI) are a group of drugs whose main action is a pronounced & long-lasting reduction of gastric acid production”. GIT Problems, Gastritis, Dyspepsia, Peptic Ulcer disease (PUD) & Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is the main uses of Proton Pump Inhibitors. Gastritis Dyspepsia Peptic Ulcer GERD Gastritis is an inflammation, irritation or erosion of the lining of the stomach. It can occur suddenly or gradually. Dyspepsia is an uncomfortable feeling in the upper middle part of the stomach. Peptic ulcer disease refers to painful sores or ulcers in the lining of the stomach or first part of the small intestine, called the duodenum. GERD is a digestive disorder that affects the lower esophageal sphincter the ring of muscle between the esophagus & stomach. Examples: Omeprazole, Lansoprazole, Esomeprazole, Pantoprazole & Rabeprazole etc. Causes & Symptoms PROTON PUMP INHIBITORS ❑. Question:01 Discuss about Proton Pump Inhibitors? ❑. Question:02 Draw the Chemical Structure of Proton Pump Inhibitors? Omeprazole Lansoprazole Pantoprazole Rabeprazole
- 12. Mechanism of blocking Na/K ATPase or Proton Pump ➢ Benzimidazole PPI’s are prodrug that are converted into sulfenamide within the acidic environment of parietal cells in stomach. ➢ The consumption of food stimulates acid secretion and acid secretion activates PPIs. ➢ Then activated PPI is converted to a sulfenamide in the acidic secretory canaliculi of the parietal cell. ➢ The sulfenamide interacts covalently with sulfhydryl groups (in cysteine amino acid of the binding site) in the proton pump to create a disulphide bond between drug and pump and thereby irreversibly inhibiting its activity. • Irreversible covalent inhibitors are either substituted 2- (pyridinemethylsulfinyl)benzimidazoles or a similar structure, pyridylmethyl sulfinyl pyrido-imidazole, because they mainly inhibits the pump enzyme by covalently binding to the α-subunit of the H+ ,K+ -ATPase. ❑. Question:03 Explain the Mechanism of Action of Proton Pump Inhibitors? ❑. Question:04 Why Proton Pump Inhibitors are irreversible?
- 13. Mechanism of Acid Secretion: The H+ concentration in parietal cell secretions roughly 3 million- fold higher than in blood, and Cl- is secreted against both a concentration and electric gradient. The parietal cell to secrete acid is dependent on active transport. Acid secretion through "Proton Pump" located in the canalicular membrane. This ATPase is Mg+ dependent. The current model for explaining acid secretion in above. • H+ are generated within parietal cell from dissociation of water. The H+ formed in this process rapidly combine with CO2 to form HCO3 - , a reaction catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase. • HCO3 - transport out from basolateral membrane in exchange for Cl- . The outflow of bicarbonate into blood results in a slight elevation of blood pH known as the "alkaline tide". This process maintains intracellular pH in the parietal cell. • Cl- and K+ are transport into lumen of the canaliculus by conductance channels, necessary for secretion of acid. • H+ is pump out of cell, into the lumen, in exchange for K+ through the action of the proton pump; K+ is thus effectively recycled. • Accumulation of osmotically-active H+ generates an osmotic gradient across the membrane, the resulting gastric juice is 155 mM HCl and 15 mM KCl with a small amount of NaCl. ❑. Question:05 Explain Secretion of Acid through the Proton Pump?
- 14. Neoplasm means: Tumour/Cancer. Cancer is an uncontrolled proliferation express varying degree of fidelity to their precursors. It can be “benign” or “Malignant”. Benign: non-cancerous and not an immediate threat to life, even though treatment eventually may be required for health. Malignant: tending to worsen and cause death, invasive and metastasis. 01. Cancer involves the development and reproduction of abnormal cell. 02. Cancer cells are usually nonfunctional. 03. Cancer cell growth is not subject to normal body control mechanisms 04. Cancer cells eventually metastasize to other organs via the circulatory and lymphatic systems. 05. Metastasis. Categorized based on the functions/locations as following: 1. Carcinoma - Skin or in tissues that line or cover internal organs. Ex: Epithelial cells, Glands. 80- 90% reported cancer cases are carcinomas. 2. Sarcoma - Bone, cartilage, fat, muscle, blood vessels, or other connective or supportive tissue. 3. Leukemia - White blood cells and their precursor cells such as the bone marrow cells, causes large numbers of abnormal blood cells to be produced and enter the blood. 4. Lymphoma - Cells of the immune system that affects lymphatic system. 5. Myeloma - Beta-cells that produce antibodies- spreads through lymphatic system. 6. Central Nervous System Cancers - Cancers that begin in the tissues of the brain and spinal cord. Characterstics Antineoplastic Drugs (Cancer) ❑. Question:01 Define Cancer with its Characteristics? ❑. Question:02 Classify Tumors on the basis of their functions/locations?
- 15. Antineoplastic agents are drugs used for the treatment of cancer. • The fraction of tumor cells that are in the replicative cycle (“Growth factor”), influence their susceptibility to most cancer chemotherapeutic agent. Rapidly dividing cells are generally more sensitive to anticancer drugs, whereas non proliferating cells [those in G0 phase] usually survive the toxic effect of these drugs. • Normal cells and tumor cells go through growth cycle. However, normal and neoplastic tissue may differ only in the number of cells that are in the various stages in the cycle. Chemotherapeutic agents that are effective only in replicating cells. 01. Phase Specific Agents: These drugs act at particular phase of cell cycle and more effective in proliferating cells. ❑ G1 – Vincristine ❑ S– Methotrexate, Cytarabine, 6-TG, 6-MP, 5-FU, Daunorubicin, Doxorubicin ❑ G2 – Daunorubicin, Bleomycin ❑ M – Vincristine, Vinblastne, Paclitaxel etc. 02. Phase Non-Specific Agents: Nitrogen Mustards, Cyclphosphamide, Chlorambucil, Carmustine, Dacarbazine, Busulfan, L-Asparginase, Cisplatin, Procarbazine and Actinomycin D etc. a) These drugs are specifically effective against proliferating cells but they are not phase specific: Ex: Fluorouracil, cyclophosphamide, Dactinomycin. ❑. Question:03 Explain the Cell cycle & relation with cancer drugs? ❑. Question:04 Classify Anticancer Agents based on its site of Action?
- 16. A. Alkylating Agents 1. Nitrogen Mustards – Mechlorethamine, Cyclophosphamide, Ifosfamide, Melphalan, Chlorambucil. 2. Ethylenimine - Thio-Tepa, Hexamethyl melamine. 3. Alkyl Sulphonate – Busulphan. 4. Nitrosoureas – Carmustine, Lomustine, Streptozocin. 5. Triazines - Procarbazine, Dacarbazine, Temozolomide. B. Platinum Coordination Complexes – Cisplatin, Carboplatin, Oxaliplatin. C. Antimetabolites I. Pyrimidine Analogs - 5-Fluorouracil, Cytarabine (cytosine arabinoside), Capecitabine, Gemcitabine. II.Purine Analogs – 6-Mercaptopurine, 6-Thioguanine, Azathioprine, Fludarabine, Cladribine, Pentostatin. II. Folic acid analogues – Methotrexate, Pemetrexed, Trimetrexate. D. Anticancer Antibiotics – Actinomycin-D (Dactinomycin), Bleomycin, mitomycin- C, anthracyclines (e.g. Doxorubicin, Daunorubicin, Idarubicin, epirubicin, Valrubicin), Streptozocin. E. Plant Products- Vincristine, vinblastine, podophyllotoxin, etoposide, camptothecin, paclitaxel. F. Protein Kinase Inhibitors- Imatinib, Dasatinib, Gefitinib, Erlotinib. G. Miscellaneous – L-Asparaginase, Arsenic trioxide. H. Hormonal Drugs – 1.Glucocorticoids – Prednisolon. 2. Estrogens – Fosfestrol, Ethinylestradiol. 3.Selective estrogen receptor modulator – Tamoxifen. 4.Selective estrogen receptor down regulator – Fulvestrant. 5. Aromatase Inhibitor – Anastrazole. 6. Antiandrogen – Flutamide, Bicalutamide. 7. 5 α Reductase Inhibitor – Finasteride. 8.GnRH Analog – Leuprorelin. 9. GnRH Antagonist – Cetorelix, Abarelix 10. Progestins – Hydroxyprogesterone acetate ❑. Question:05 Classify Anticancer Agents based on their chemical Structure?
