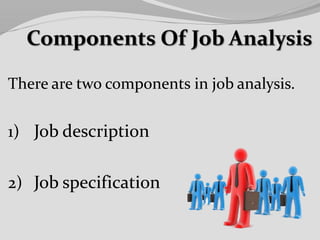
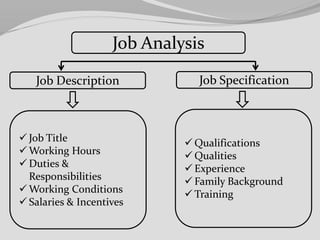
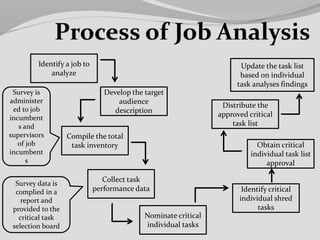
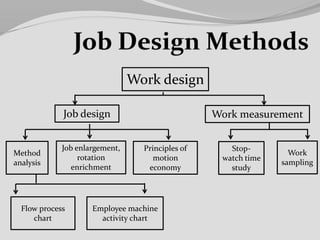
This document discusses job analysis and job design. It contains the names and registration numbers of group members for an HRM course. The contents section lists topics to be covered related to job analysis, such as definitions, methods, uses and advantages/disadvantages. It also discusses job analysis steps and components. Job design topics include approaches, processes and methods. The document provides definitions and discussions of key concepts.