The document discusses the components, working principle, and programming of a line following robot. It contains the following key points:
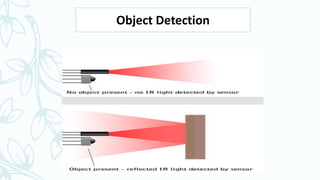
1. A line following robot uses IR sensors to sense a black line on a white surface and maneuvers itself to stay on the line by constantly correcting its position.
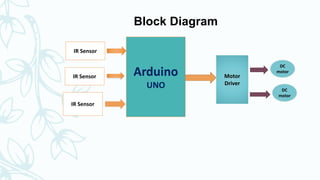
2. The main components are an Arduino microcontroller, IR sensors to detect the line, and motors controlled by an L298N motor driver.
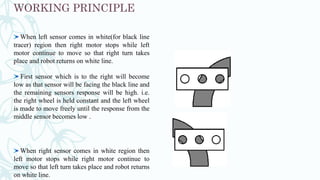
3. The IR sensors detect the line and send signals to the Arduino, which determines if the robot needs to turn left, right, or go straight to stay centered on the line.