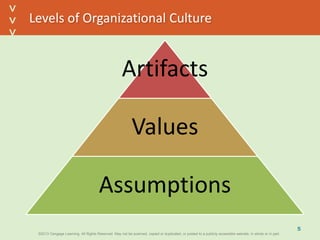
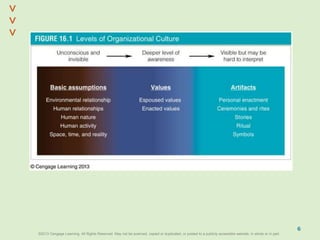
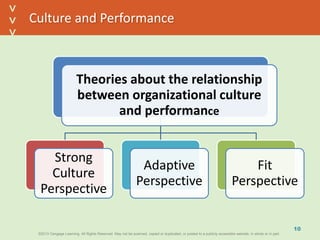
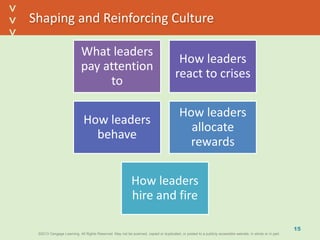
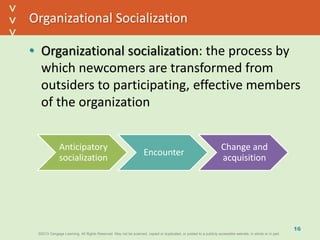
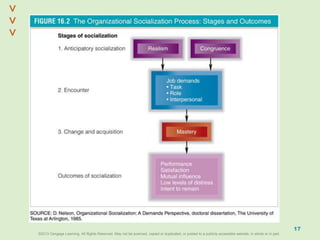
This document discusses organizational culture and related concepts. It defines organizational culture as shared basic assumptions that guide how new members perceive and behave. Cultures have three levels - artifacts (visible symbols), values (beliefs about what's important), and deep assumptions. Culture provides identity, interpretation, values reinforcement, and behavioral control. An adaptive culture encourages change, while strong cultures align goals but may resist change. Leaders shape culture through attention, reactions, behaviors, rewards and hiring. New members learn the culture through socialization stages of anticipation, encounter, and change.