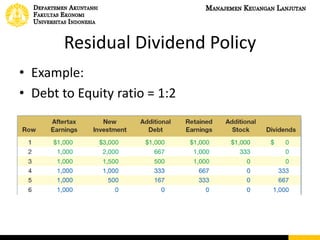
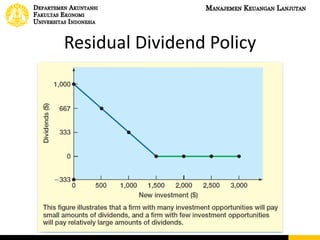
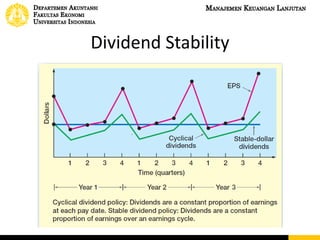
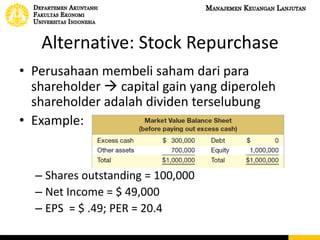
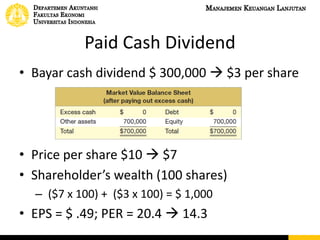
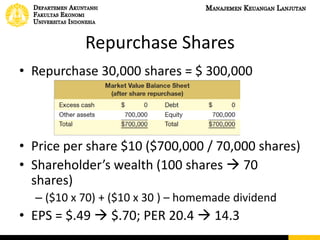
This document discusses dividend policy and different types of dividends. It introduces the concepts of cash dividends, stock dividends, and liquidating dividends. It also discusses approaches to dividend policy including the residual dividend approach and compromise dividend policy. The residual approach determines how much funds can be generated without new equity and whether to pay a dividend. The document provides an example comparing paying a cash dividend versus doing a share repurchase and their impact on shareholder wealth and EPS.