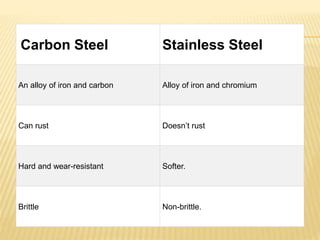
Metallic or non-metallic elements are added to base metals in specified amounts to make alloys with new properties. This process is called alloying. Alloying elements include aluminum, boron, chromium, cobalt, copper, manganese, nickel, silicon, titanium, tungsten, vanadium, and zirconium. Alloys have superior qualities like corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, hardness, or strength compared to base metals. Common alloys used in daily life include those used in kitchen utensils, vehicles, computers, phones, and medical and engineering equipment. Steel is an important alloy of iron and carbon, and different amounts of carbon or additional alloying elements give steel properties suitable for different applications.