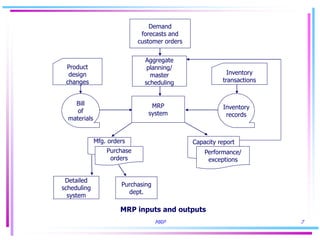
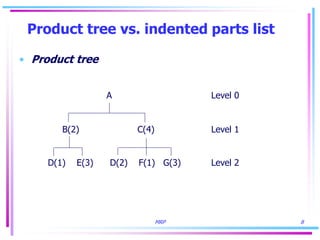
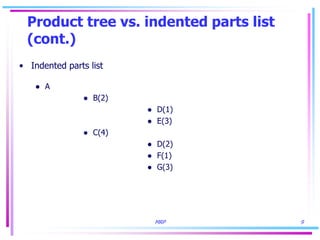
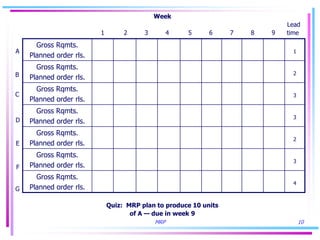
The document discusses key concepts in Material Requirements Planning (MRP), including:
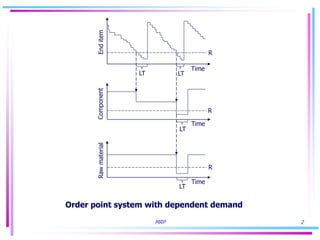
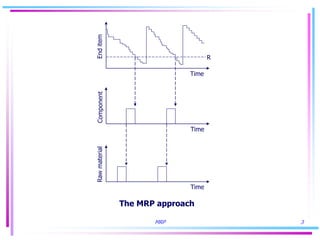
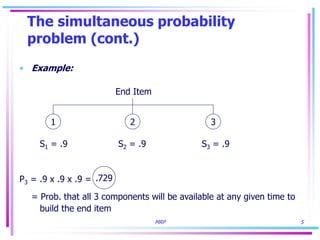
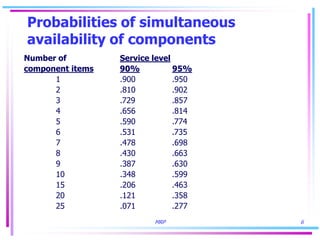
1) MRP addresses the simultaneous probability problem by accounting for the likelihood that all components of an end item will be available at the same time for production.
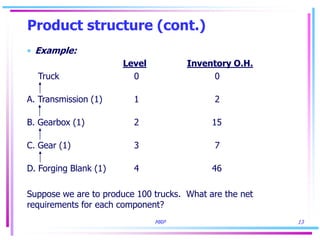
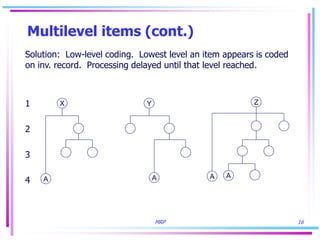
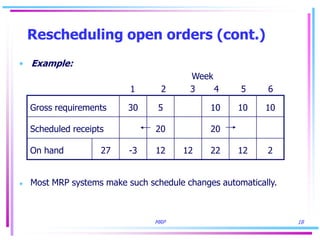
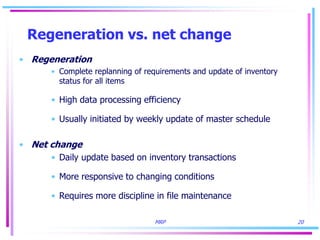
2) Product structures, recurring requirements, multilevel items, and rescheduling open orders are challenges in computing accurate requirements in MRP.
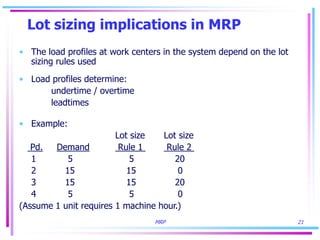
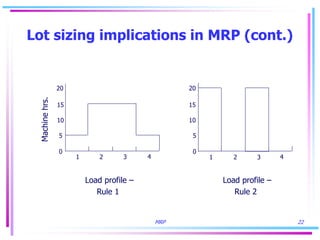
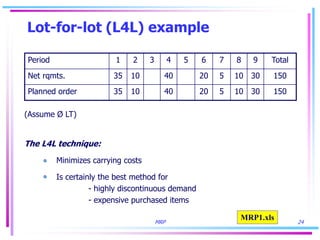
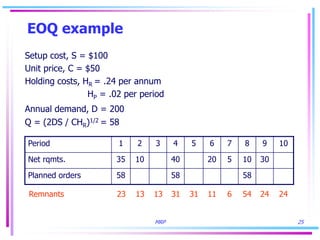
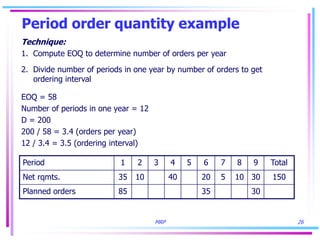
3) Lot sizing techniques like lot-for-lot, economic order quantity, and period order quantity impact load levels at work centers.
4) Safety stocks are needed in MRP to address demand and supply variations; options include fixed quantity buffers, increasing safety lead times, or inflating gross requirements.