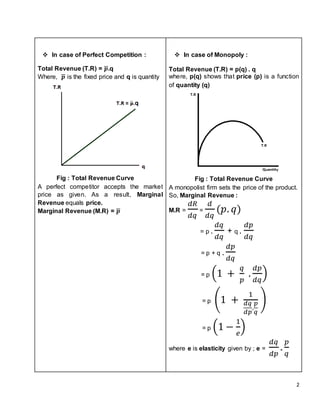
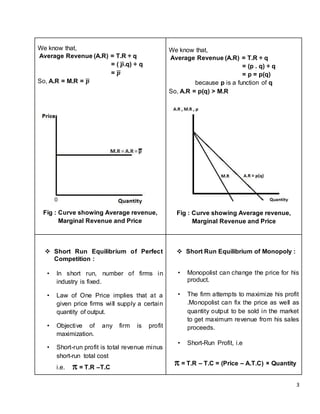
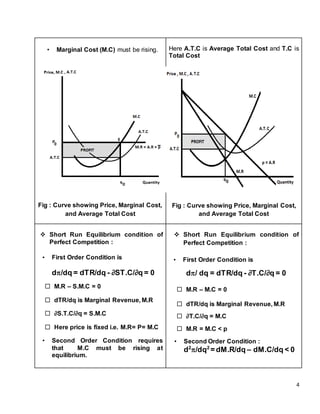
Perfect competition and monopoly represent opposite extremes of market structure. Under perfect competition, many small firms produce identical goods, with no barriers to entry or exit. Firms are price takers. In monopoly, there is a single seller of a unique good, with barriers preventing other firms from entering the market. The monopolist is a price maker that faces a downward sloping demand curve. In both short-run equilibrium, marginal revenue equals marginal cost, but under perfect competition price equals marginal cost, while under monopoly price exceeds marginal cost.