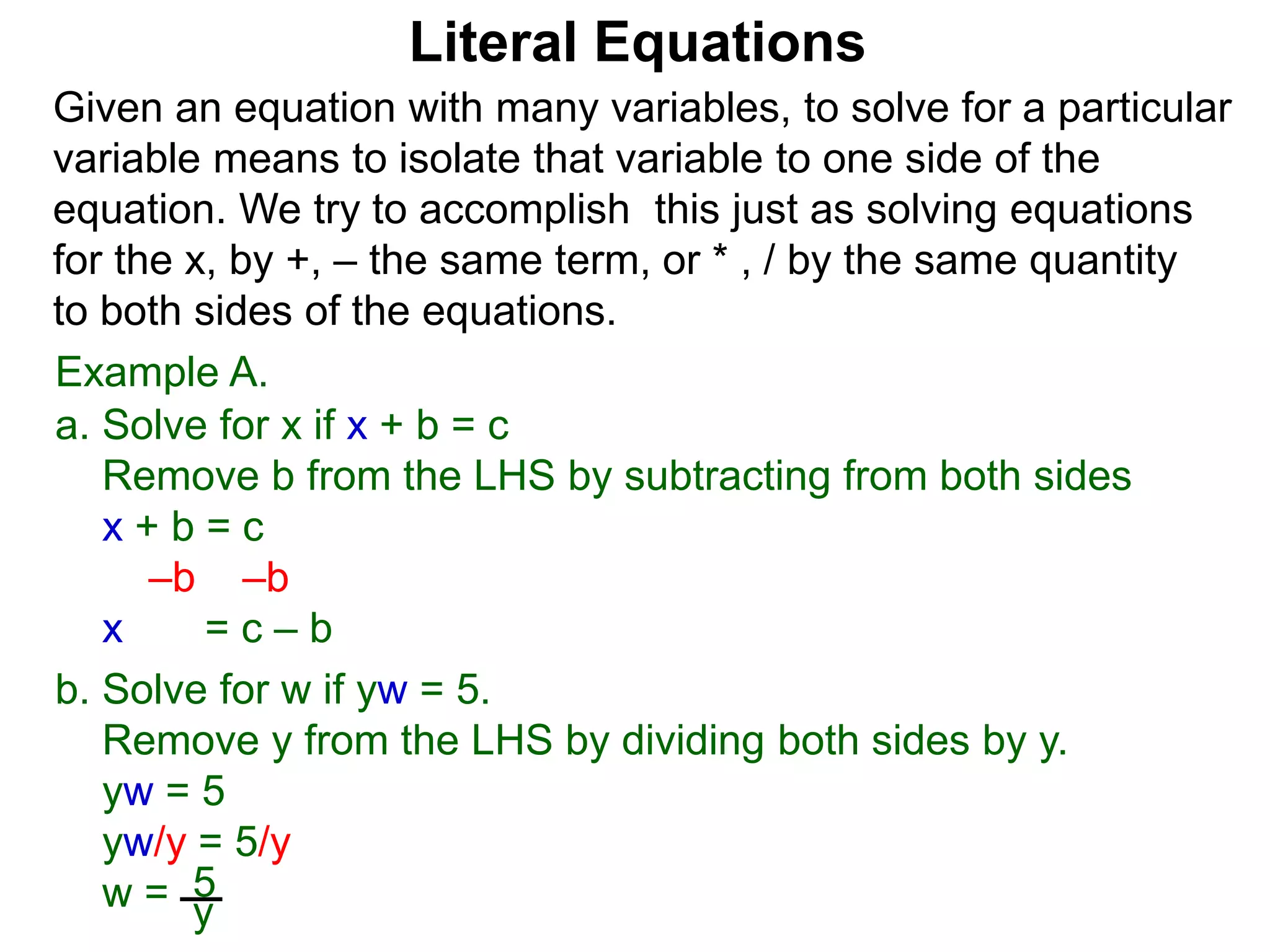
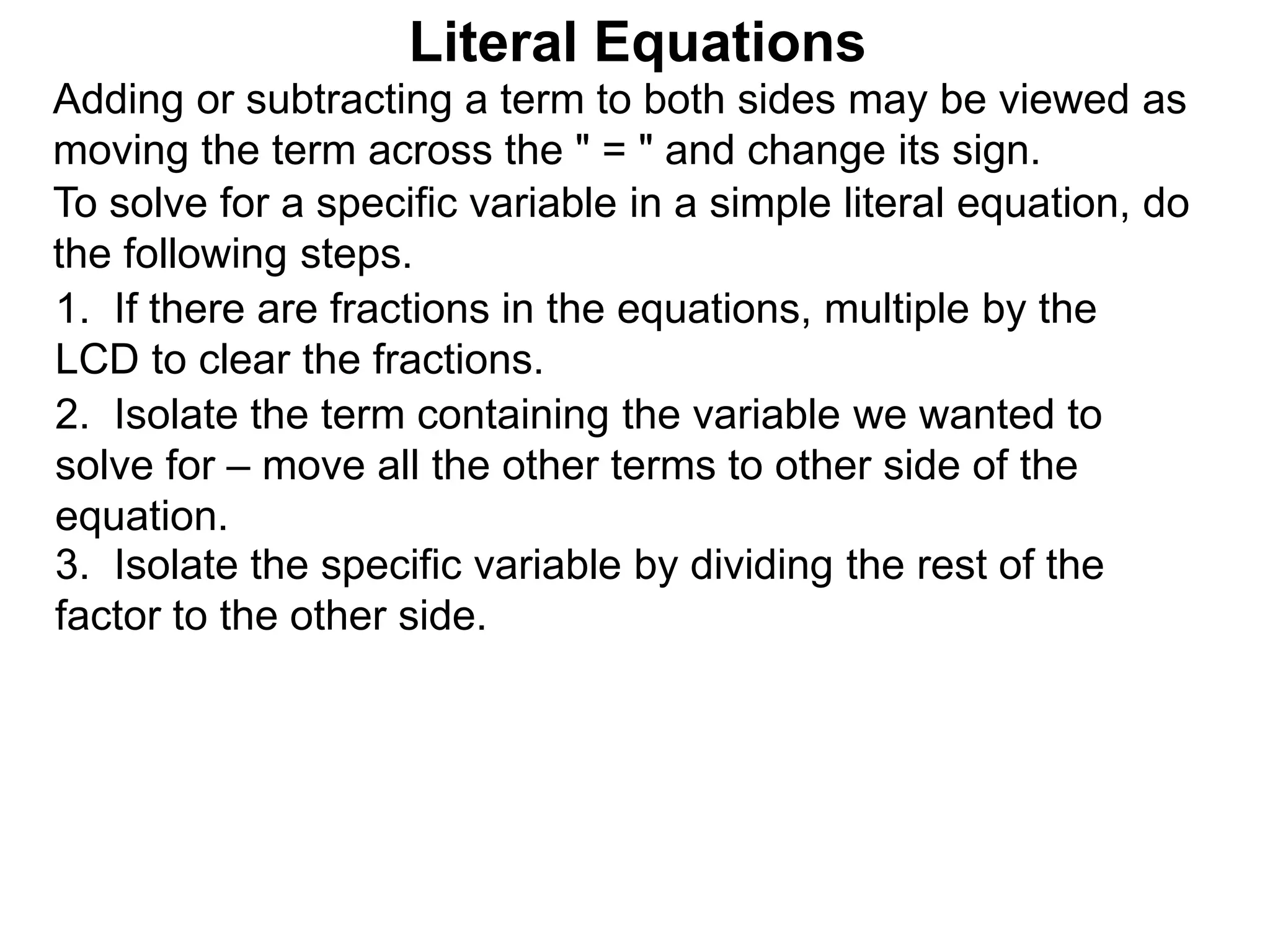
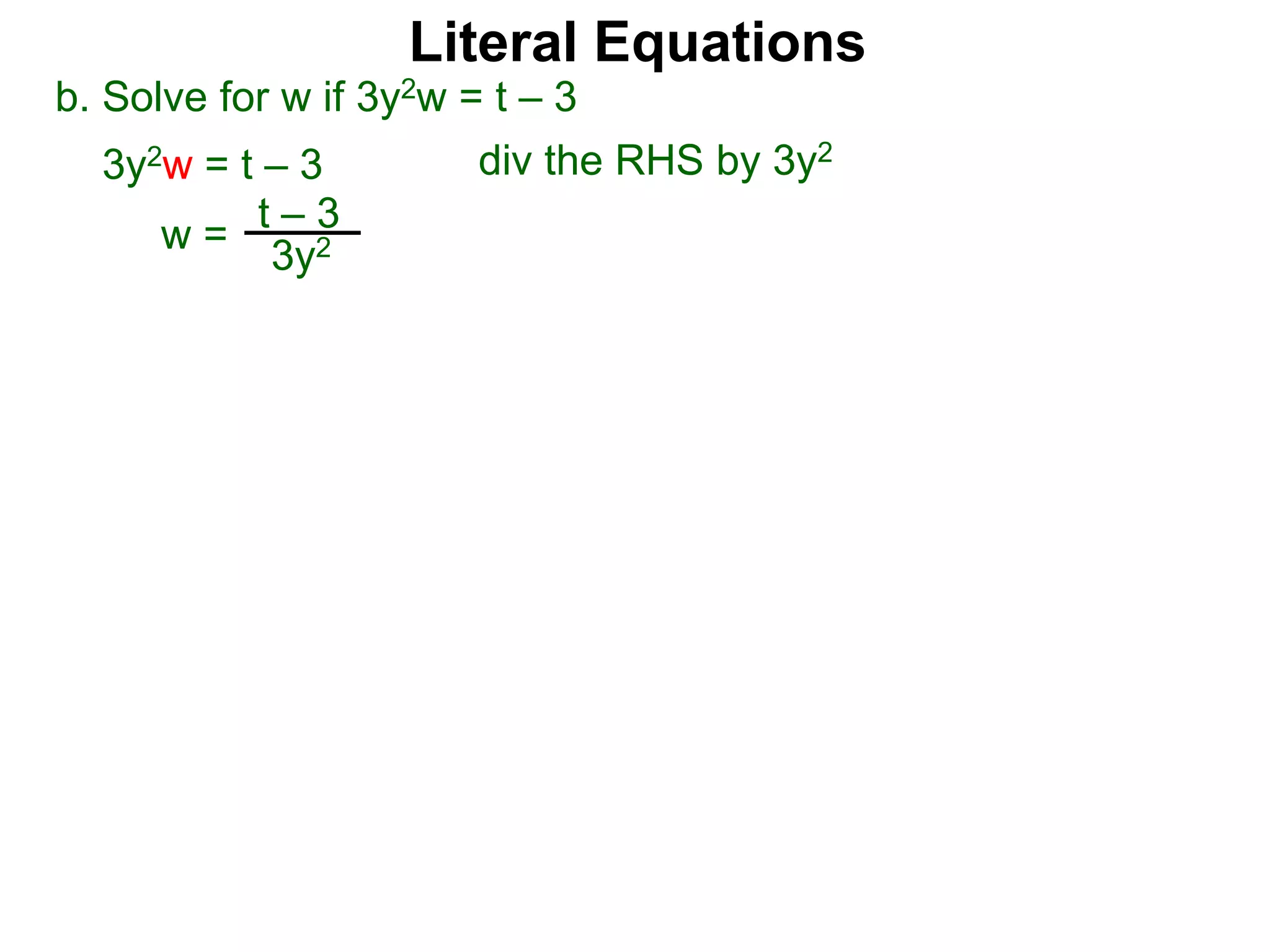
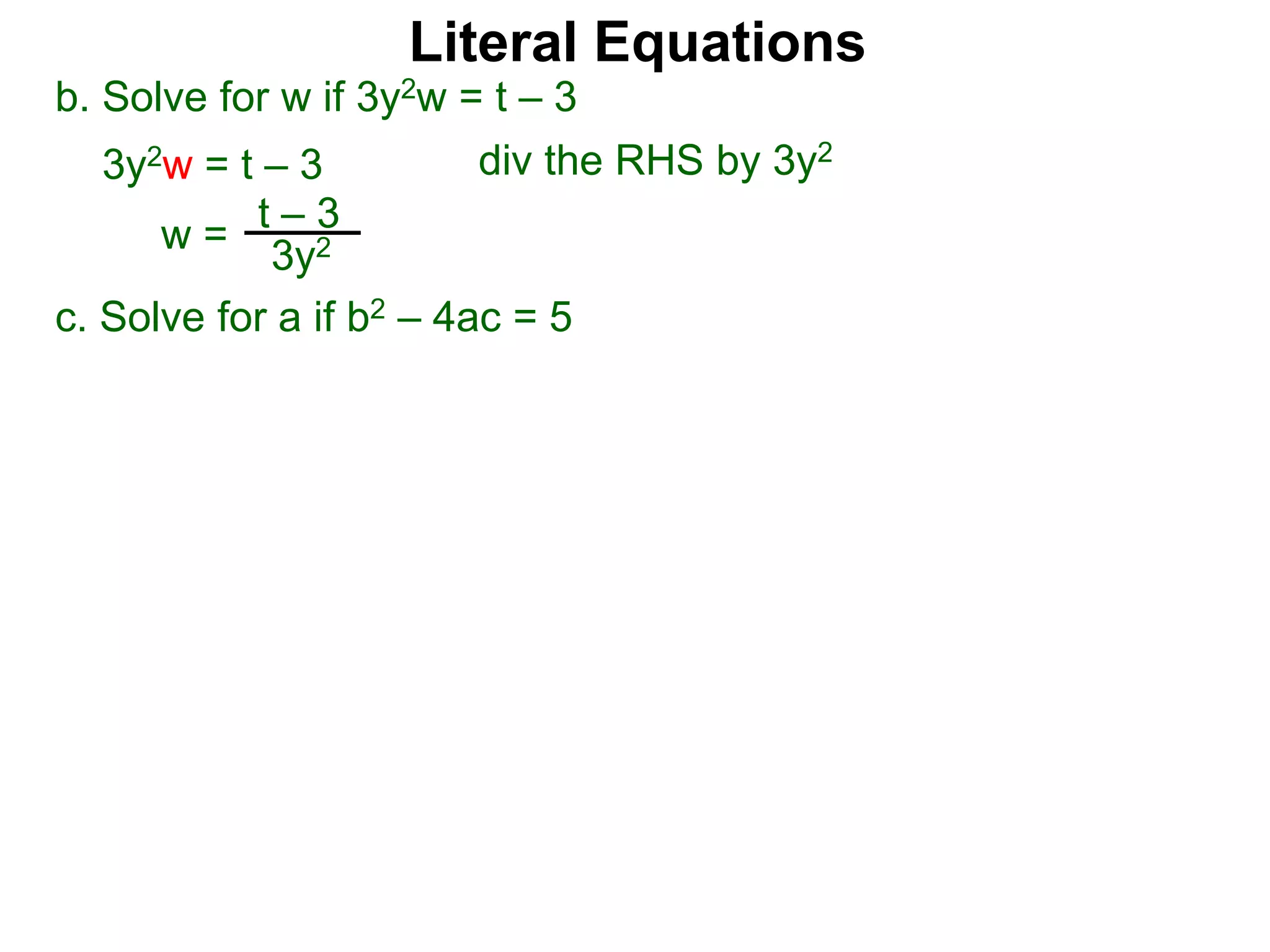
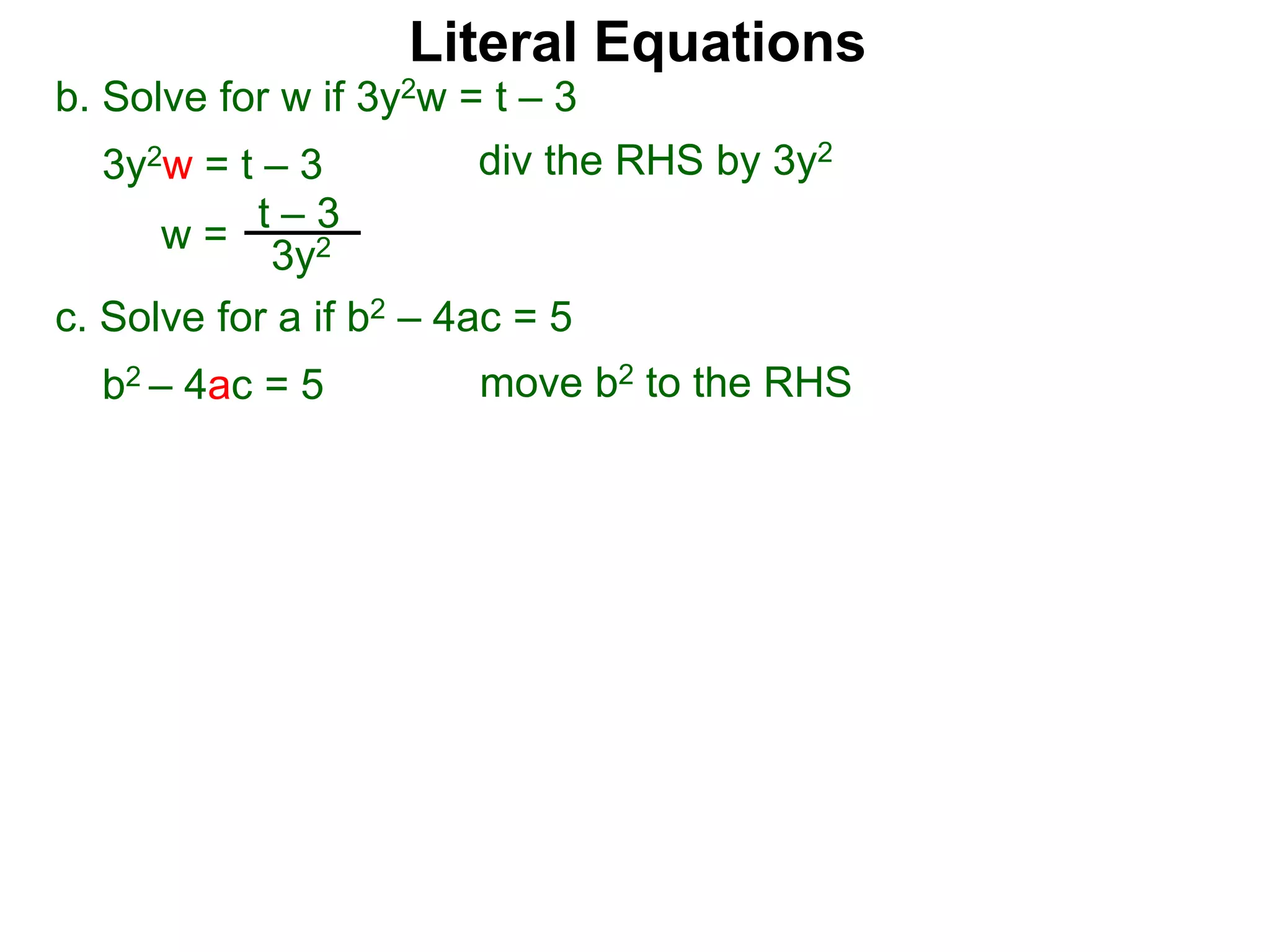
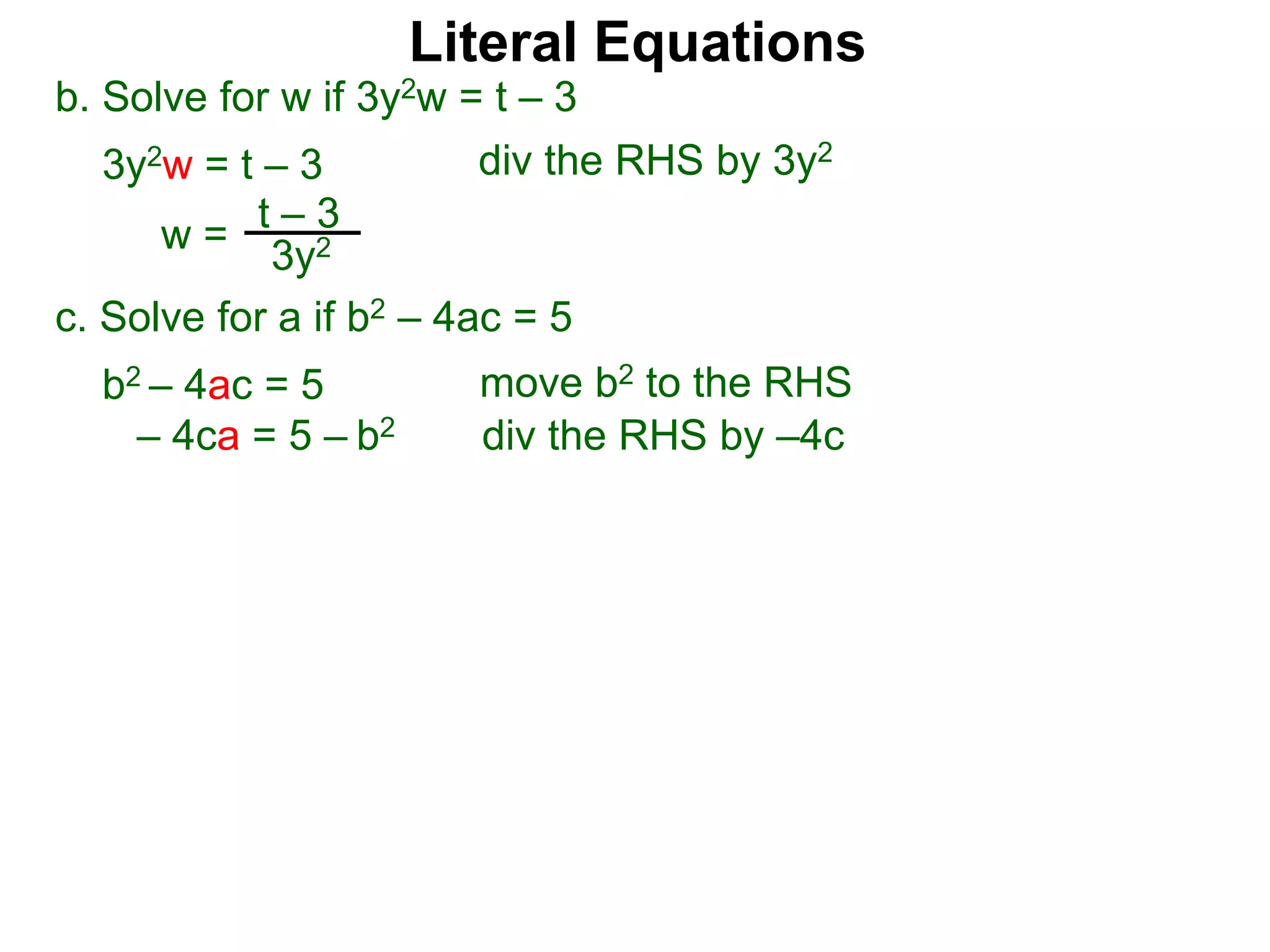
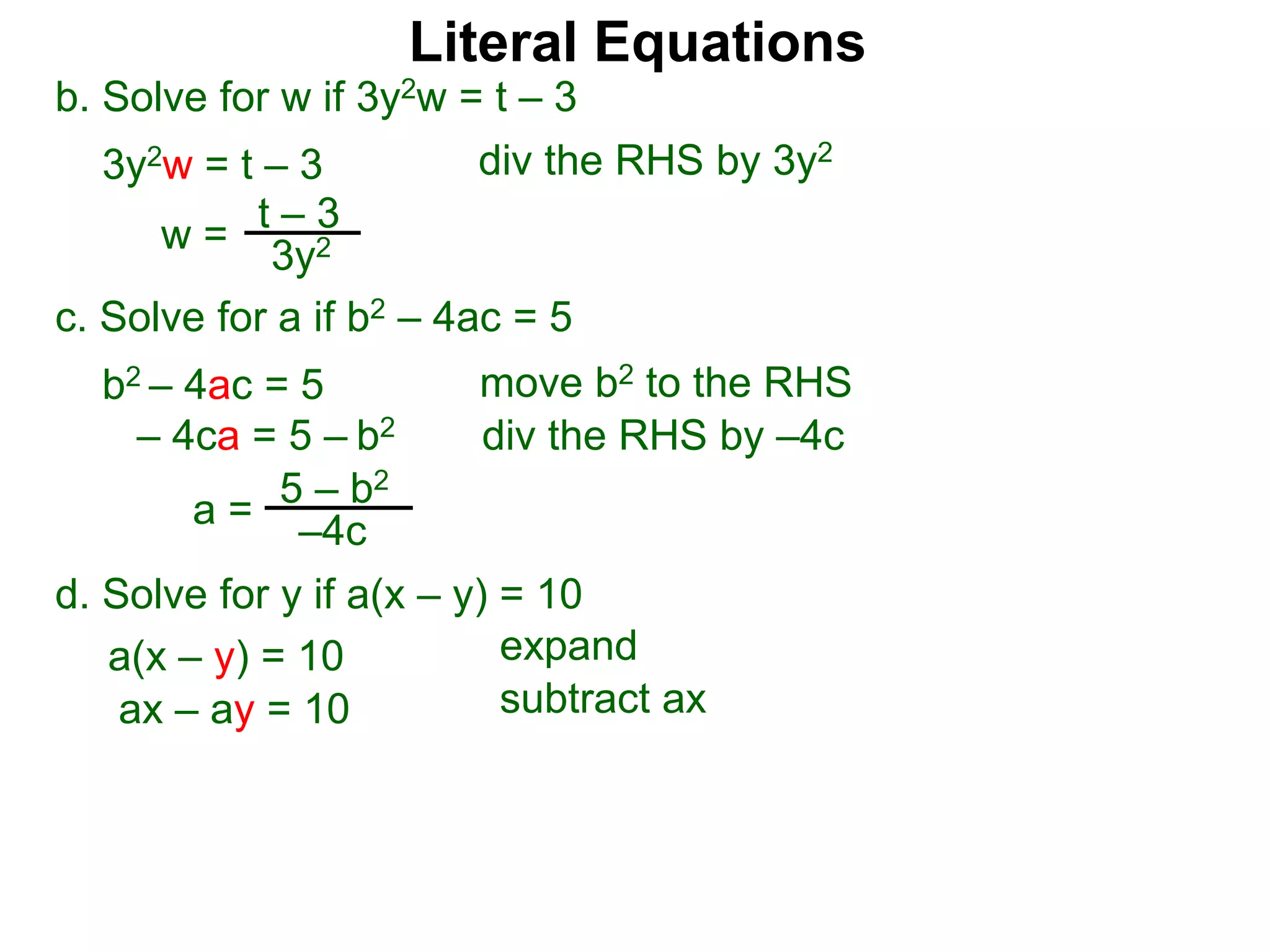
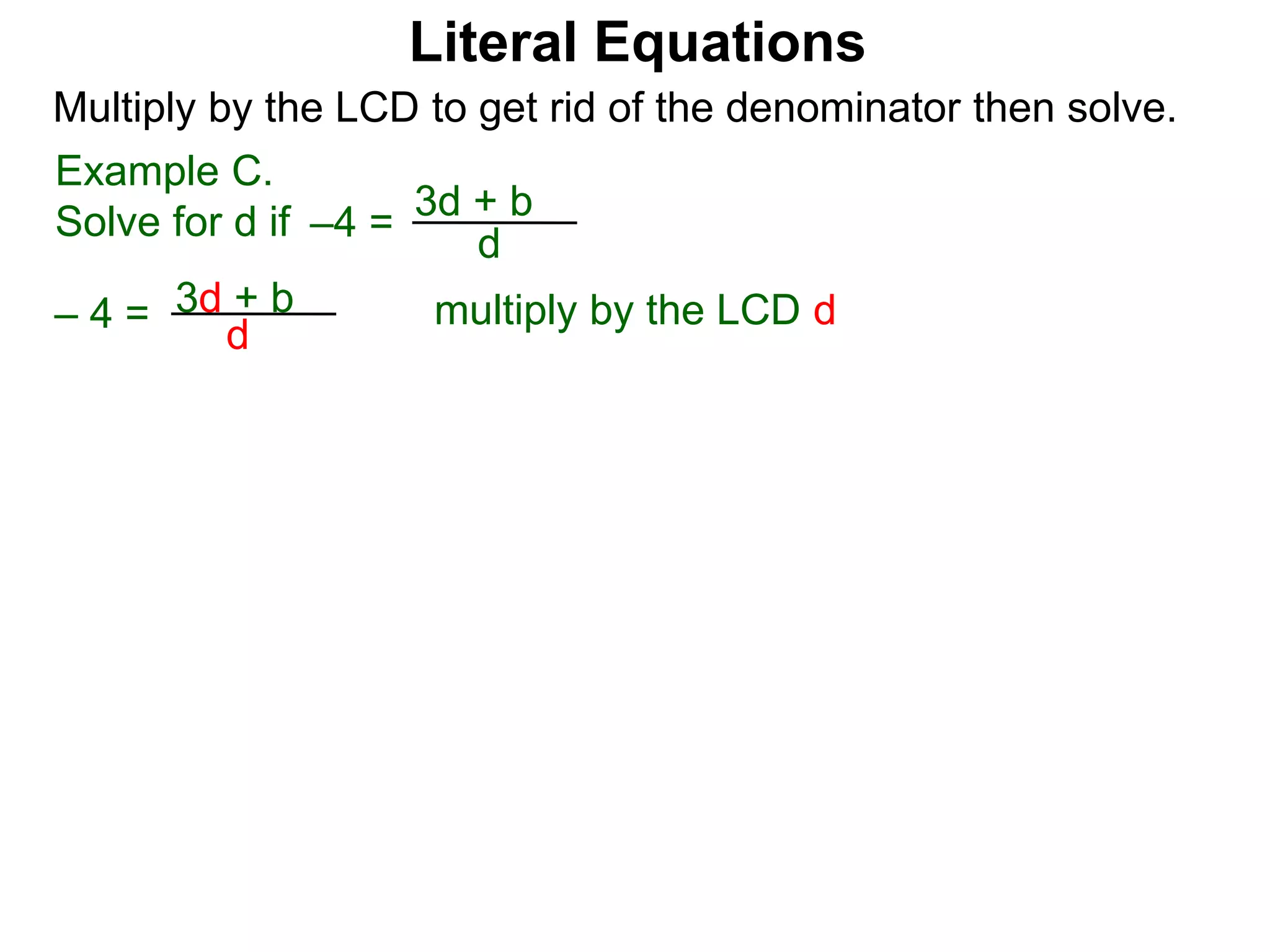
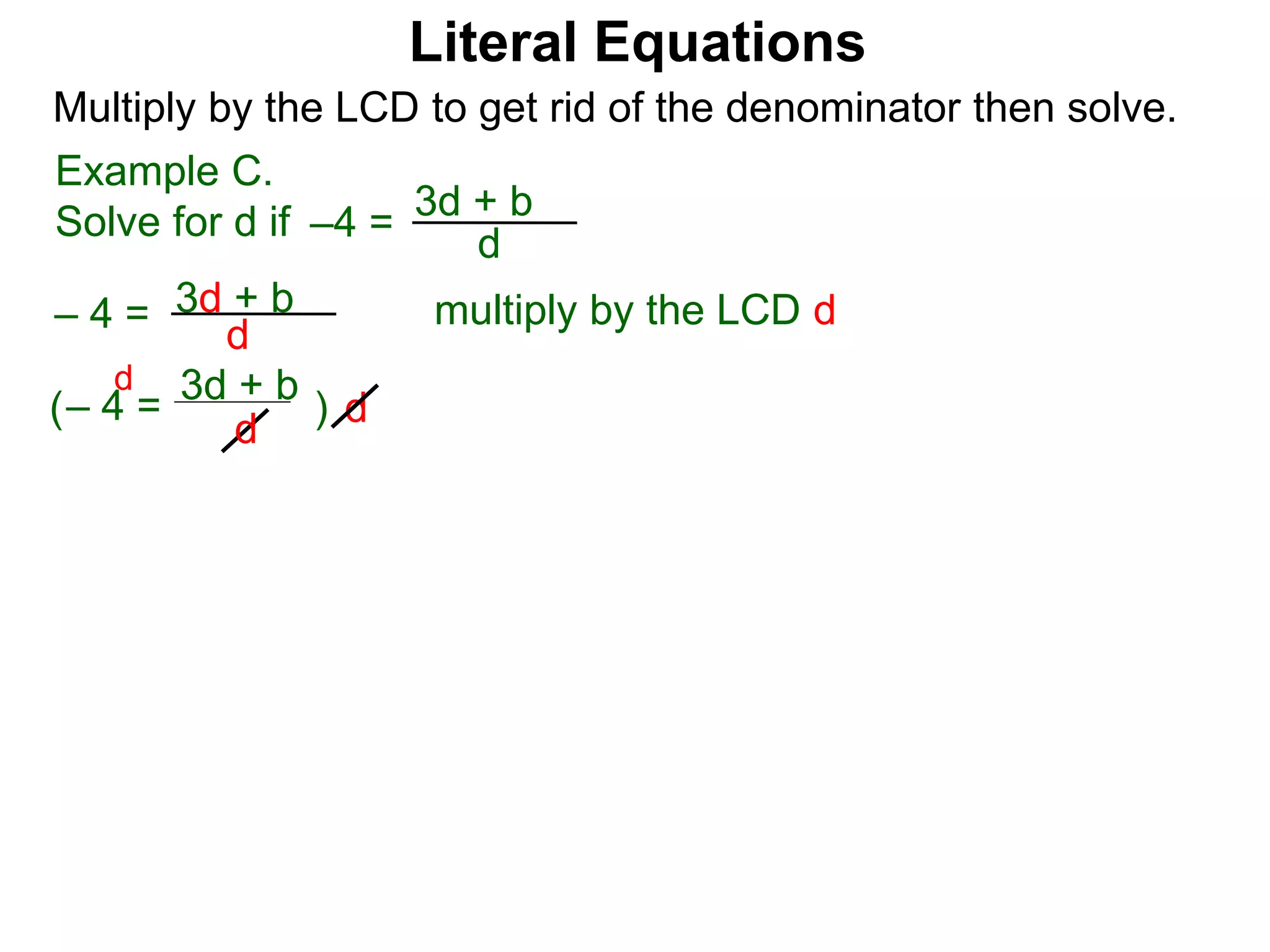
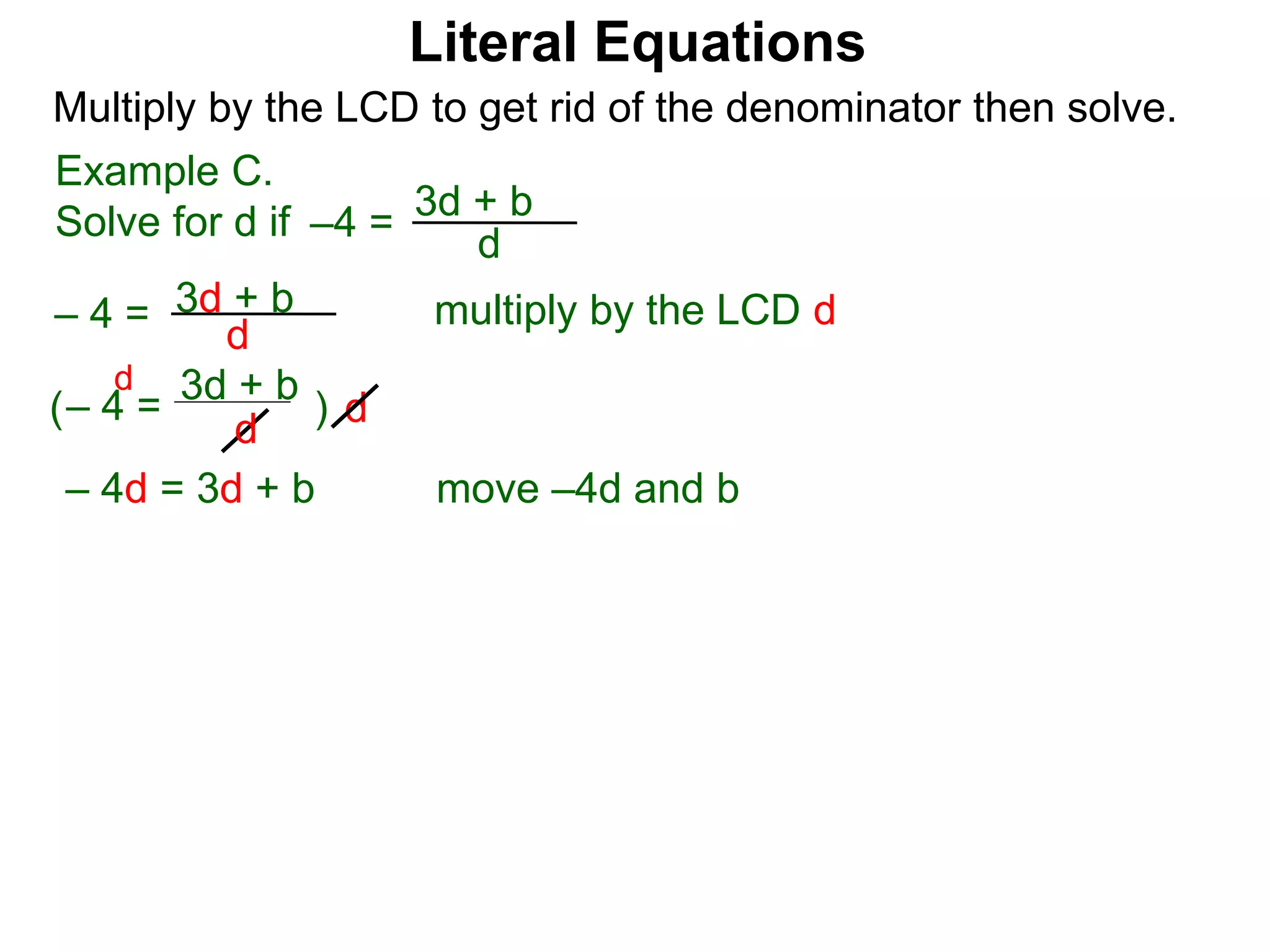
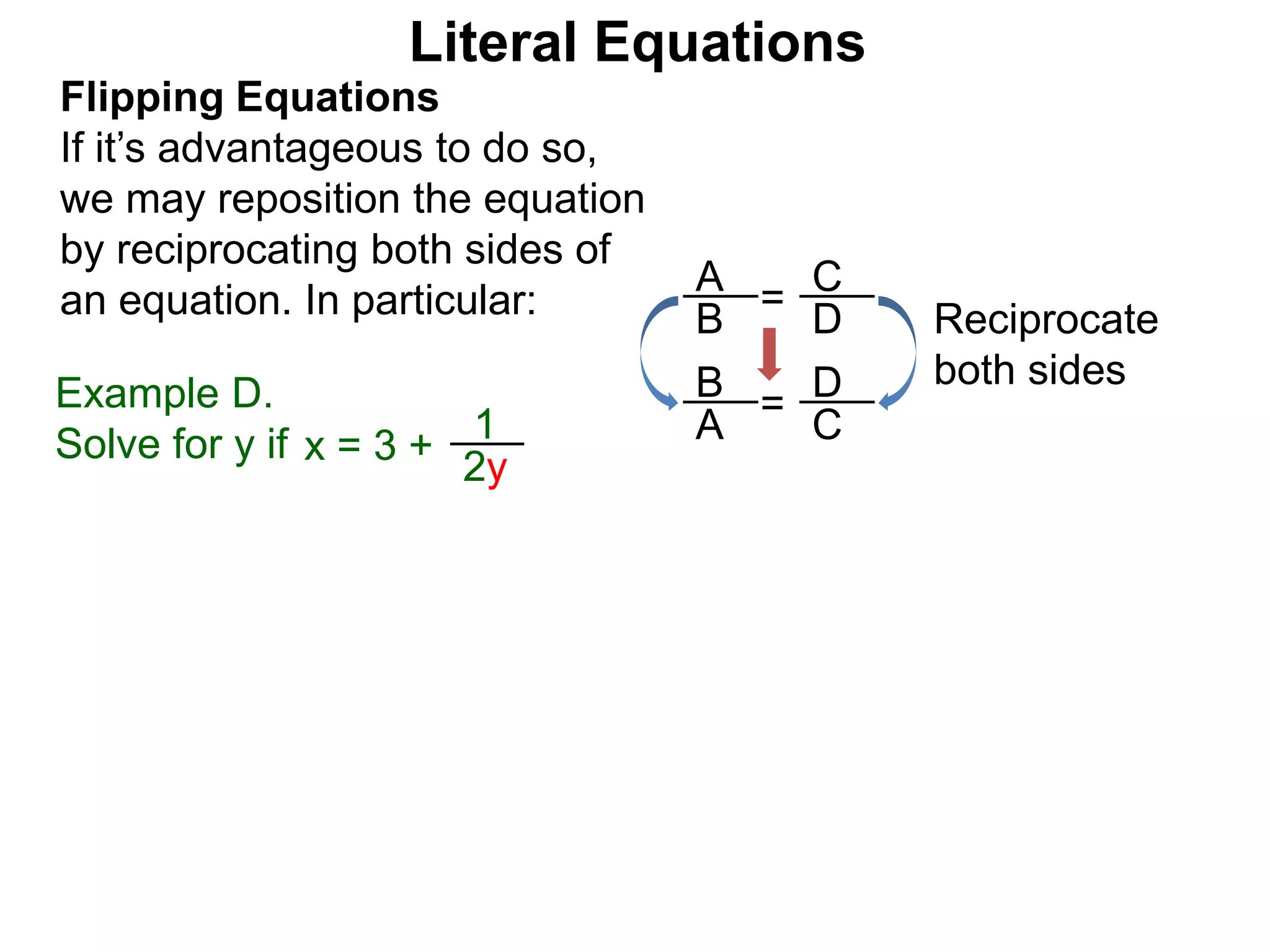
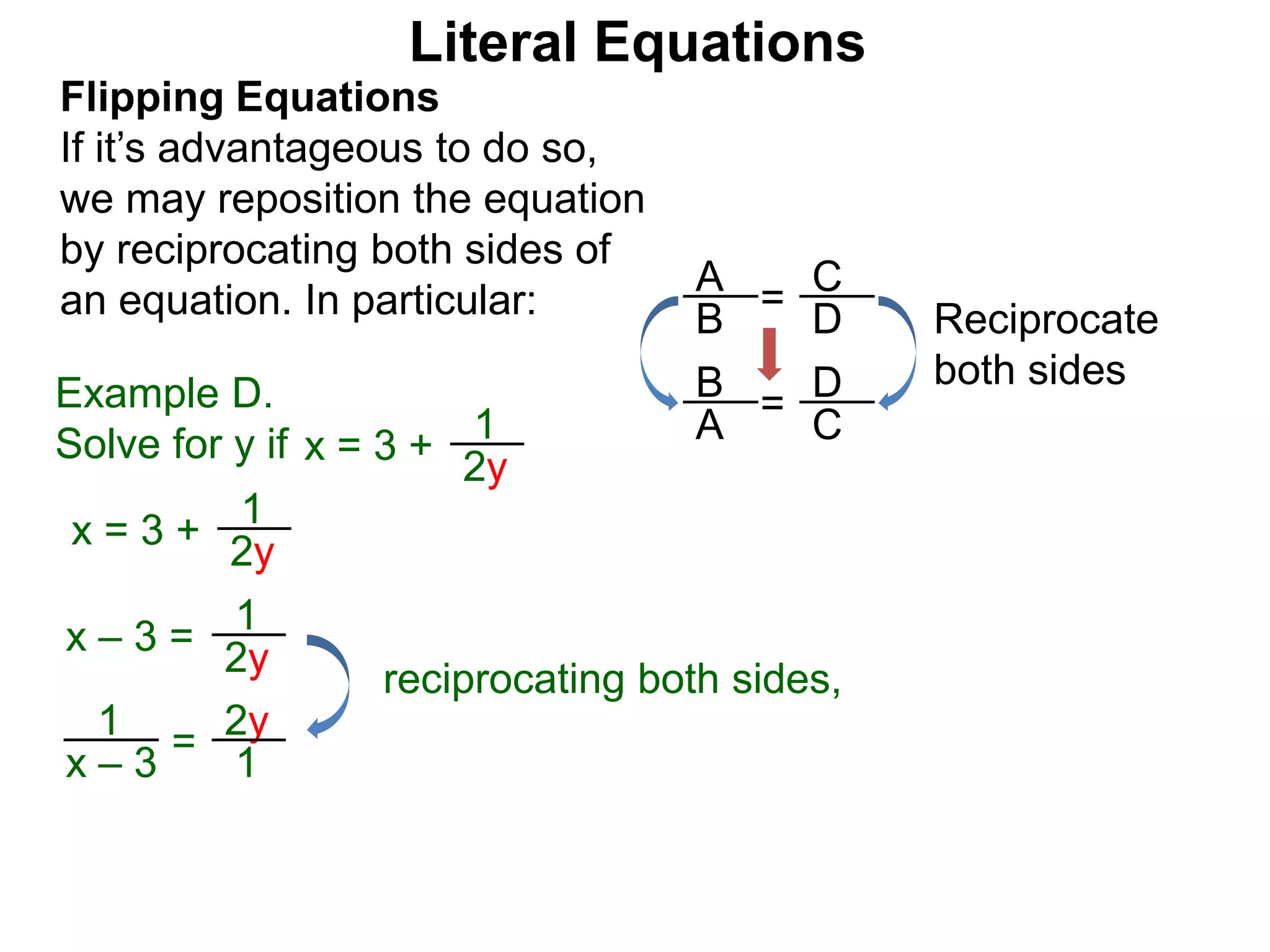
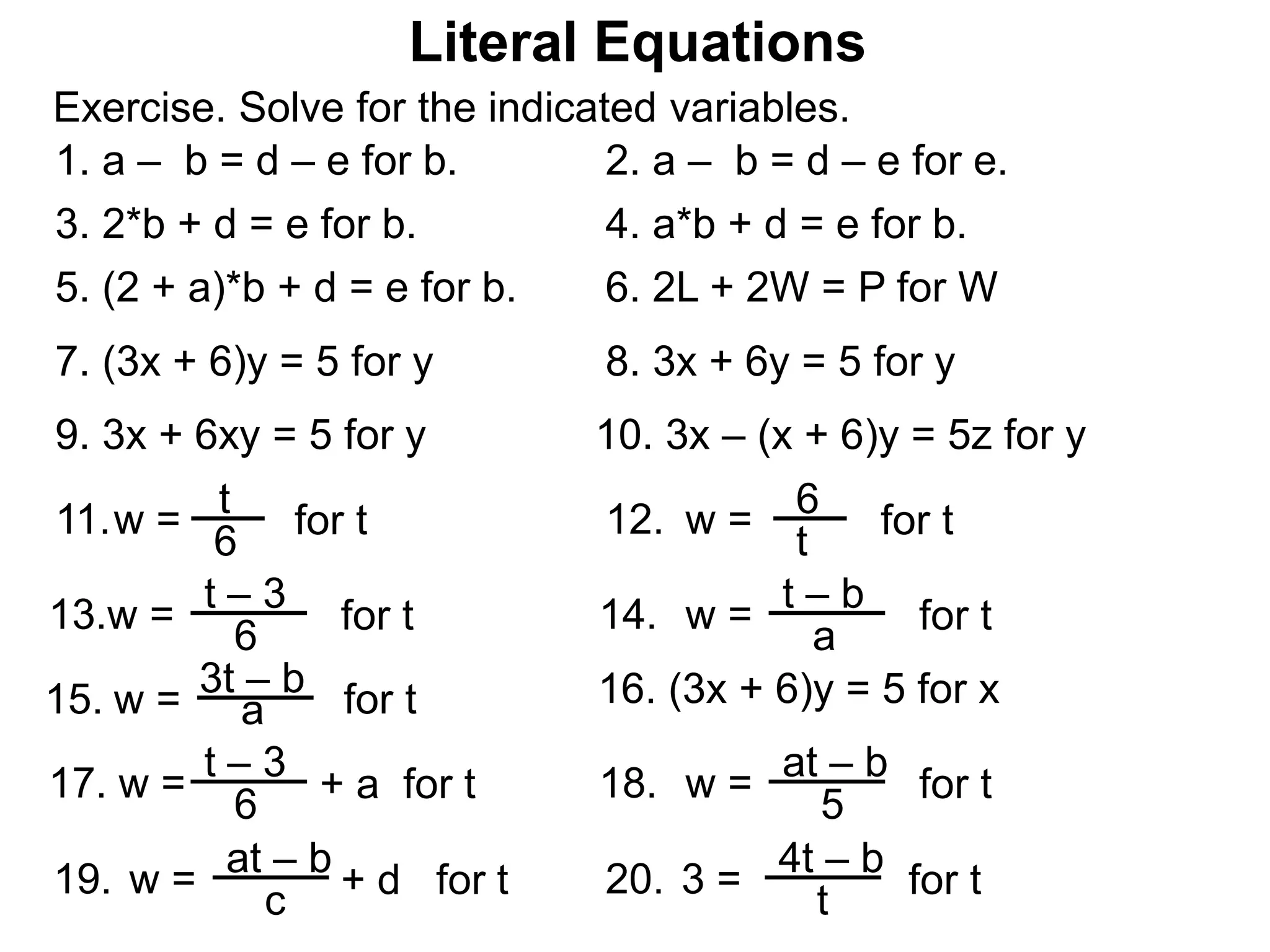
The document discusses solving literal equations by isolating the variable of interest on one side of the equation. It provides examples of solving equations for various variables by adding, subtracting, multiplying, or dividing both sides of the equation by the same quantity. The goal is to isolate the variable being solved for so it stands alone on one side of the equal sign. Steps include clearing fractions, moving all other terms to the other side of the equation, and then dividing both sides by the coefficient of the variable being solved for.