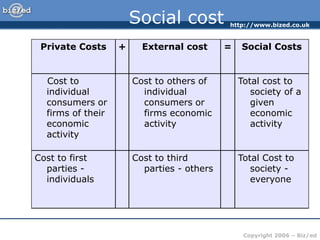
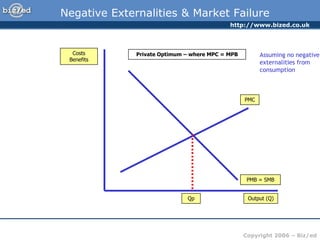
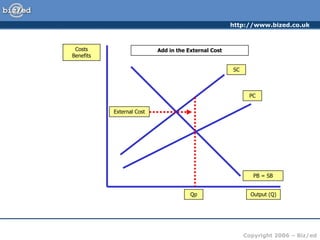
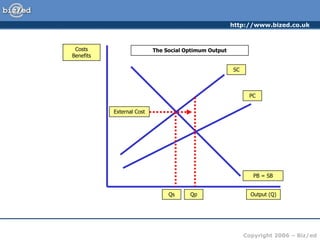
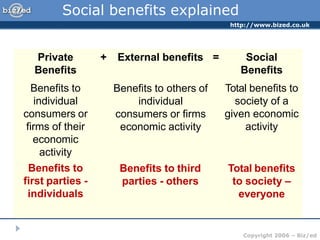
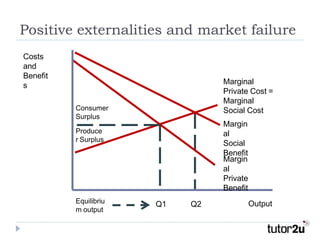
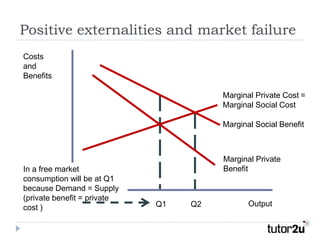
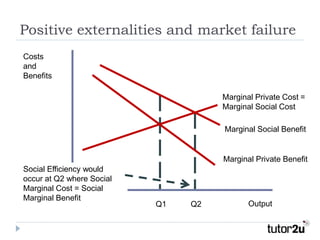
This document discusses positive and negative externalities and how they can lead to market failures. It defines externalities as unintended impacts of economic activity on third parties. Positive externalities provide benefits to others, while negative externalities impose costs on others. The market equilibrium is inefficient when externalities are present because private costs and benefits diverge from social costs and benefits. When there are negative externalities, the competitive market will produce too much of a good, and when there are positive externalities it will produce too little. Government intervention may be needed to correct for market failures from externalities.