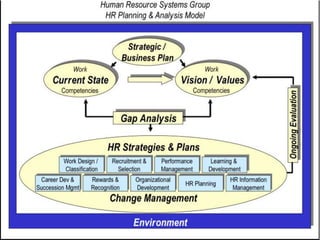
Human resource planning is a process that identifies an organization's current and future human resource needs to achieve its goals. It involves forecasting demand and supply of human resources, developing a HR plan to balance them, and implementing and evaluating the plan. The key steps are analyzing organizational objectives, forecasting demand through techniques like management judgment, work study methods, and ratio-trend analysis, forecasting supply using turnover rates, absenteeism, and productivity levels, developing a HR programming to reconcile demand and supply, implementing the HR plan, and controlling and evaluating it.