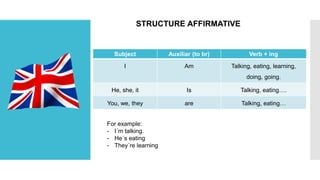
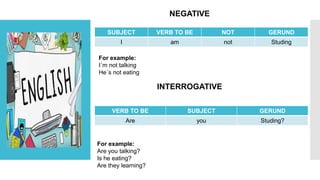
The document discusses the present continuous tense in English. It provides the structure, examples, and main uses of the present continuous tense. It is used to describe actions happening at the moment of speaking or ongoing actions in general. The document also lists common verbs that are not usually used in the present continuous form, such as verbs of senses, emotions, states, possession, and verbs of agreement.