The document discusses key concepts in welfare economics including consumer surplus, producer surplus, market efficiency, and the deadweight loss from taxation. It explains that:
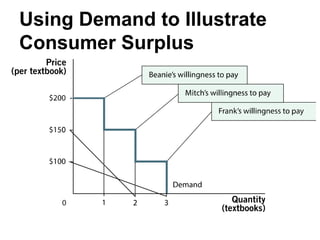
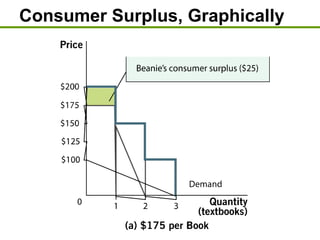
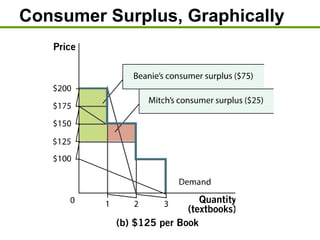
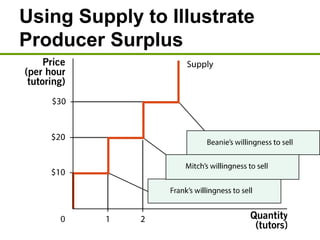
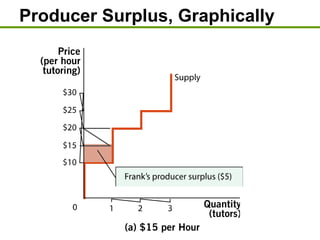
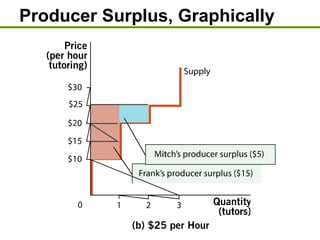
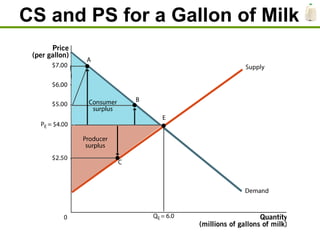
1) Consumer surplus is the difference between what consumers are willing to pay and the actual price paid, while producer surplus is the difference between the price received and the lowest price producers are willing to accept.
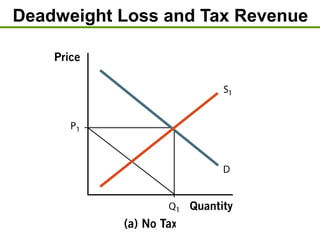
2) A market is efficient when it maximizes total surplus, the sum of consumer and producer surplus.
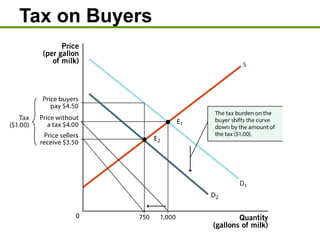
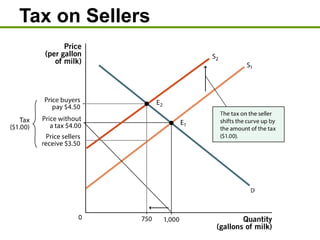
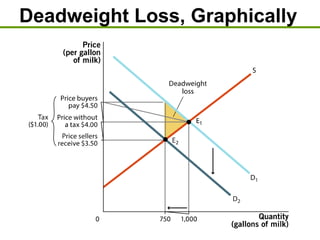
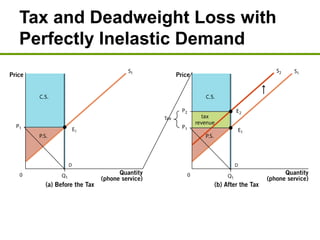
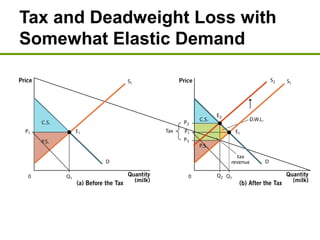
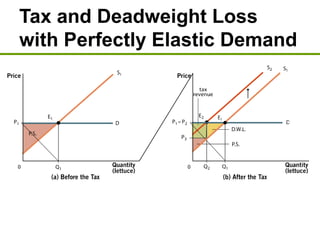
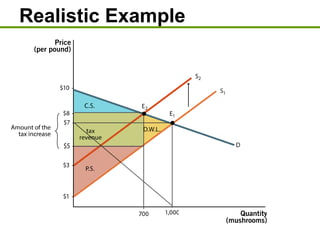
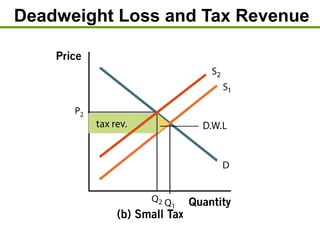
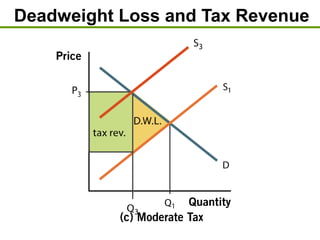
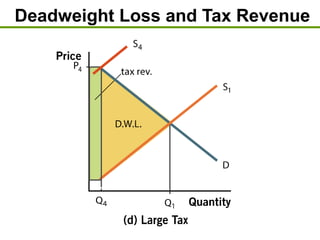
3) Taxes create deadweight loss, which is a loss of total surplus, by reducing the quantity of goods traded and moving the market away from the efficient equilibrium. The deadweight loss is largest when demand and supply are more elastic.