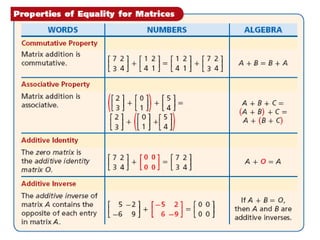
The document provides a lesson on matrices and matrix operations including addition, subtraction, and scalar multiplication of matrices. It begins with examples of displaying data in matrix form and finding entries, dimensions, and addresses of matrices. It then covers adding and subtracting matrices if they have the same dimensions, as well as multiplying matrices by scalars. The document concludes with examples of simplifying matrix expressions and a quiz to assess understanding.










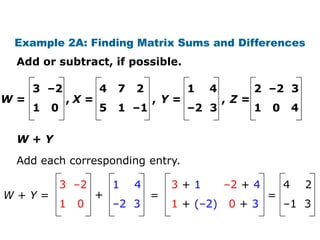







![Check It Out! Example 4a
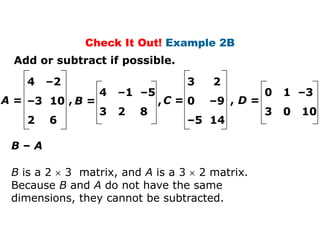
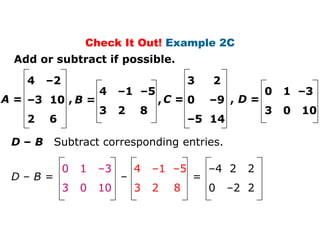
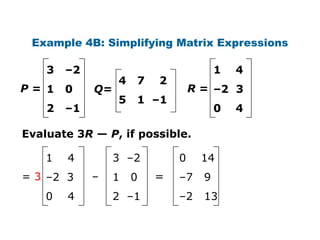
4 –2 4 –1 –5 3 2
A= B= C= D = [6 –3 8]
–3 10 3 2 8 0 –9
Evaluate 3B + 2C, if possible.
B and C do not have the same dimensions; they
cannot be added after the scalar products are found.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matrices-120114000630-phpapp02/85/Matrices-24-320.jpg)
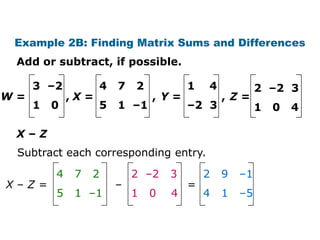
![Check It Out! Example 4b
4 –2 4 –1 –5 3 2
A= B= C= D = [6 –3 8]
–3 10 3 2 8 0 –9
Evaluate 2A – 3C, if possible.
4 –2 3 2 2(4) 2(–2) –3(3) –3(2)
=2 –3 = +
–3 10 0 –9 2(–3) 2(10) –3(0) –3(–9)
8 –4 –9 –6 –1 –10
= + =
–6 20 0 27 –6 47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matrices-120114000630-phpapp02/85/Matrices-25-320.jpg)
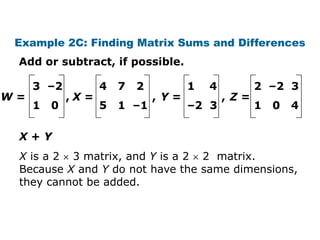
![Check It Out! Example 4c
4 –2 4 –1 –5 3 2
A= B= C= D = [6 –3 8]
–3 10 3 2 8 0 –9
Evaluate D + 0.5D, if possible.
= [6 –3 8] + 0.5[6 –3 8]
= [6 –3 8] + [0.5(6) 0.5(–3) 0.5(8)]
= [6 –3 8] + [3 –1.5 4]
= [9 –4.5 12]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matrices-120114000630-phpapp02/85/Matrices-26-320.jpg)