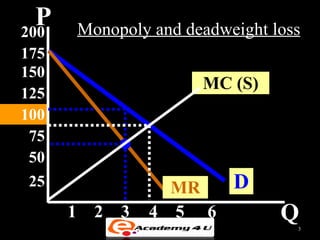
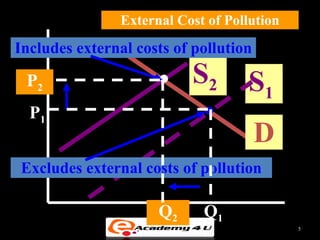
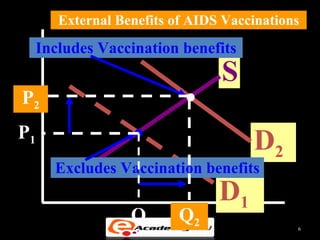
Market failure occurs when the free market does not allocate resources efficiently. There are several sources of market failure, including lack of competition, externalities, public goods, and income inequality. Externalities happen when the actions of consumers or producers impose costs or benefits on third parties not involved in the market transaction. For example, pollution is a negative externality while vaccination programs provide positive externalities. Public goods are non-exclusive and non-rivalrous, meaning many can consume them without reducing availability. While controversial, government intervention through taxes, regulations, or direct provisioning can potentially correct for market failures.