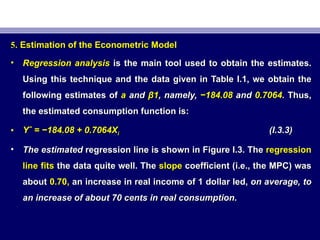
This document discusses the methodology of econometrics. It begins by defining econometrics as applying economic theory, mathematics and statistical inference to analyze economic phenomena. It then outlines the typical steps in an econometric analysis: 1) stating an economic theory or hypothesis, 2) specifying a mathematical model, 3) specifying an econometric model, 4) collecting data, 5) estimating parameters, 6) hypothesis testing, 7) forecasting, and 8) using the model for policy purposes. As an example, it walks through Keynes' consumption theory using U.S. consumption and GDP data to estimate the marginal propensity to consume.