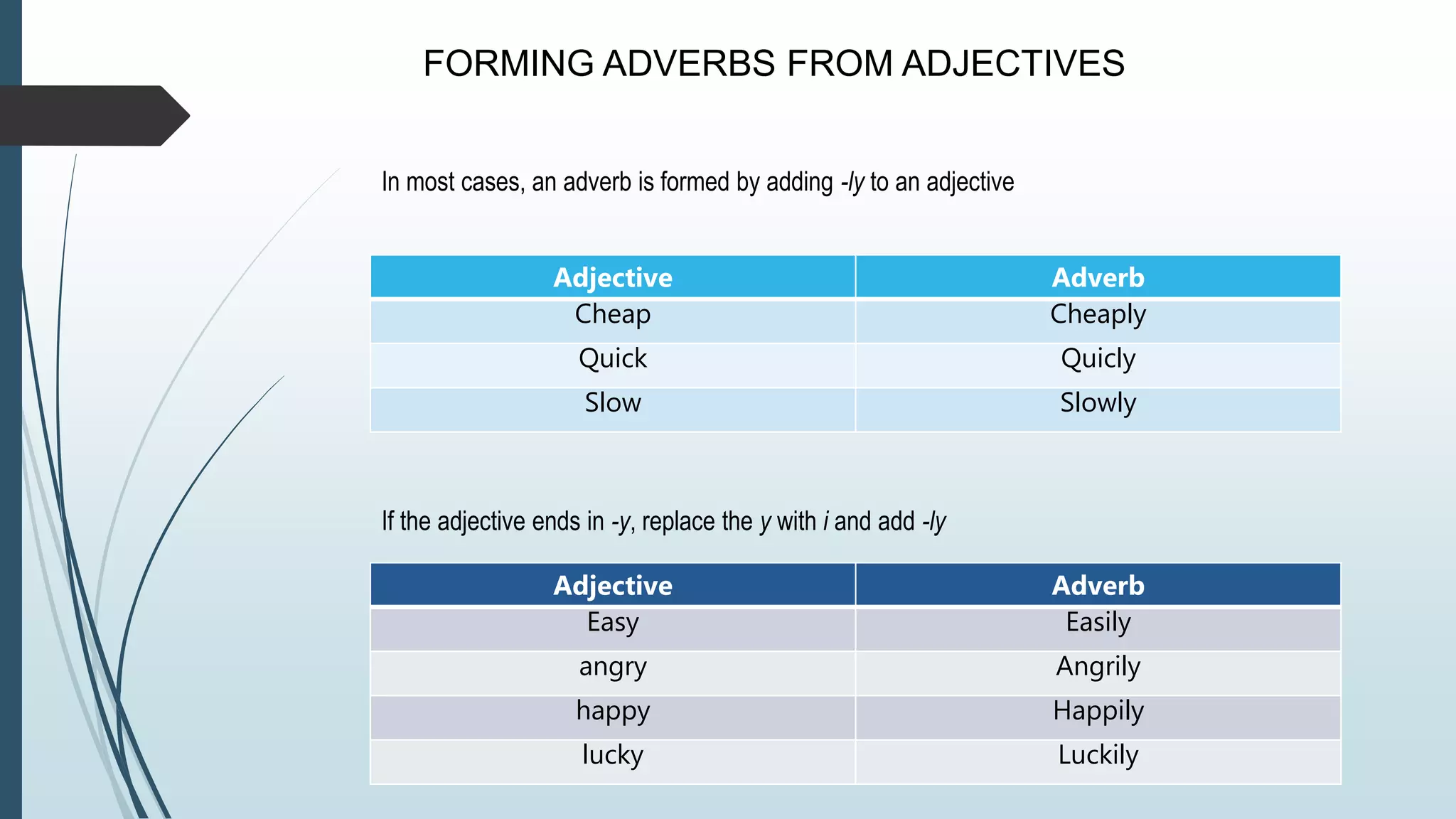
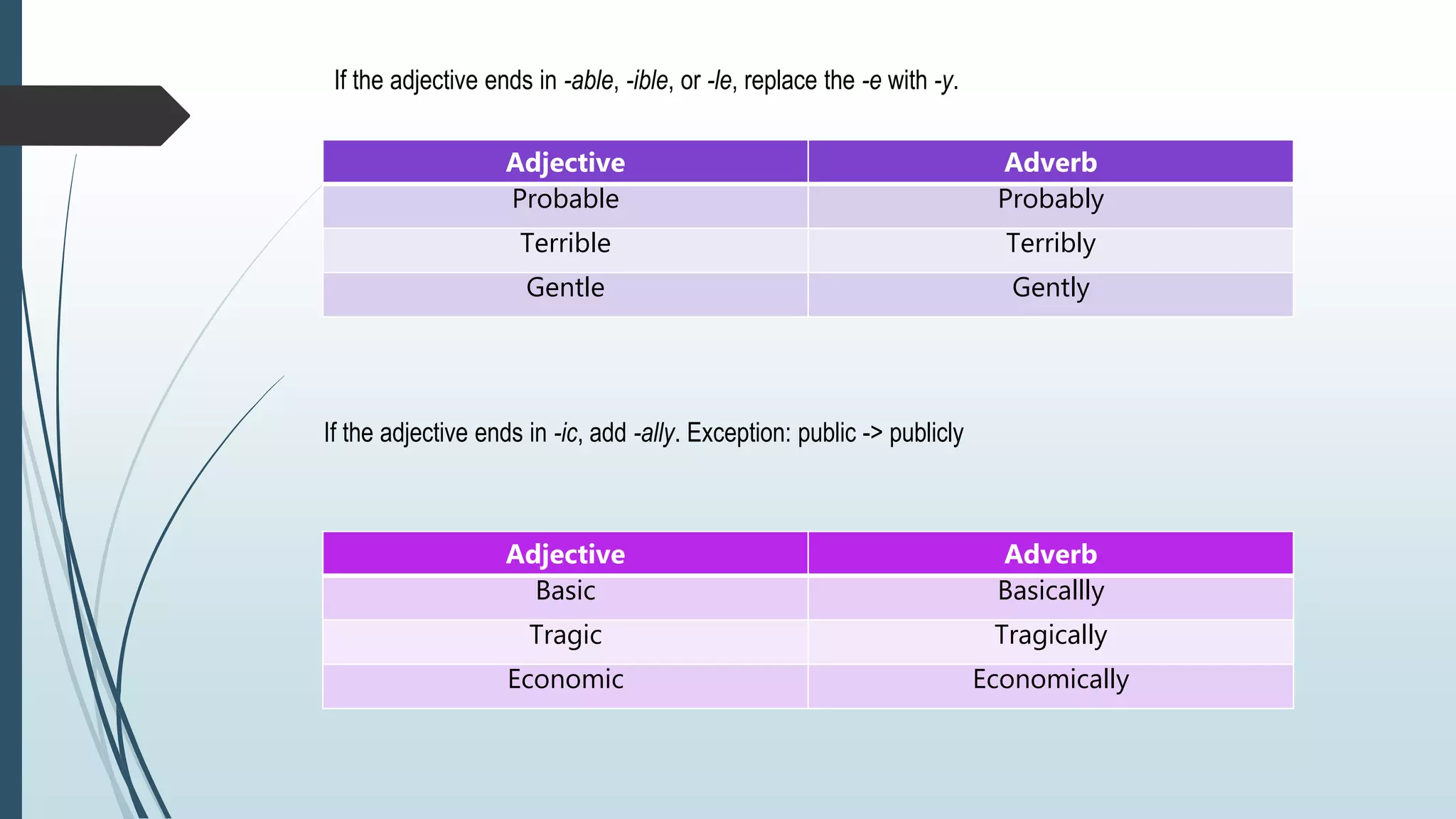
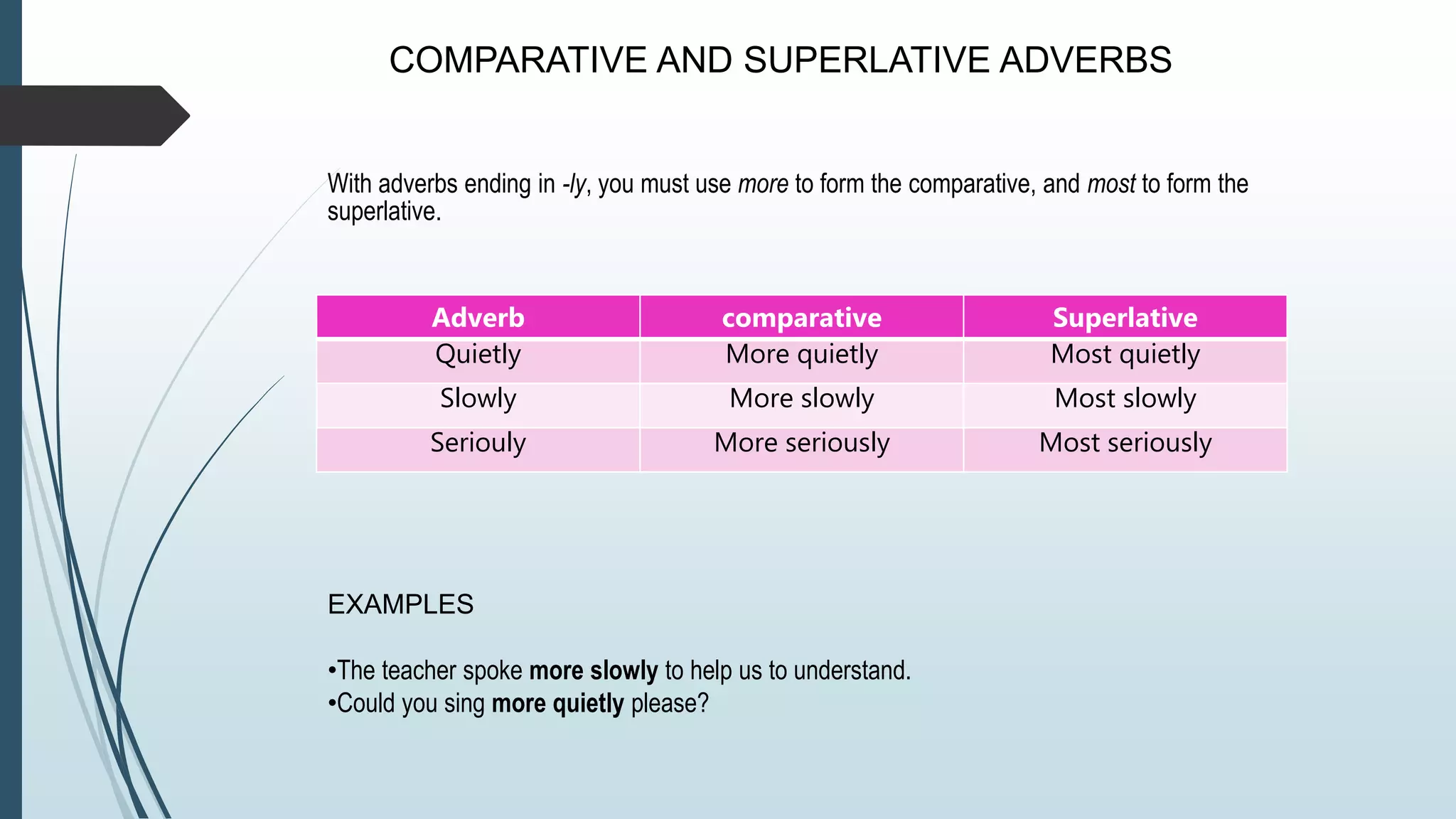
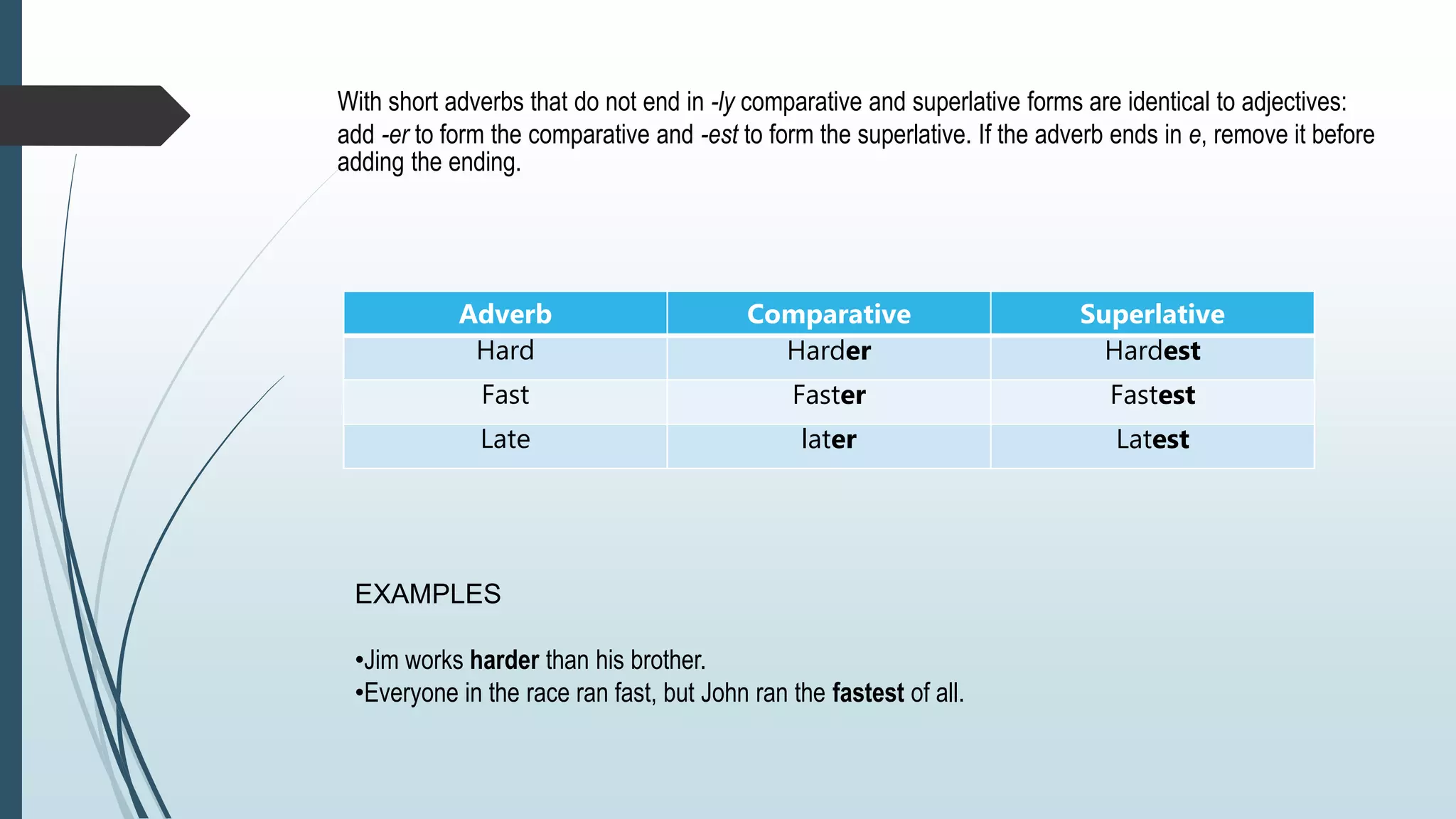
Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs to provide information about how, when, where, or how often an action occurred. Adverbs are usually formed by adding -ly to adjectives. Comparative adverbs ending in -ly use "more" and superlative adverbs use "most". Adverbs of time tell us when, how long, or how often an action occurred and have standard sentence positions. Common types of adverbs include adverbs of manner, place, time, frequency, degree, and doubt.