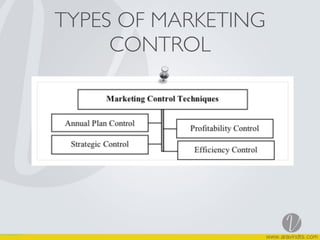
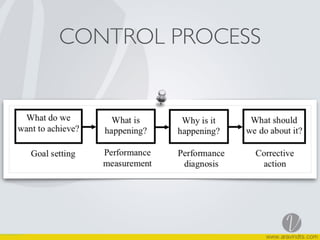
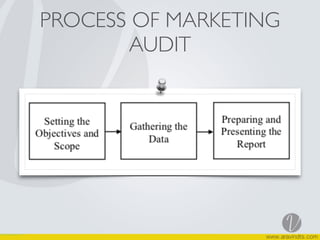
The document discusses marketing control systems and marketing audits. It describes that marketing control involves establishing standards, measuring performance, identifying strengths and weaknesses of programs, and setting corrective actions. Marketing audits comprehensively analyze objectives, environment, strategies, activities to identify problems and opportunities and recommend actions. Features of marketing audits include being comprehensive, systematic, independent, and conducted periodically. The process of a marketing audit is also outlined.