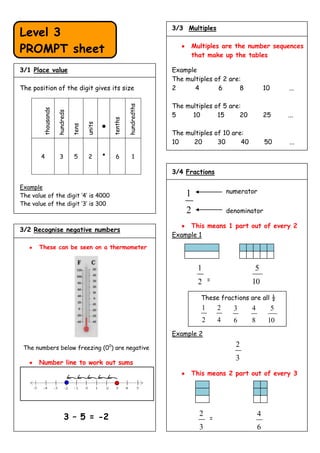
The document provides examples and explanations of various math concepts including place value, multiples, fractions, decimals, addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, measuring units, classifying shapes, and representing data visually using charts, diagrams and tables. It covers essential math topics for levels 3-4 such as number sequences, operations, geometry, measurement, and data handling.