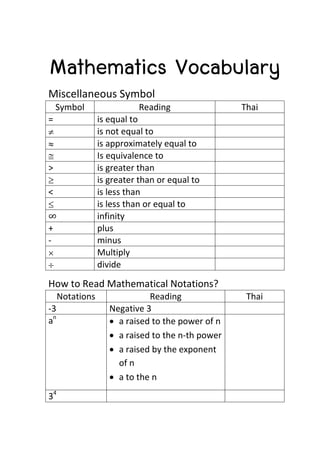
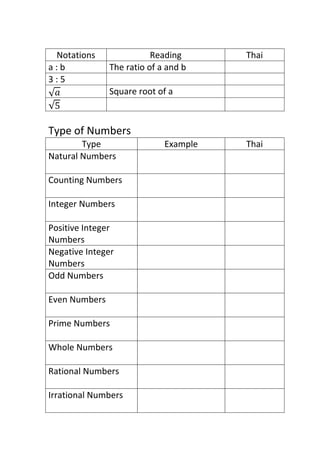
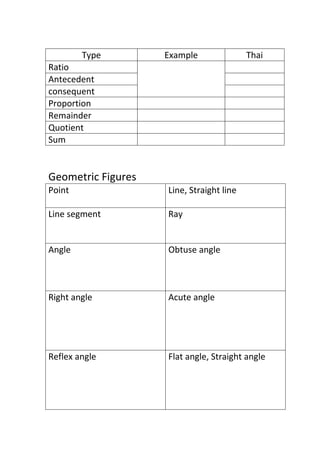
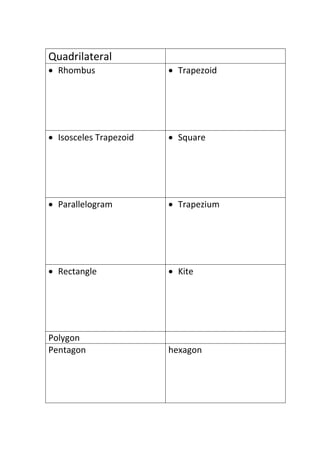
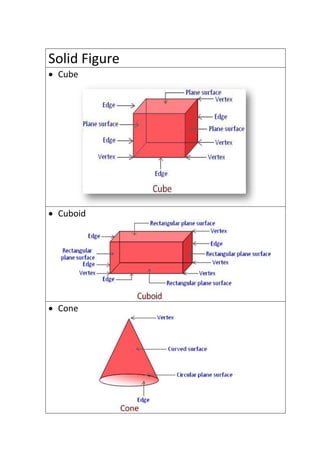
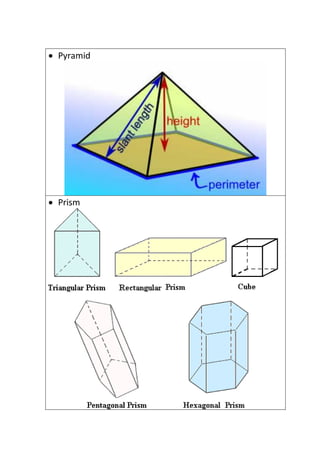
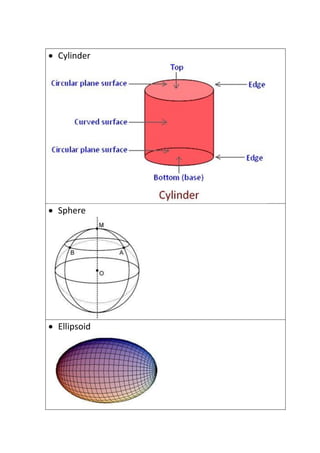
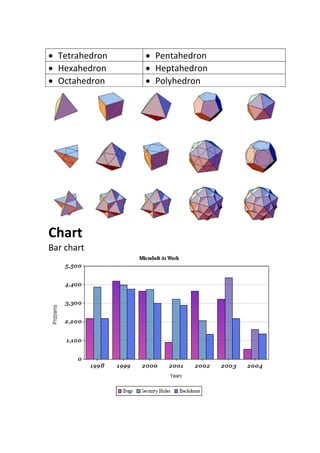
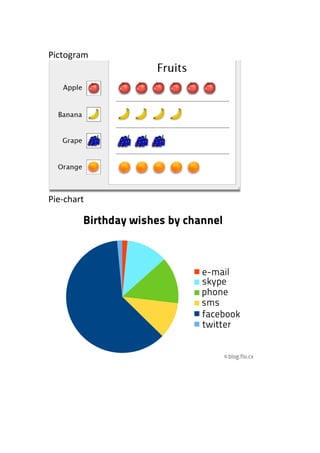
The document provides definitions and explanations of common mathematical symbols, notations, vocabulary terms, types of numbers, geometric figures, and charts. It defines symbols for equality, inequality, approximation, equivalence, operations like addition and multiplication. It explains how to read exponent notation, fractions, decimals, ratios, and more. It also lists examples of types of numbers, angles, triangles, quadrilaterals, polygons, circles, solids, and charts; and includes examples of solving simple equations by expanding, collecting like terms, and isolating the variable.