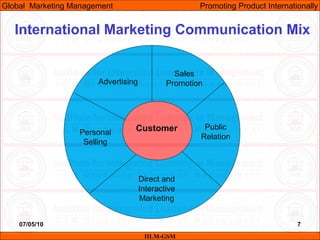
The document discusses factors that influence international marketing communication decisions. It provides examples of how culture, language, and education can impact whether communication strategies and messages need to be standardized or adapted for different global markets. Culture is a major factor, as messages that work well domestically may be misunderstood abroad due to differences in cultural norms and traditions. Language translation errors can also undermine communication if the translated text conveys an unintended meaning. Education levels affect the appropriate tools and content, as markets with lower literacy may respond better to visual versus written messages. Standardizing communication ignores these important factors that shape customer understanding in global contexts.