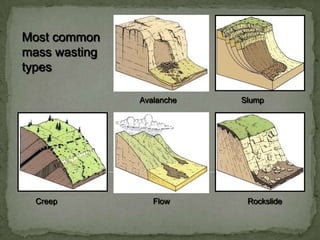
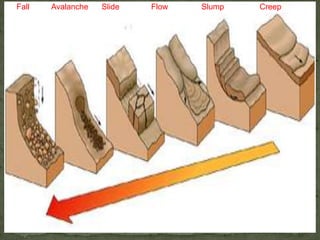
Mass wasting refers to the downslope movement of rock and soil due to gravity. It occurs when gravitational forces exceed the frictional or shear strength of the material. The document discusses the key factors that influence mass wasting, including slope steepness, water content, vegetation, and earthquakes. It also describes different types of mass wasting processes such as slides, flows, slumps, creeps, and falls, which are classified based on the material and speed of movement. The document emphasizes that mass wasting is an important geologic hazard, and outlines some methods to lessen its effects, such as removing weight from slopes, using engineering controls, and stabilizing slopes with vegetation.