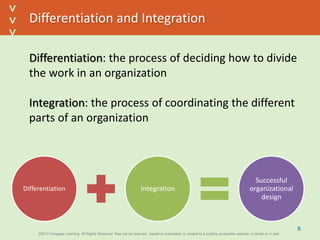
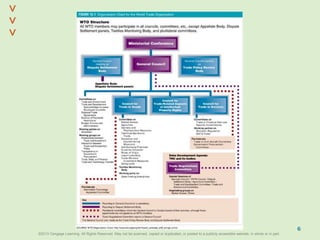
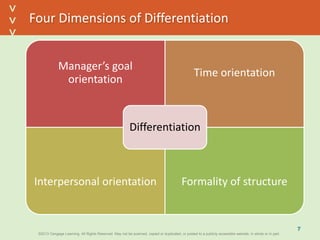
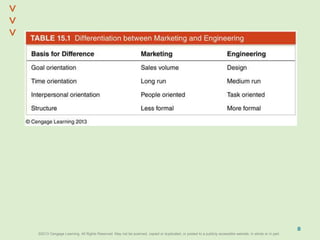
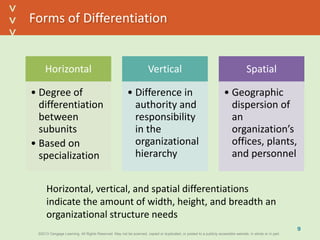
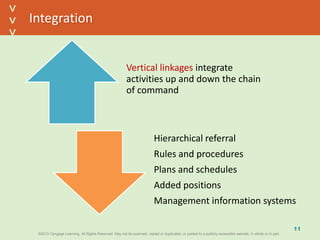
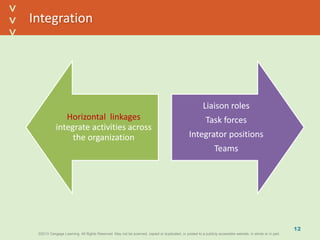
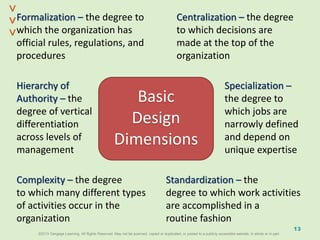
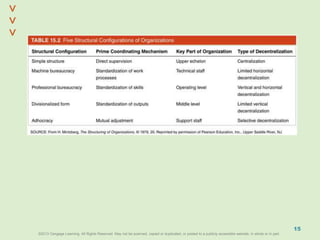
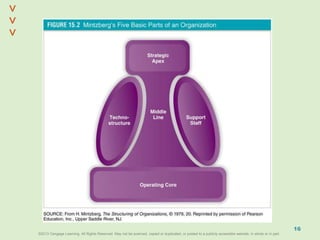
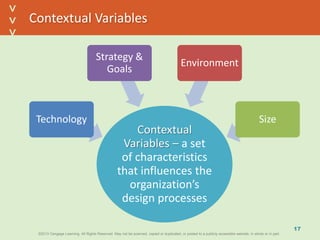
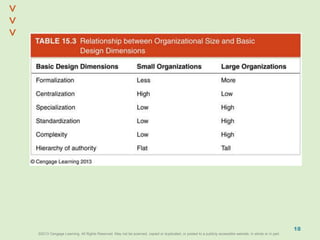
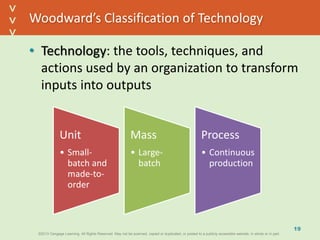
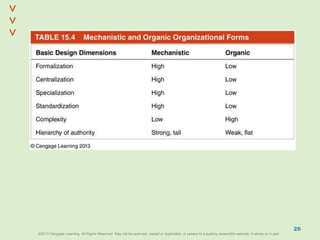
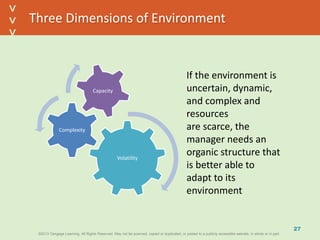
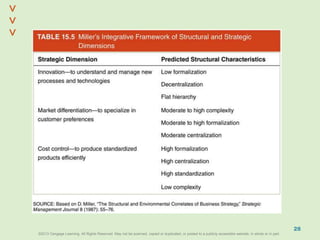
This document discusses organizational design and structure. It defines key terms like differentiation, integration, and organizational structure. It outlines learning objectives related to design dimensions, structural configurations, contextual variables, and emerging structures. It also discusses how differentiation, integration, technology, environment, and other contextual variables influence organizational design. The purpose is to explain how organizations can be structured through concepts like hierarchy, specialization, and centralization.