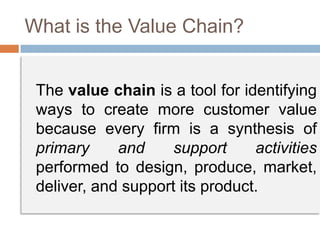
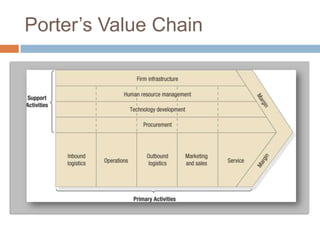
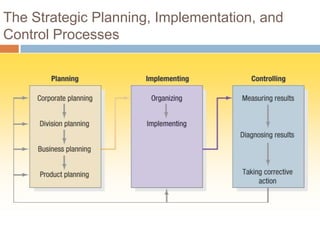
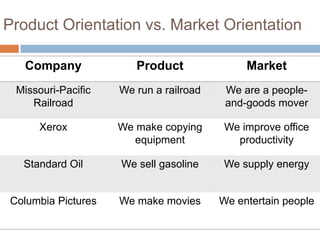
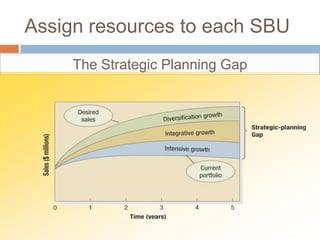
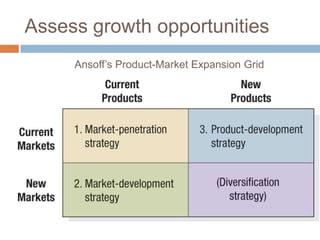
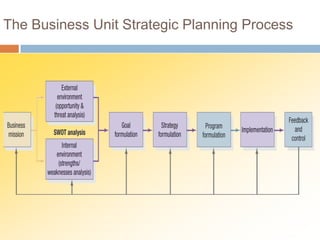
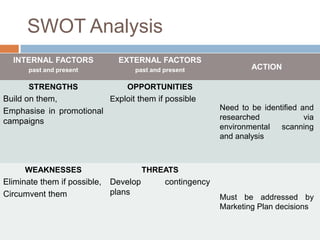
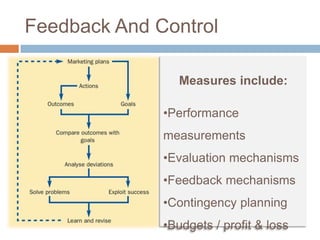
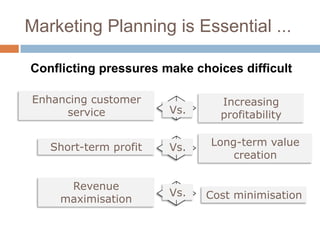
The document outlines the concepts of the value chain and marketing plans, emphasizing their importance in creating customer value and strategic direction. It details the characteristics of core competencies, the functions of strategic and tactical levels in marketing, and the significance of mission statements and strategic business units. Additionally, it discusses methods such as SWOT analysis, market opportunity analysis, and the formulation of goals and strategies to enhance organizational performance.