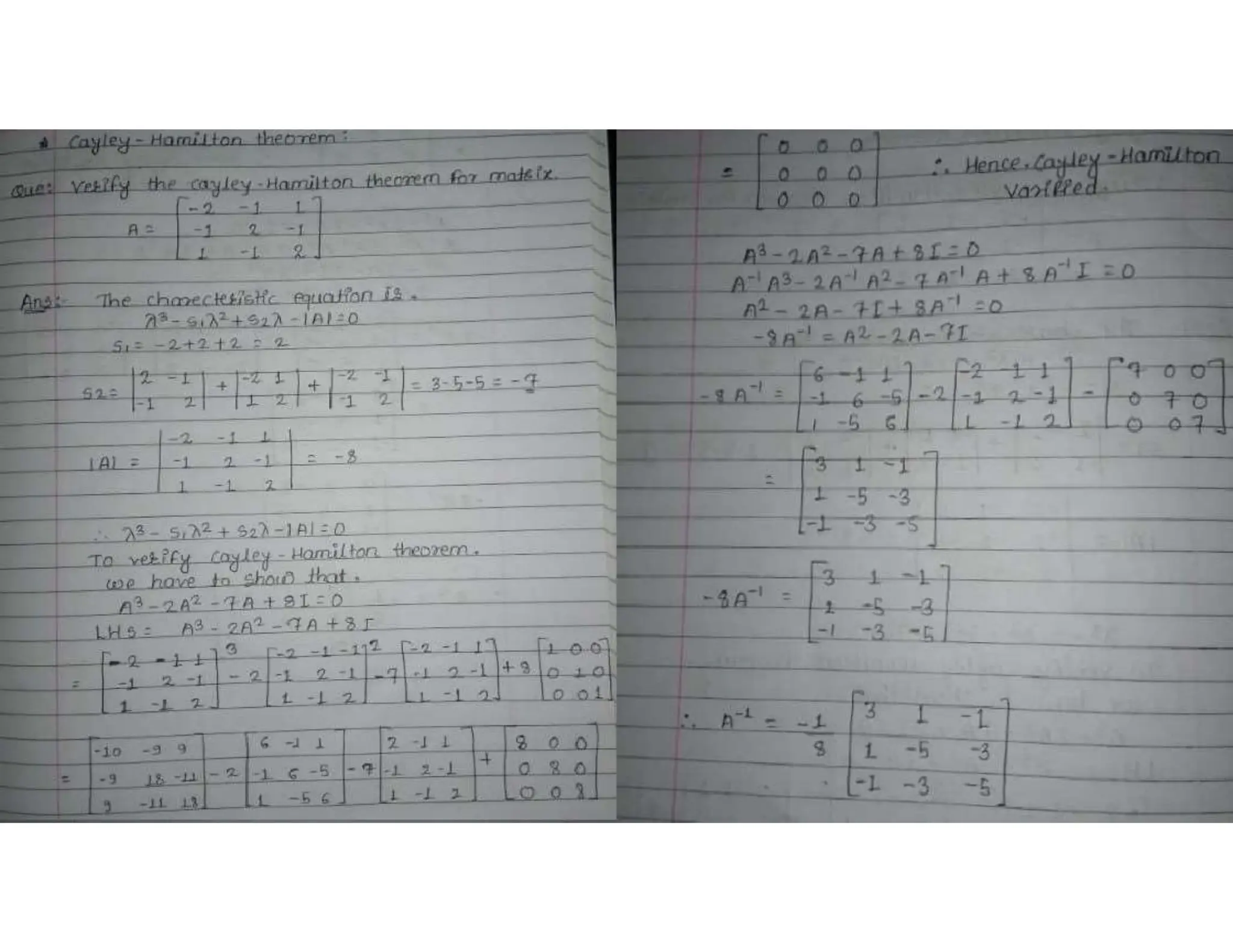
The document discusses key concepts in linear algebra, including the rank of a matrix, which indicates the maximum number of linearly independent rows or columns, and is important for solving linear systems. It also covers the Cayley-Hamilton theorem, which asserts that any square matrix satisfies its own characteristic polynomial, resulting in the zero matrix. Additionally, the document explains diagonalization of a matrix, which involves finding a matrix that transforms a square matrix into a diagonal form if it has enough linearly independent eigenvectors.



![DIAGONALIZATION OF MATRIX
BAB =
1
If ‘A
’ is square matrix of order n having n linearly independent Eigen
vector, then a non singular matrix B can be found such that B-1
AB is a
diagonal form . If A is a square of order 3, having 3 linearly independent
Eigen Vectors corresponding to Eigen Value λ1, λ2 , λ3 then
[λ 0 0
]
0 λ 0
0 0 λ
Where B is Eigen Vector Matrix for Eigen value λ1 , λ2, λ3 and B is called
Model Matrix .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/math1-240517062437-a234abd1/75/This-a-math-presentation-in-engineering-Matrix-5-2048.jpg)

