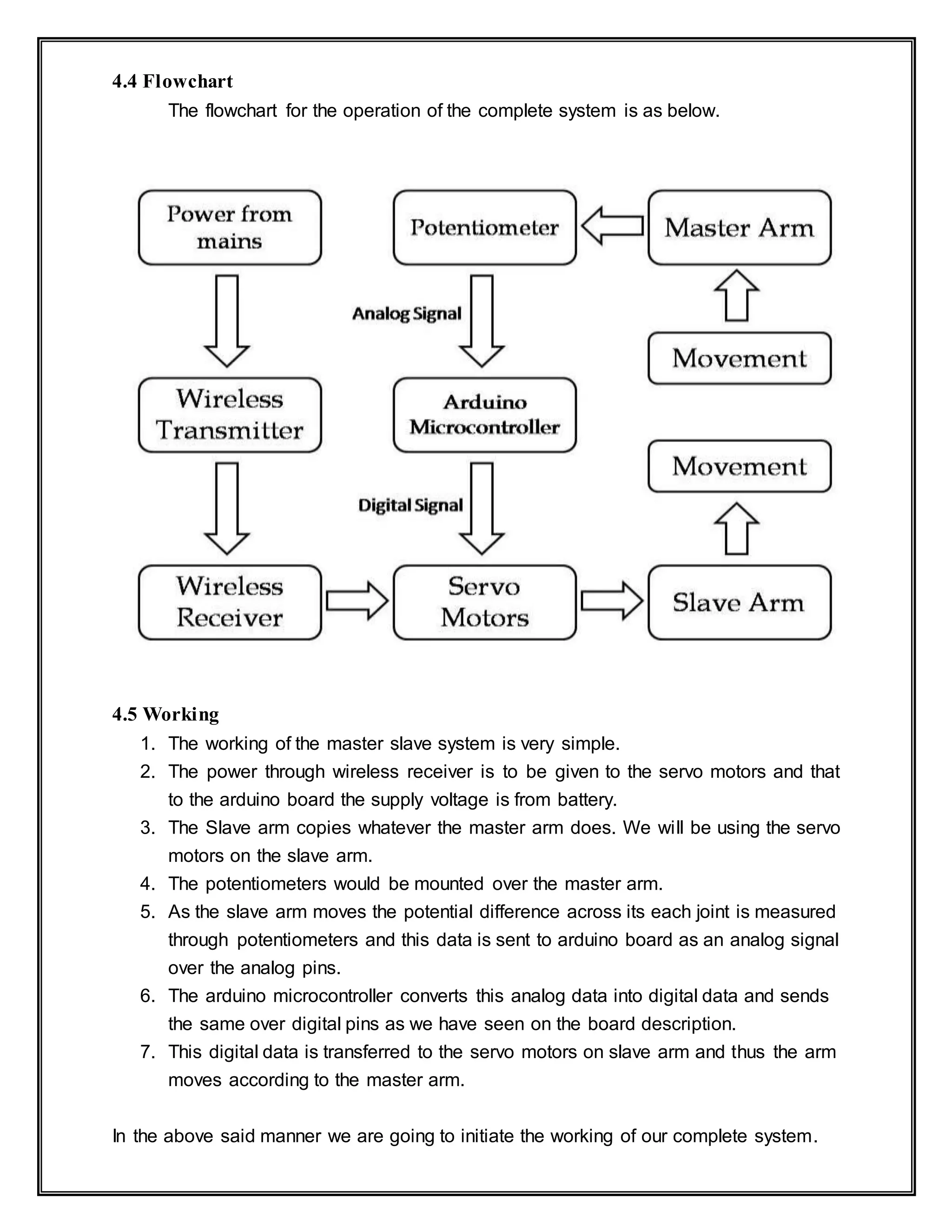
The document presents a project on developing a master-slave robotic arm powered by wireless energy transmission, using Arduino technology for control and synchronization between the master's movements and the slave arm. The project aims to enhance human-robot interaction through gesture recognition, while improving efficiency in power transmission, addressing significant energy losses associated with traditional methods. The research also delves into the design and operational methodologies required for effective robotic manipulation and wireless power implementation.


![INTRODUCTION
1.0 Introduction
Interpretation of master slave system is used for human-machine interaction in
the area of robotics. The main purpose of master slave system research is to identify
and give a particular human movement and convey information to the robot pertaining
to individual movement. Specific movement of interest can be given, and on the basis of
that, specific command for execution of action can be given to robotic system. Overall
aim is to make the microcontroller understand human body language, thereby bridging
the gap between machine and human. Hand gesture recognition can be used to
enhance human–machine interaction without depending on traditional input devices
such as keyboard and mouse. Hand gestures are extensively used for telerobotic
control applications. Robotic systems can be controlled naturally and intuitively with
such telerobotic communication. A prominent benefit of such a system is that it presents
a natural way to send geometrical information to the robot such as: left, right, etc.
Robotic hand can be controlled remotely by hand movements. Research is being
carried out in this area for a long time. Several approaches have been developed for
sensing hand movements and controlling robotic hand. Glove based technique is a well-
known means of recognizing hand gestures. It utilizes sensor attached mechanical
glove devices that directly measure hand and/or arm joint angles and spatial position.
Although glove-based gestural interfaces give more precision, it limits freedom as it
requires users to wear cumbersome patch of devices. Technologists have used entropy
analysis to extract hand region in complex background for master slave robotic system.
Robot controlling is done by fusion of hand positioning and arm gestures using dummy
arm. Although it gives more precision, it limits freedom due to necessity of dummy arm
movement. For capturing hand gestures correctly, proper pots and angles are required.
The problem of précised position recognition and tracking is quite challenging. Many
early approaches used lengthy programming and different codes to make the problem
of position recognition easier, but due to their inconvenience, they cannot be considered
as a natural interface for the robot control. The use of specific pots, servos and arduino
microcontroller board could be the best solution for this as arduino can be coded in
higher level languages. It can be extended to any robotic system with a number of
specific commands suitable to that system.
One of the major issue in power system is the losses occurs during the
transmission and distribution of electrical power. As the demand increases day by day,
the power generation increases and the power loss is also increased. The major
amount of power loss occurs during transmission and distribution. The percentage of
loss of power during transmission and distribution is approximated as 26%. The main
reason for power loss during transmission and distribution is the resistance of wires
used for grid. The efficiency of power transmission can be improved to certain level by
using high strength composite overhead conductors and underground cables that use
high temperature super conductor. But, the transmission is still inefficient. According to
the World Resources Institute (WRI), India’s electricity grid has the highest transmission
and distribution losses in the world – a whopping 27%. Numbers published by various
Indian government agencies put that number at 30%, 40% and greater than 40%. This
is attributed to technical losses (grid’s inefficiencies) and theft [1]. Any problem can be
solved by state–of-the-art technology. The above discussed problem can be solved by
choose an alternative option for power transmission which could provide much higher
efficiency, low transmission cost and avoid power theft. Microwave Power Transmission](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/synopsisreport-151130110543-lva1-app6892/75/Master-Slave-Robotic-Arm-Using-Wireless-Transmission-Of-electricity-4-2048.jpg)







![REFERENCES
PDF EDITION OF CARL DAVID TODD (ED), "THE POTENTIOMETER
HANDBOOK",MCGRAW HILL, NEW YORK 1975 ISBN 0-07-006690-6
UPSON, A.R; BATCHELOR, J.H. (1978) [1965]. SYNCHRO ENGINEERING
HANDBOOK . BECKENHAM: MUIRHEAD VACTRIC COMPONENTS. PP. 7, 67–90.
ROBOTICS, AUTOMATION AND MECHATRONICS, 2004 IEEE CONFERENCE ON
(VOLUME:1 ) PAGES 37 - 42 VOL.1 ISBN:0-7803-8645-0
HU, A.P. (2009). WIRELESS/CONTACTLESS POWER SUPPLY: INDUCTIVE
COUPLED RESONANT CONVERTER SOLUTIONS, SAARBRUCKEN, GERMANY:
VDM VERLAG, DR. MULLER.
SYSTEM FOR TRANSMISSION OF ELECTRICAL ENERGY, U.S. PATENT NO. 645,576
MARCH 20, 1900.
OWI ROBOTIC ARM EDGE ASIN: B0017OFRCY
BUILD YOUR OWN ROBOTIC ARM LESSON PDF MANUAL.
"PROGRAMMING ARDUINO GETTING STARTED WITH SKETCHES" . MCGRAW-
HILL . NOV 8, 2011. RETRIEVED 2013-03-28.
"THE ARDUINO SOURCE CODE" . THE ARDUINO SOURCE CODE. "POLICY" .
ARDUINO.CC. RETRIEVED 2013-01-18.
WEBSITES
www.arduino.cc
www.wikipedia.com
www.instructables.com
www.societyofrobots.com
www.letsmakerobots.com
www.google.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/synopsisreport-151130110543-lva1-app6892/75/Master-Slave-Robotic-Arm-Using-Wireless-Transmission-Of-electricity-13-2048.jpg)
