1. The document discusses classifying matter and describes the differences between elements, compounds, mixtures and pure substances.
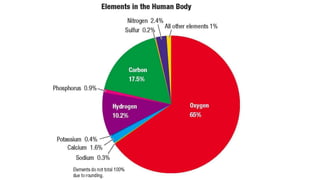
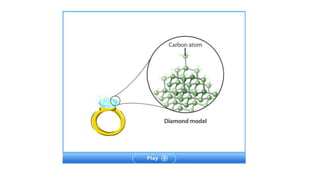
2. It explains that elements are the simplest substances that cannot be broken down further, while compounds are formed by combining two or more elements.
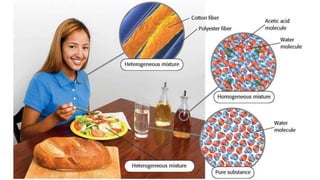
3. Mixtures contain combinations of substances that are not chemically bonded, and can be separated using physical properties, whereas compounds require chemical changes to separate.