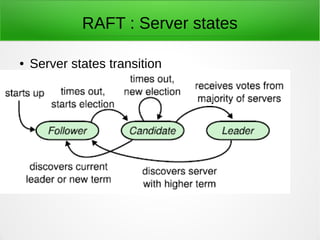
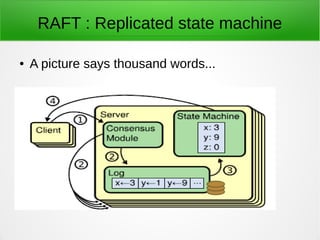
This document discusses distributed systems and consensus algorithms. It covers the CAP theorem, which states that a distributed system can only provide two of three guarantees: consistency, availability, and partition tolerance. The document then discusses challenges in designing distributed systems without a metadata server or with a single metadata server. It introduces the RAFT consensus algorithm, which uses leaders and log replication to achieve consensus. RAFT elects a single leader per term and uses heartbeat messages to ensure the leader remains active. The document concludes by discussing etcd, an open-source distributed key-value store based on RAFT that provides a consistent data store for distributed applications and services.