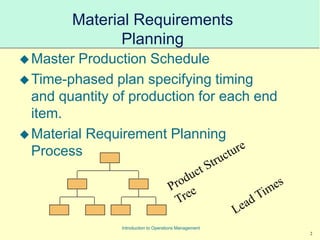
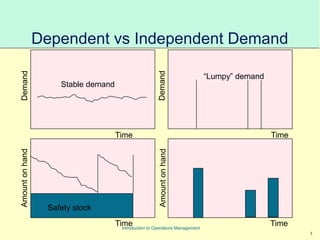
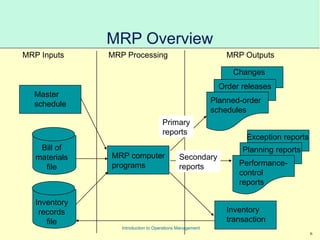
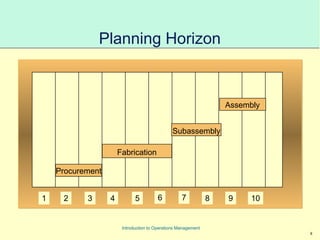
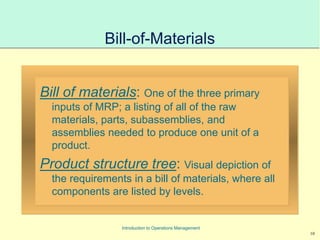
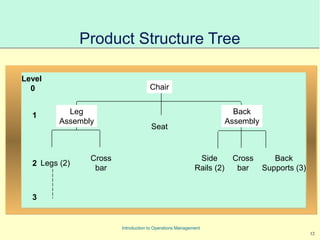
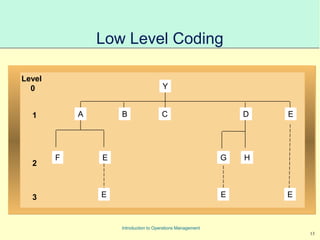
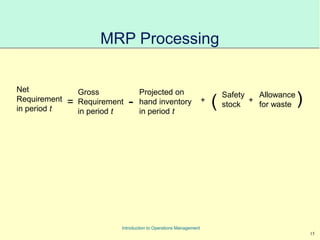
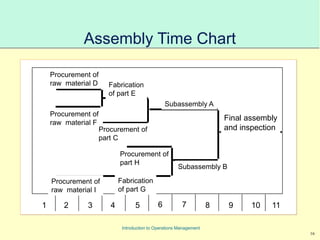
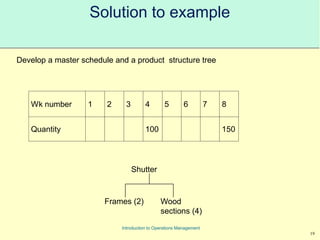
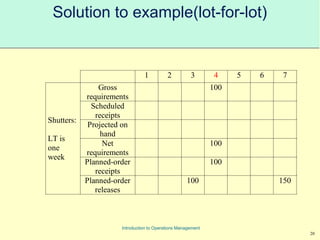
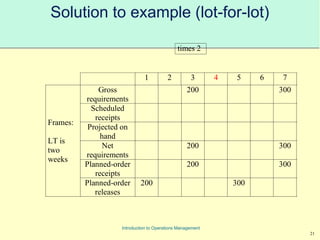
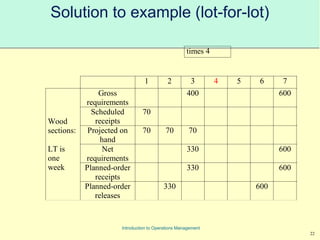
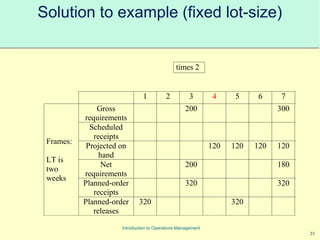
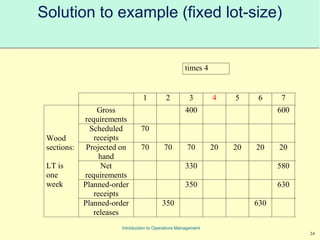
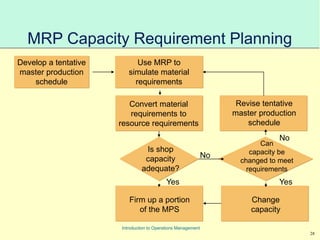
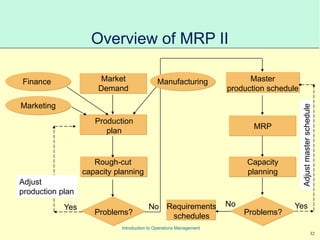
This document provides an introduction to Material Requirements Planning (MRP) and its significance in operations management, detailing its objectives, inputs, processing, and outputs. It discusses the master production schedule, bill of materials, and the importance of accurate data in the planning process. Additionally, it highlights the benefits of MRP, such as reduced inventory levels and enhanced capacity evaluation.