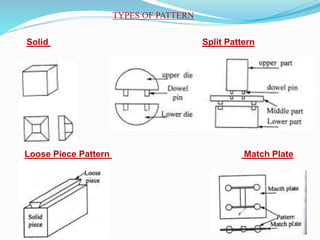
Sand casting is a process for producing metal parts by pouring molten metal into a sand mould cavity of the required shape. Patterns are used to form the cavity and are made from materials like wood, metal or plastic. Moulding sand properties like permeability and strength are tested. Molten metal is produced using furnaces like cupolas or crucibles. Special casting processes include shell moulding, investment casting, die casting and centrifugal casting. Cores are also used to create internal features and are made from mixtures of sand and binders.