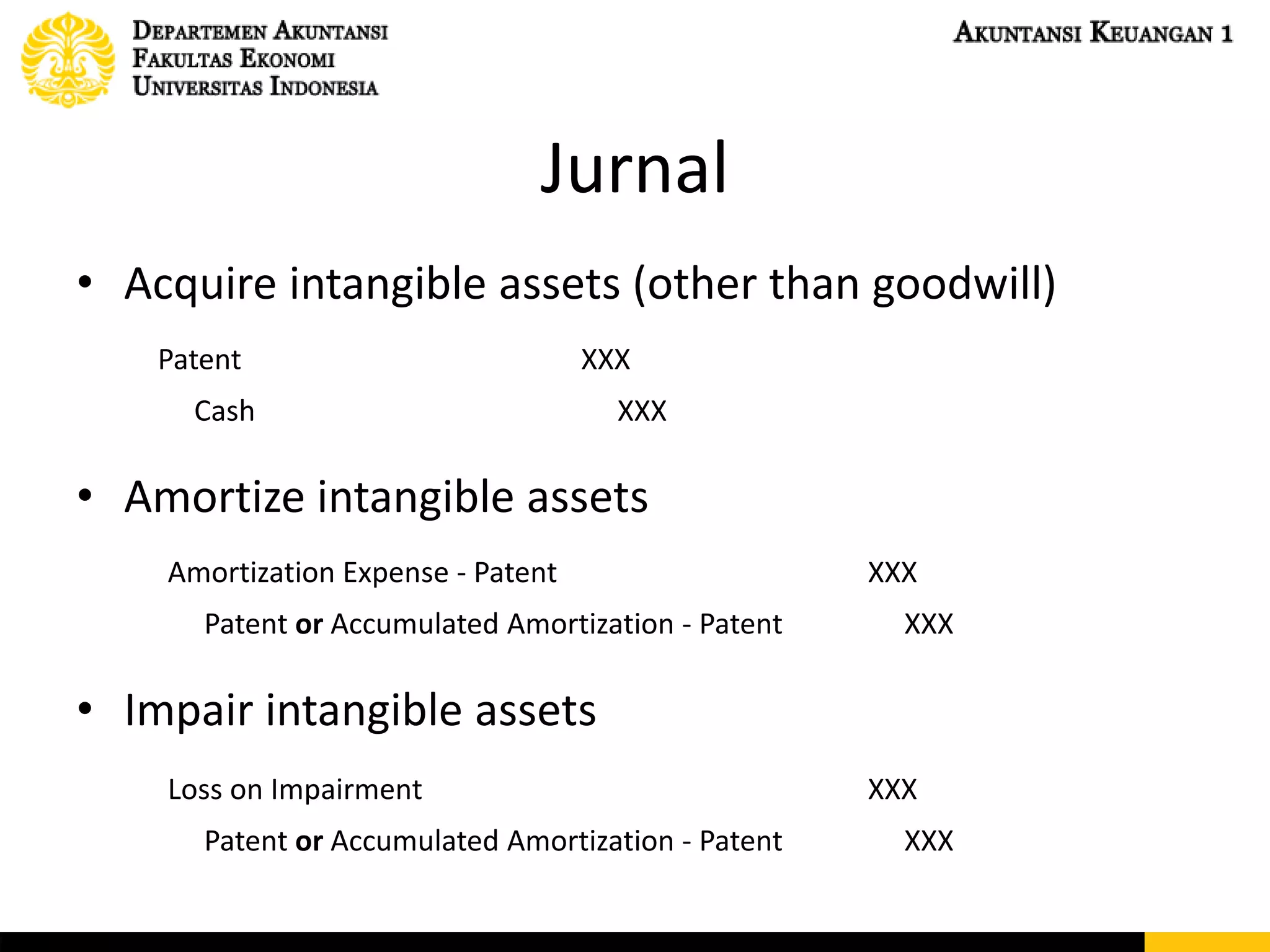
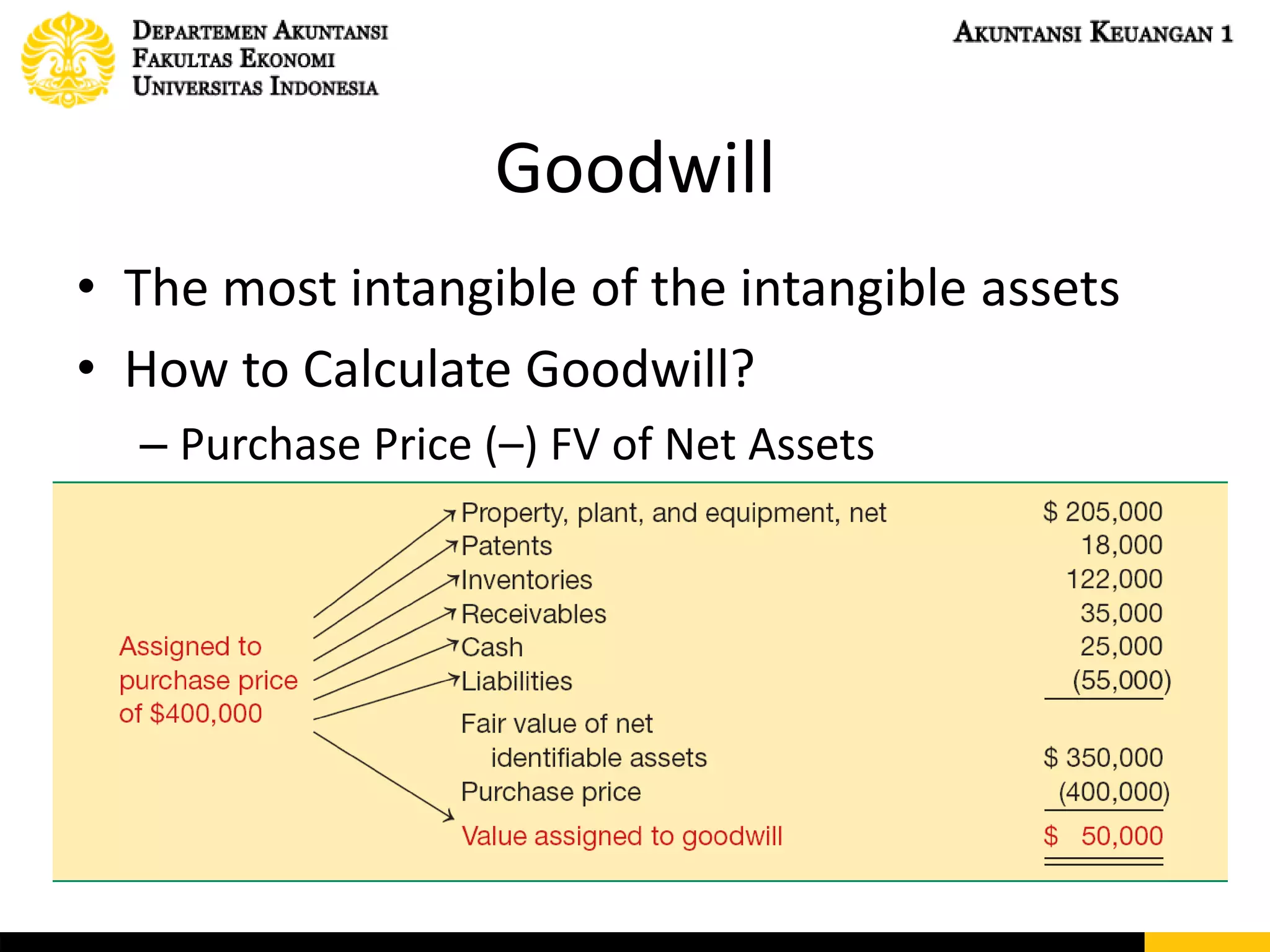
This document discusses accounting for intangible assets under PSAK 19 and IAS 38. It covers the characteristics, initial recognition, subsequent measurement, amortization, and impairment of intangible assets. Goodwill is specifically addressed, including how it is calculated and tested for impairment. The document also discusses capitalizing development costs for internally generated intangible assets once economic viability criteria are met. Examples of journal entries for acquiring, amortizing, and impairing intangible assets are provided.