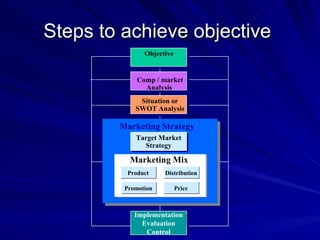
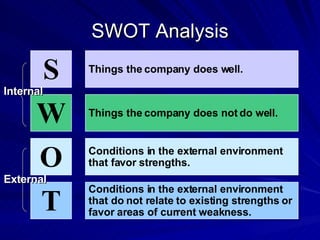
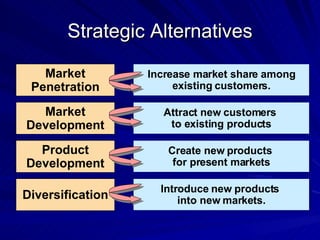
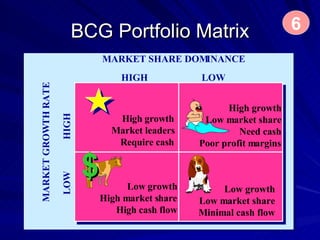
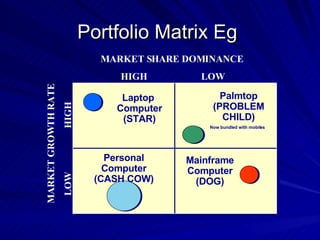
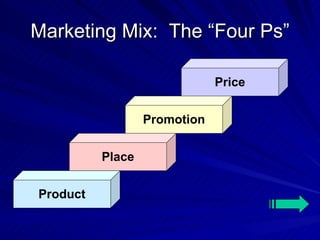
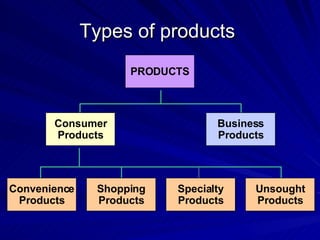
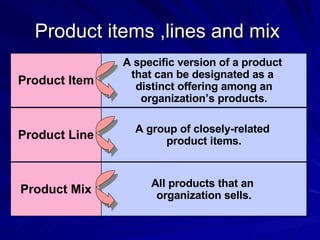
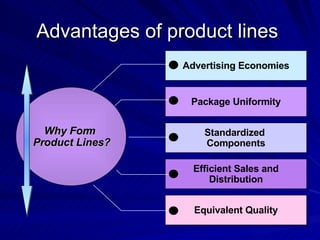
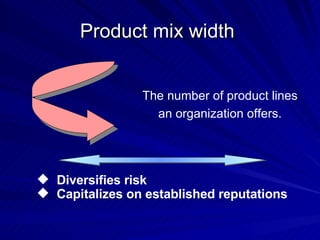
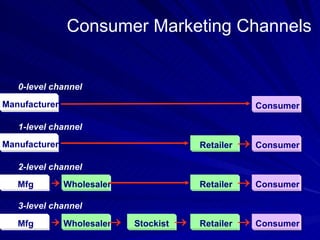
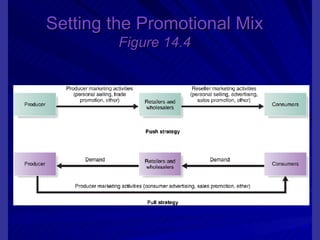
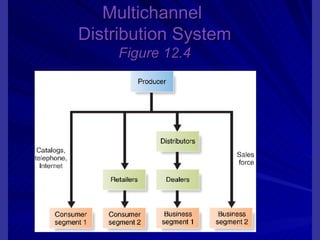
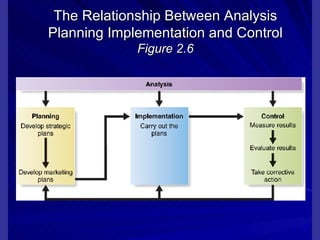
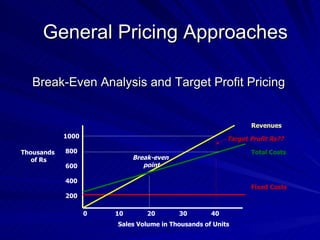
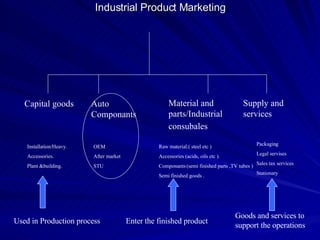
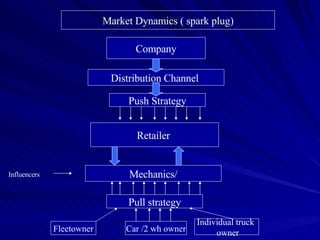
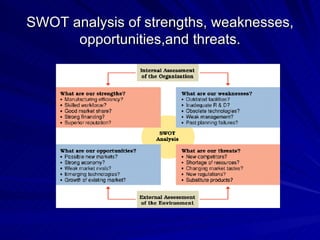
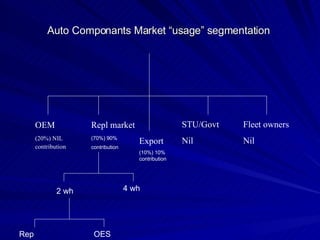
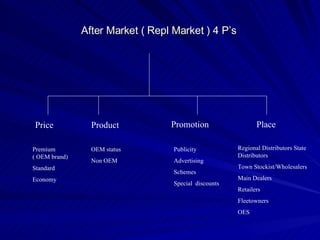
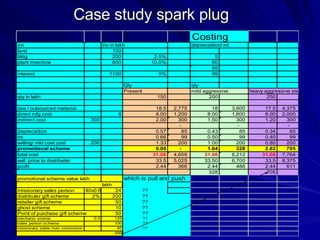
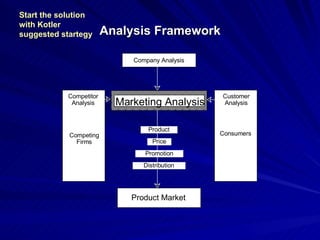
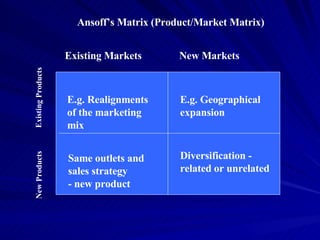
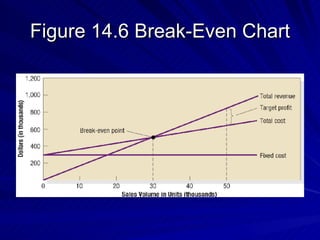
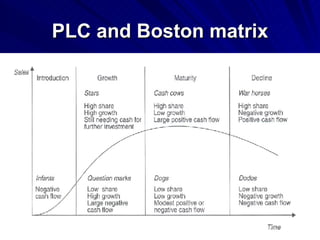
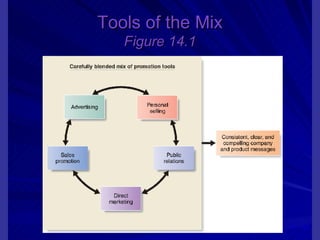
The document discusses key marketing concepts including the marketing mix, SWOT analysis, target markets, and marketing plan implementation. It provides an overview of developing a marketing plan including analyzing the market, competitors, and SWOT, then defining objectives and strategies for the marketing mix of product, price, place, and promotion. The marketing mix and distribution channels for various types of products and customers are also summarized.