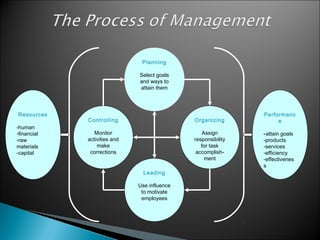
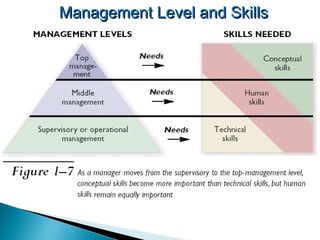
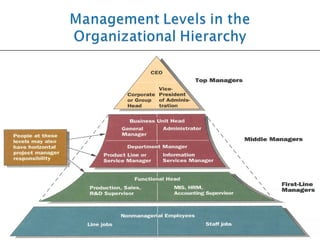
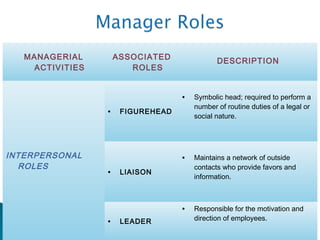
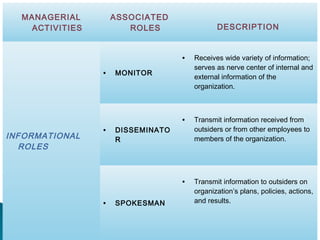
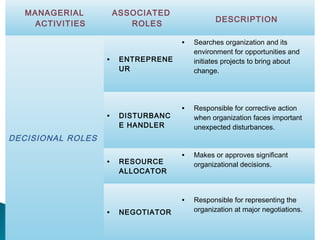
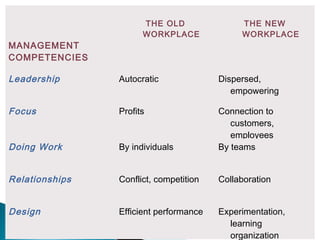
The document discusses the fundamental functions and concepts of management, including planning, organizing, leading, and controlling resources to achieve organizational goals. It outlines the different management levels, associated roles, and essential skills such as conceptual, human, and technical skills. Additionally, it contrasts characteristics of traditional and modern workplaces, emphasizing the shift towards flexible, empowered work environments driven by technology and collaboration.