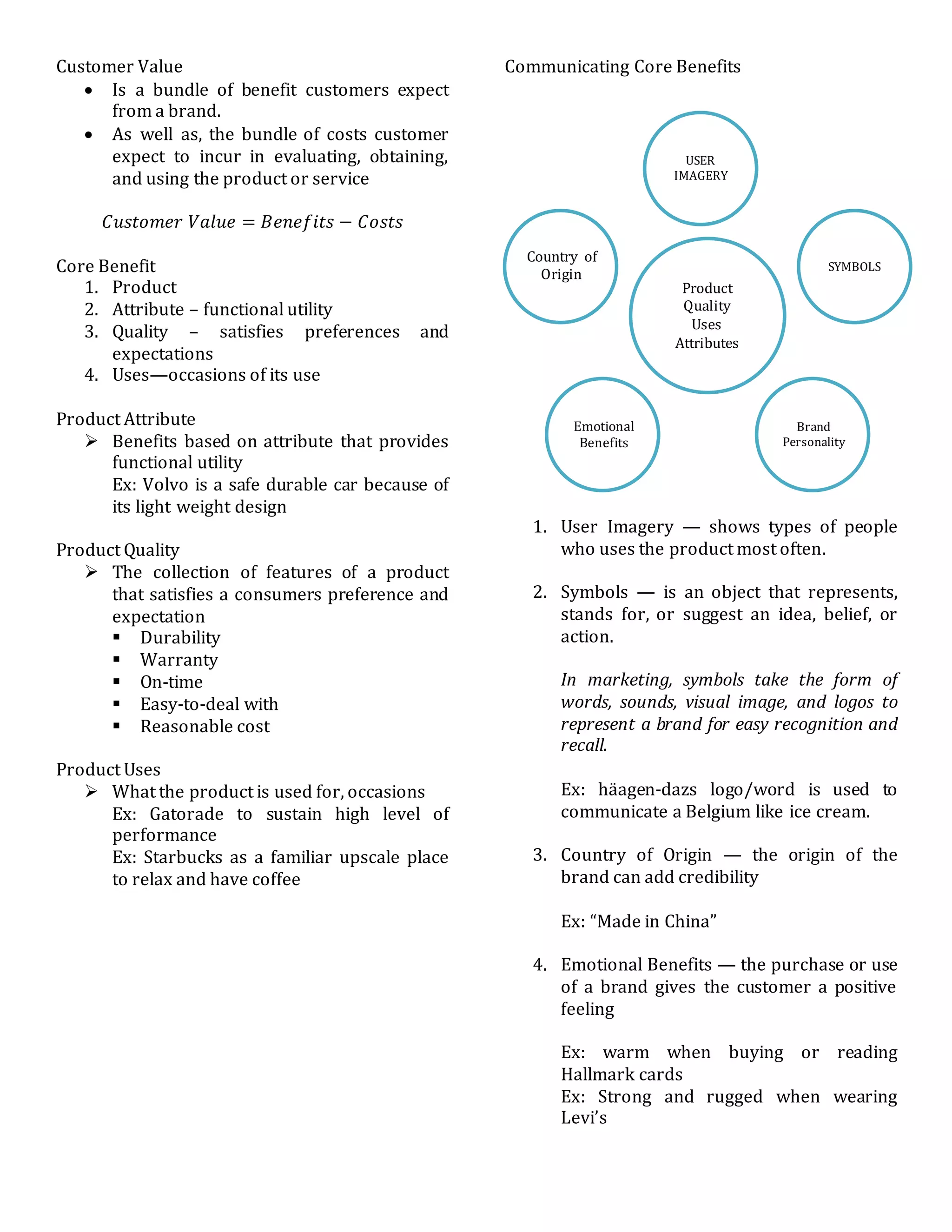
The document discusses customer value and marketing strategies. It defines customer value as the benefits customers expect from a brand minus the costs of obtaining and using the product or service. The core benefits that contribute to customer value are the product's attributes, quality, and potential uses. Marketers can communicate these core benefits through symbols, imagery, country of origin, and appealing to customers' emotional needs. The document also outlines strategies for market penetration, development, and new product development, as well as frameworks for analyzing competition, developing marketing objectives and plans, and forecasting sales.