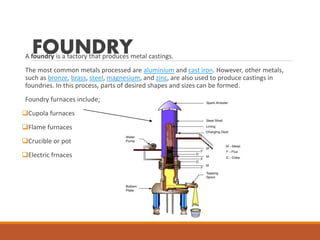
The metal casting process involves melting metal and pouring it into a mold to solidify into the shape of the mold cavity. Key steps include pattern making to create a physical model, core making to form interior surfaces, molding to prepare the mold, melting and pouring the molten metal, cleaning the casting, and inspecting the final product. Various sands are used in the molding process and properties like permeability and strength are important. The gating system delivers molten metal to the mold cavity uniformly during solidification. Foundries produce metal castings using furnaces and casting can have defects from stresses, shrinkage, gas pores, or issues with the mold material.