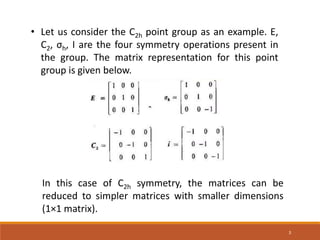
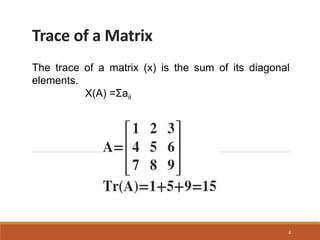
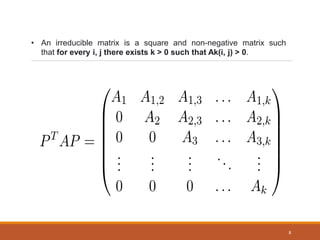
This document discusses irreducible matrix representations. It defines reducible and irreducible representations, with irreducible representations being matrices that cannot be reduced into smaller block diagonal forms through similarity transformations. The key properties of irreducible matrices are provided: 1) the sum of squares of dimensions of irreducible representations equals the group order, 2) the sum of squares of character equals the group order, and 3) characters of different representations are orthogonal. Examples of applications in quantum physics and chemistry are given related to labeling energy states based on irreducible representations.