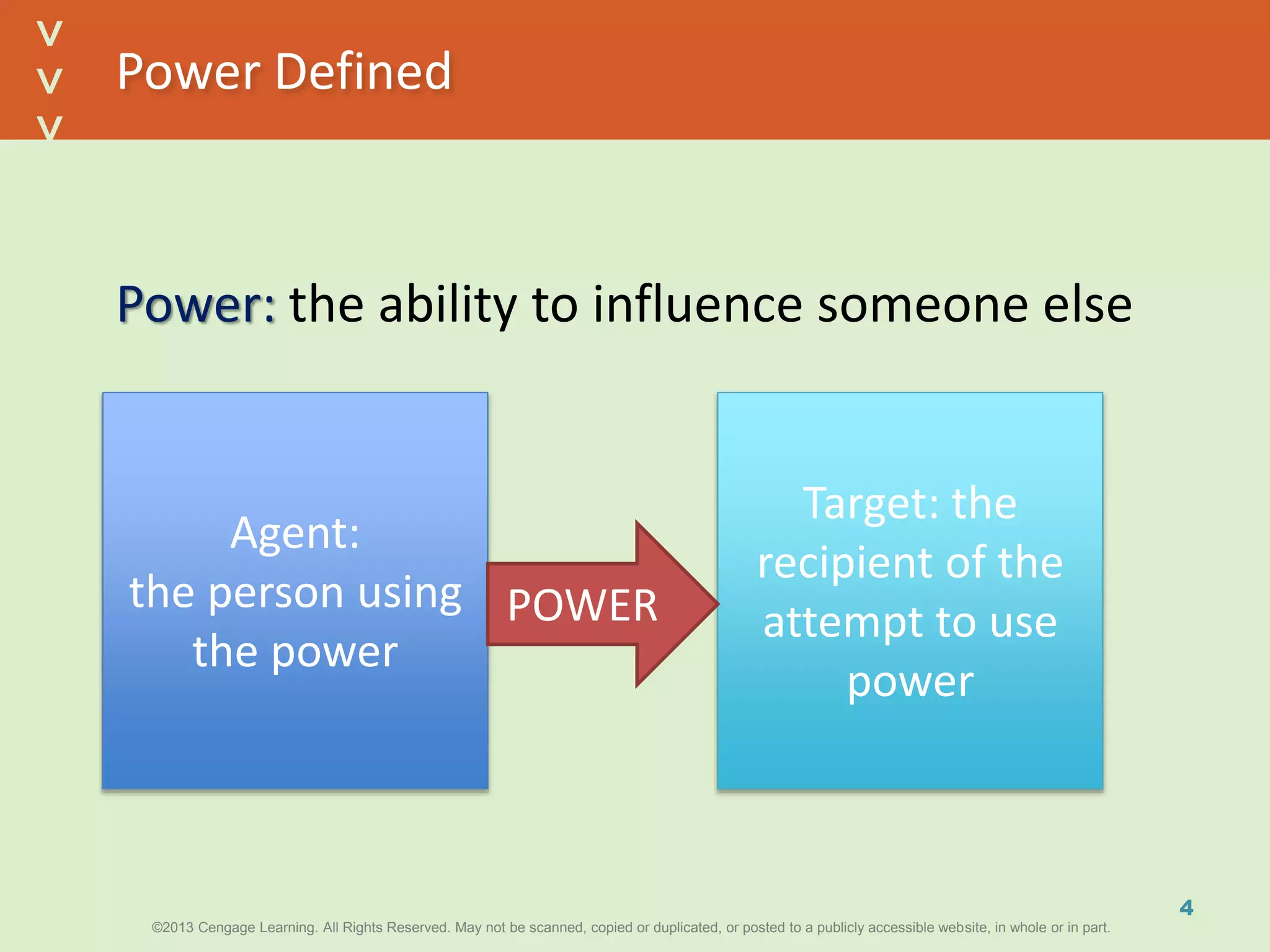
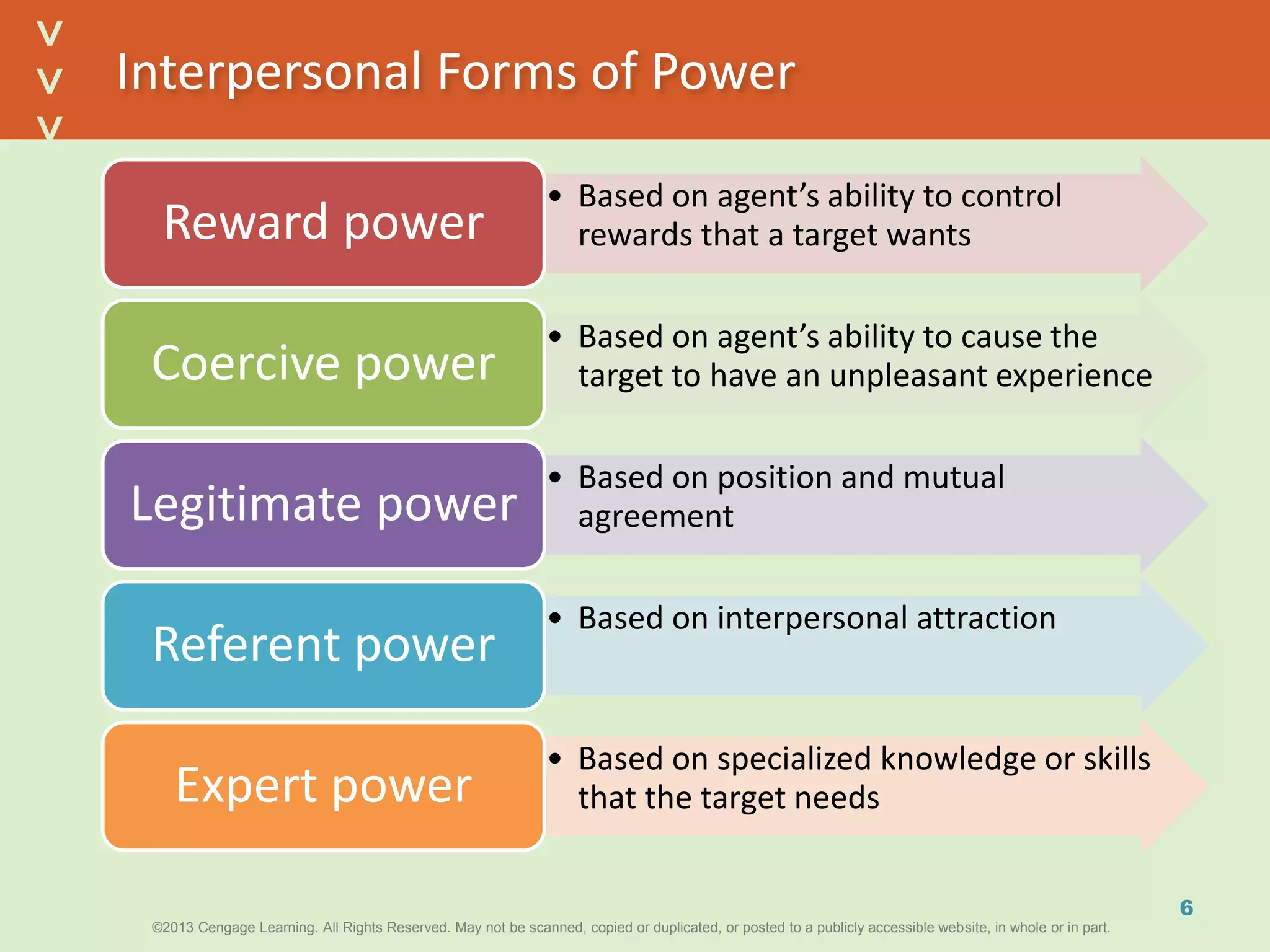
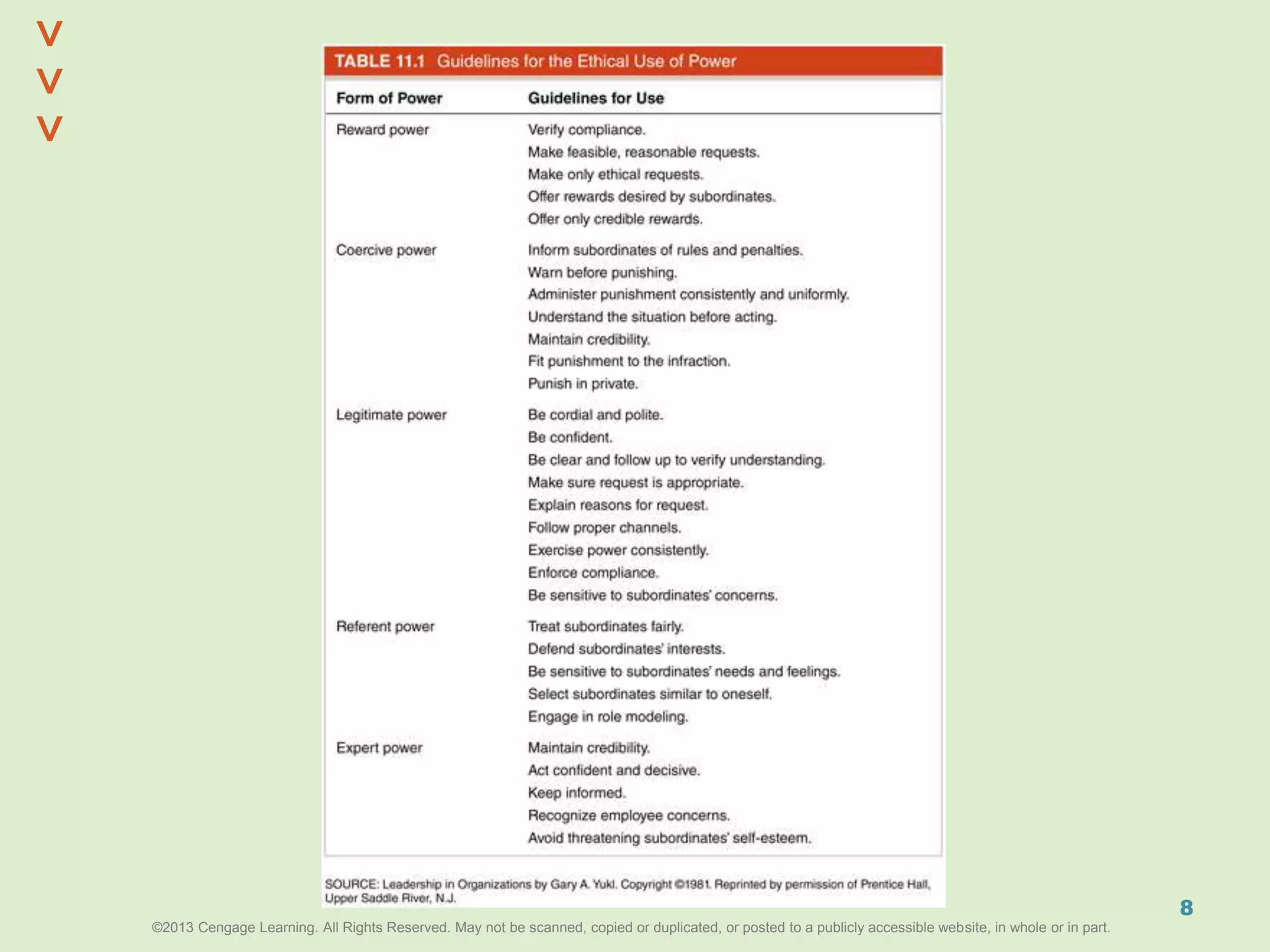
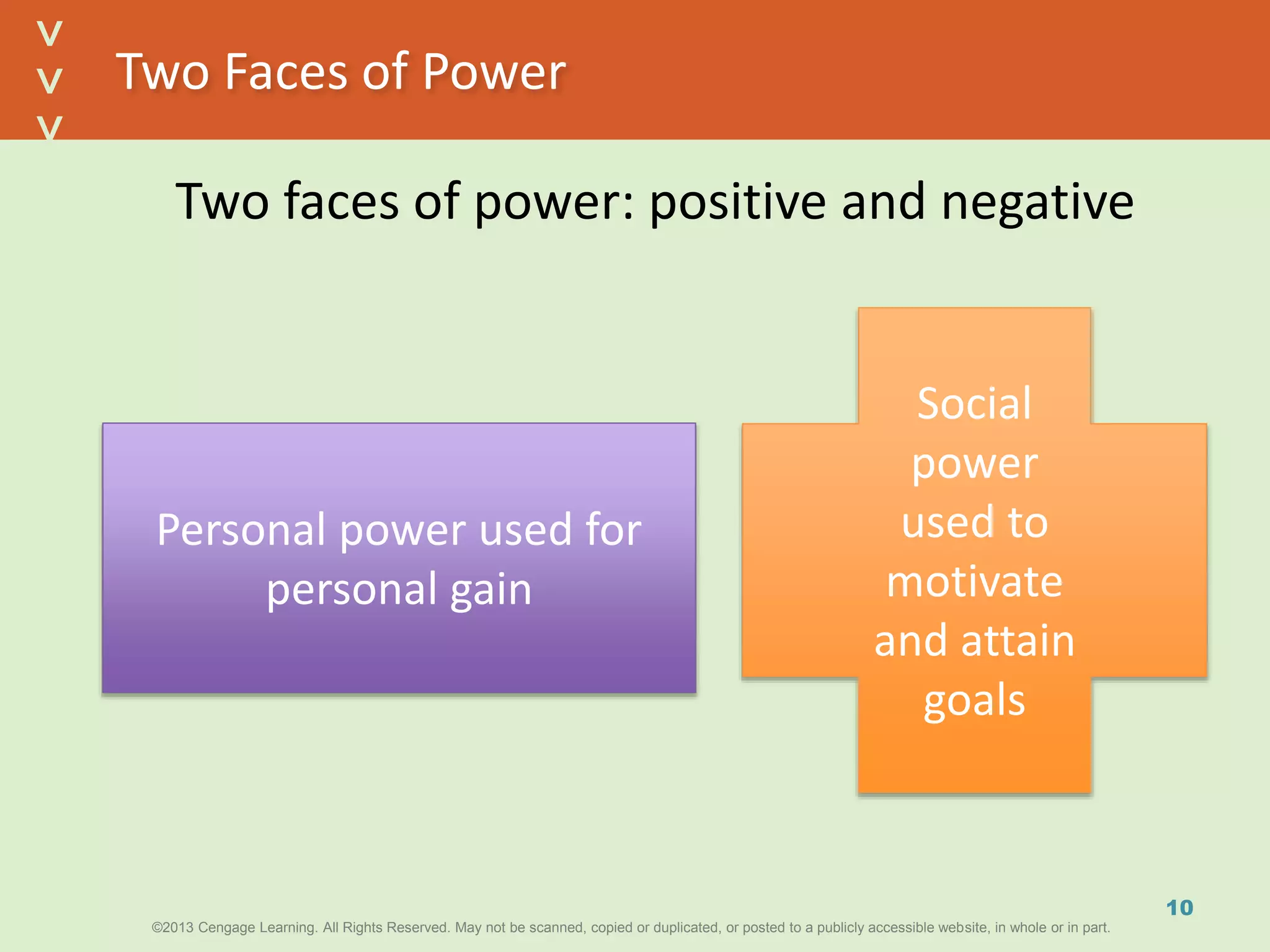
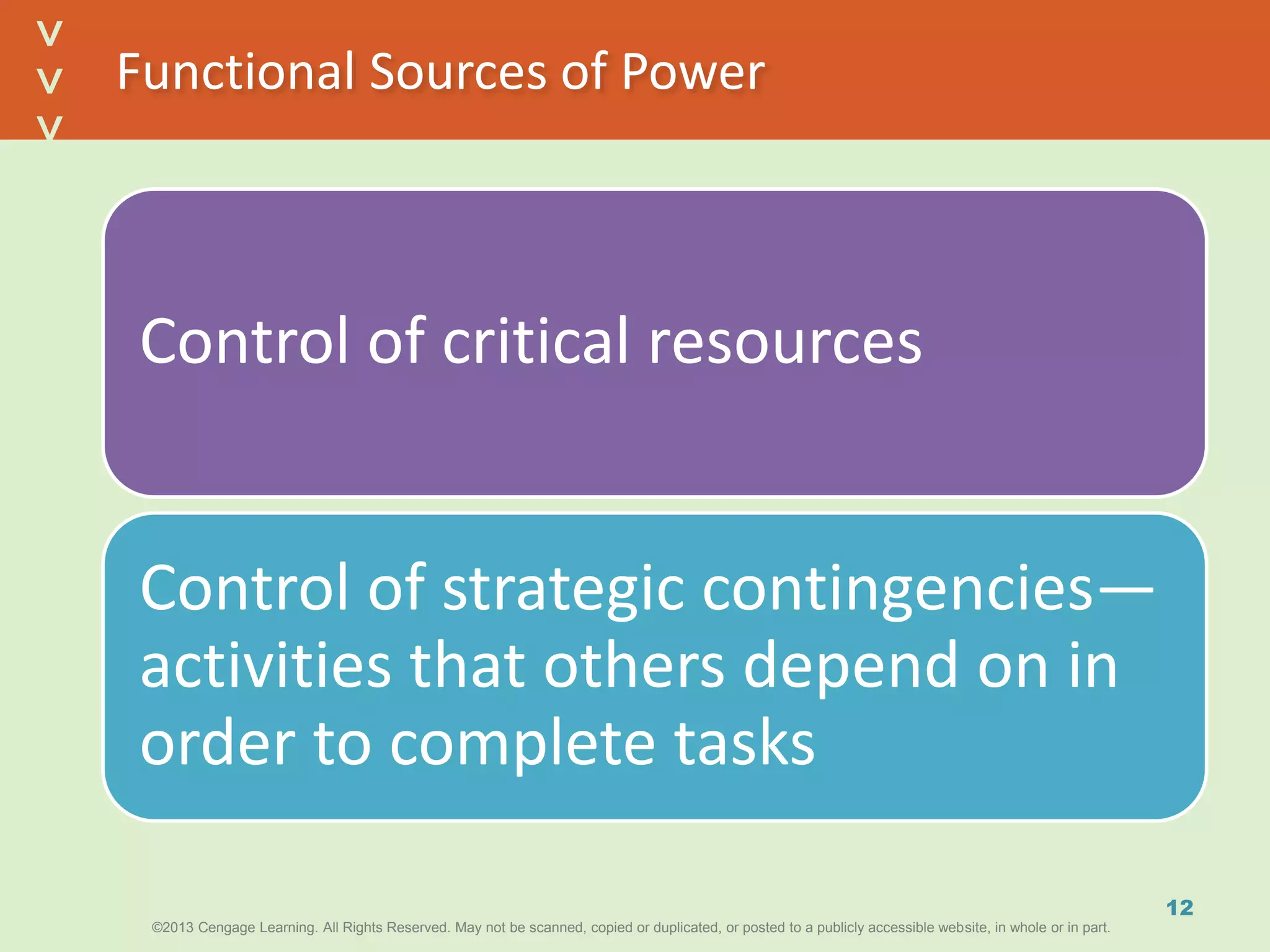
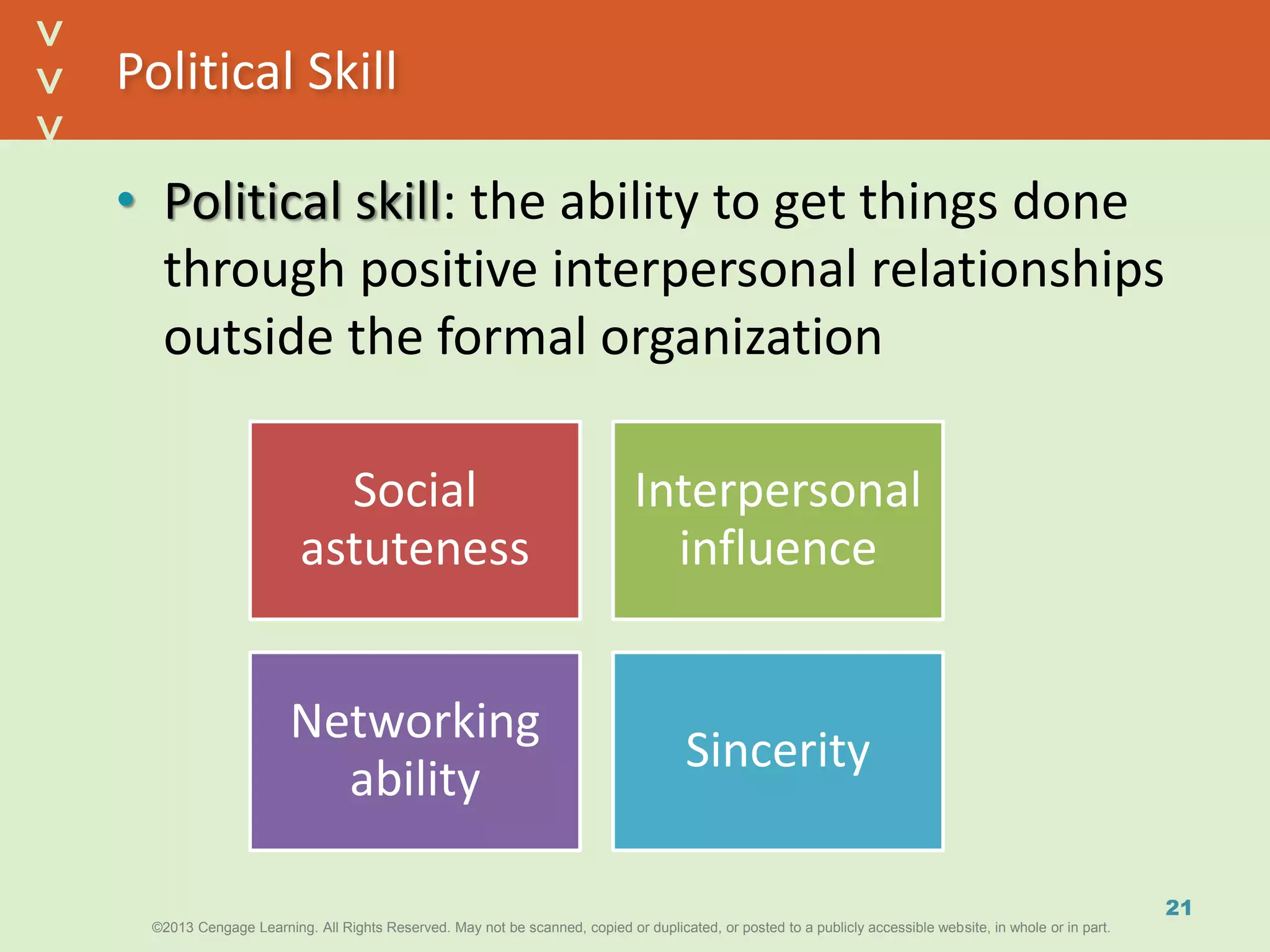
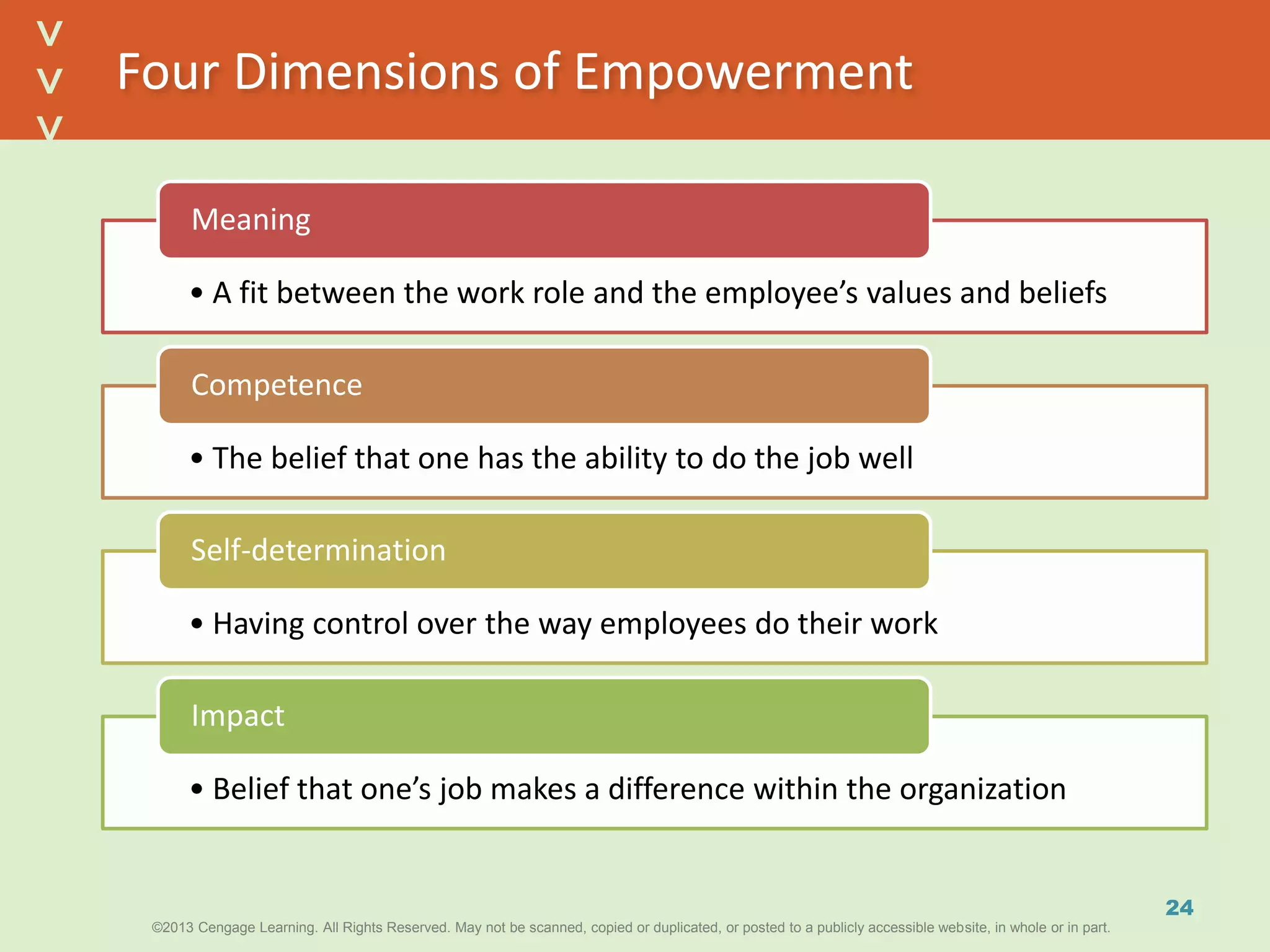
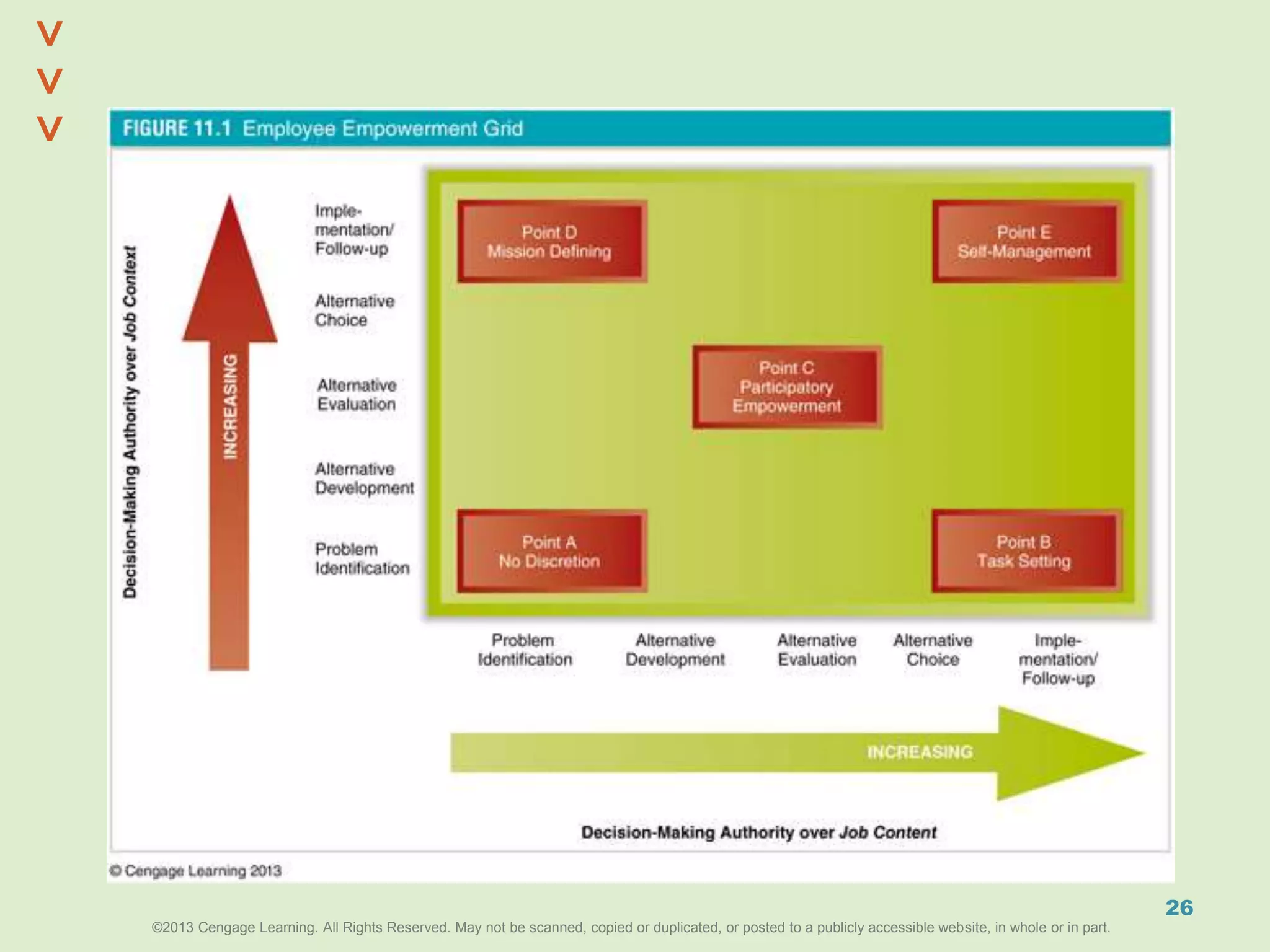
This document discusses power and political behavior in organizations. It defines power as the ability to influence others and distinguishes among power, influence, and authority. There are interpersonal sources of power like reward power and coercive power, as well as functional sources based on controlling resources or strategic contingencies. The document outlines symbols of power and powerlessness and discusses organizational politics and political behavior. It also provides guidance on the ethical use of power and empowering others.