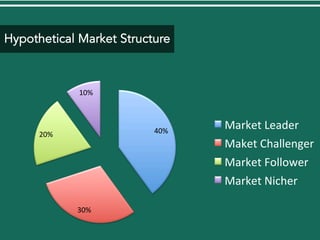
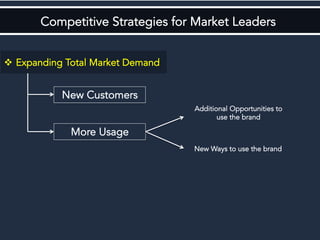
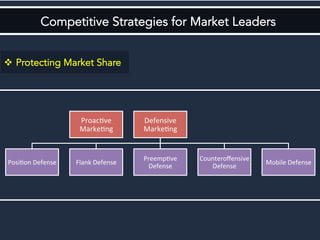
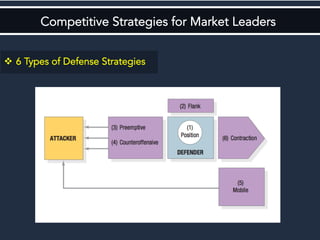
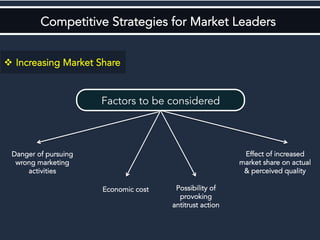
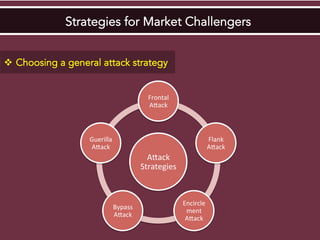
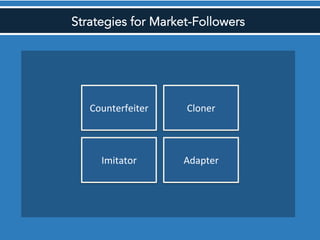
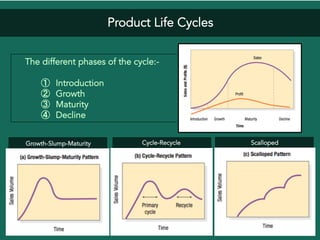
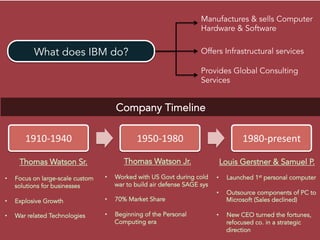
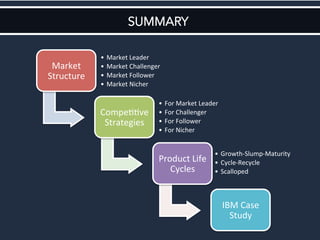
The document discusses competitive strategies for different market structures. It outlines strategies for market leaders to expand demand and protect market share. Market challengers can attack leaders or other firms. Followers imitate and adapt, while nichers focus on small, specialized markets. The product life cycle progresses through introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. The case study describes IBM's history and transformation from hardware to consulting and analytics, helping solve major problems.