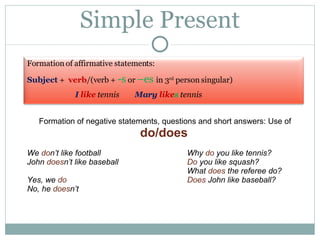
The document summarizes the simple present and present continuous tenses in English. It outlines the formation and uses of each tense. The simple present is used to describe repeated or habitual actions, permanent situations, and schedules. The present continuous emphasizes actions that are ongoing or in progress at the moment. It also expresses future arrangements and annoyance. Both tenses follow specific verb conjugation rules, and some verbs like seem are always used in simple present as they describe a state of being.