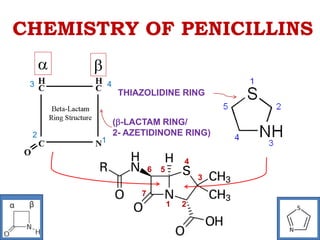
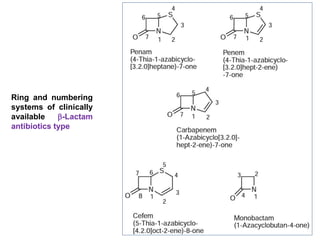
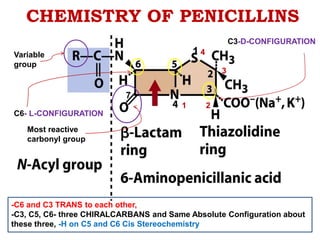
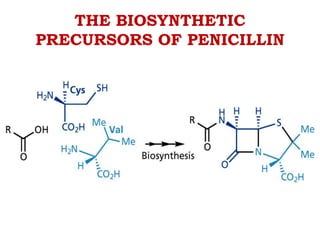
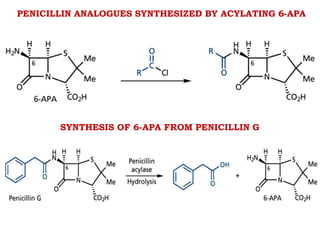
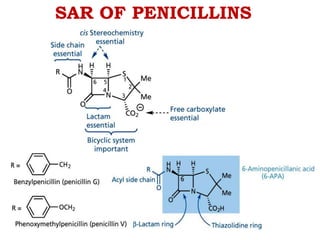
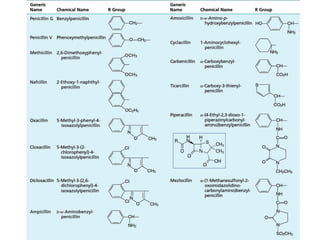
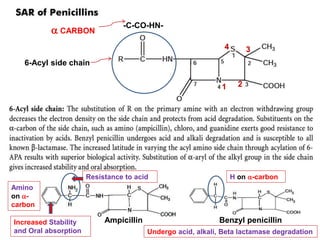
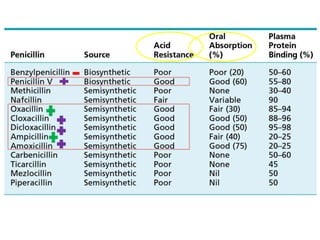
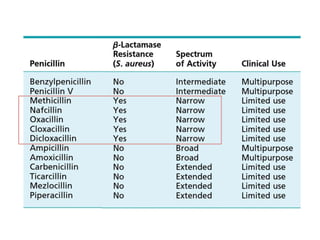
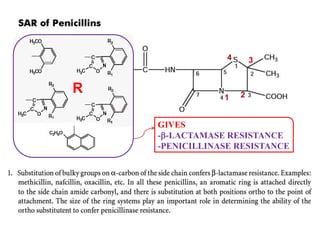
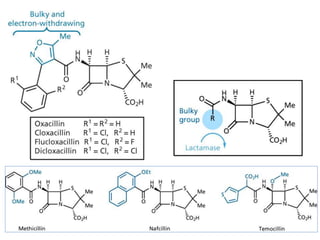
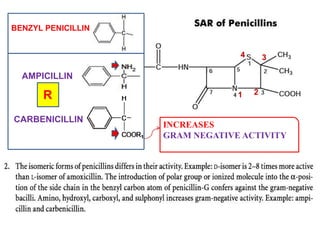
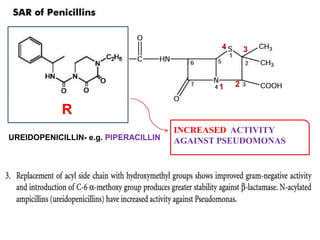
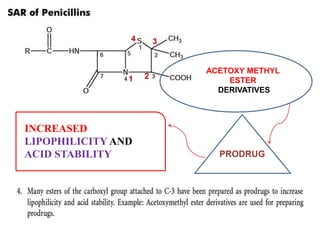
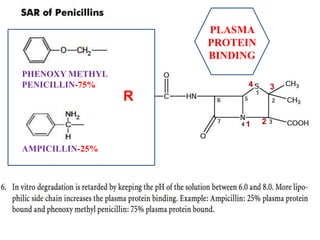
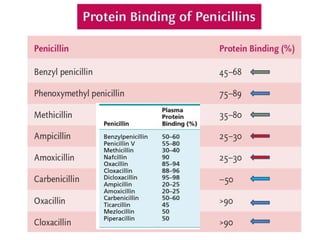
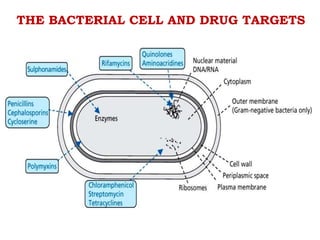
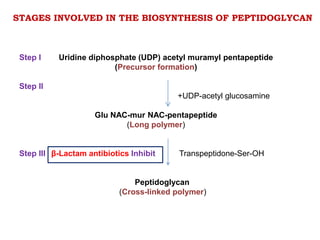
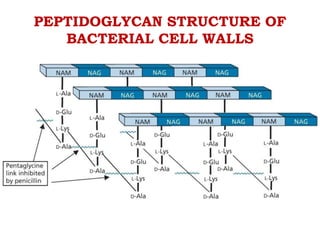
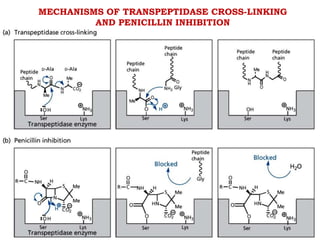
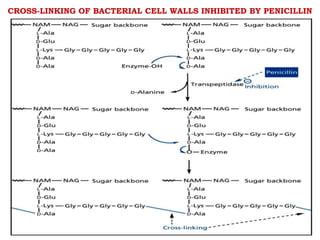
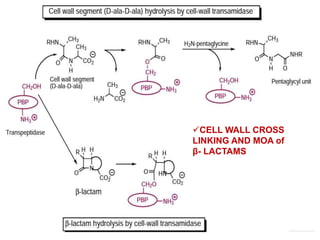
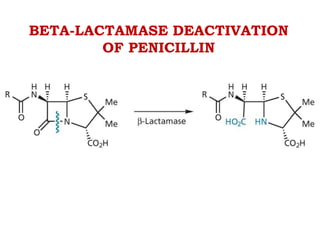
The document discusses the chemistry, structure-activity relationships (SAR), and mechanism of action (MOA) of penicillins, highlighting the β-lactam ring's role in inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. It details how penicillins target transpeptidase enzymes, leading to defects in peptidoglycan cross-linking, which ultimately causes bacterial cell lysis. The interaction between penicillins and bacterial enzymes is emphasized, showing how penicillins mimic natural substrates, resulting in irreversible inhibition.