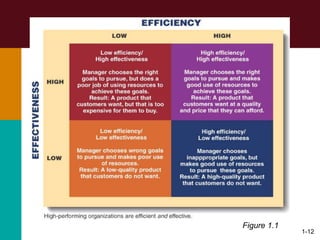
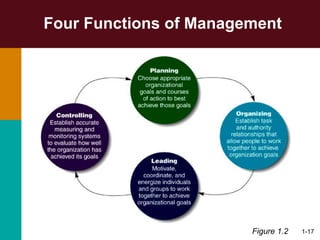
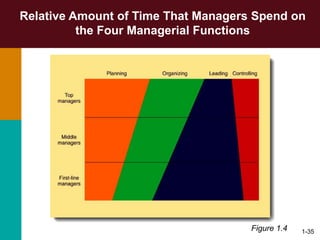
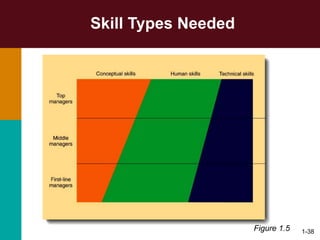
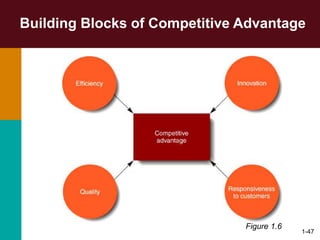
This document discusses the key concepts in management. It defines management as the planning, organizing, leading, and controlling of organizational resources to achieve goals. Managers perform four principal tasks: planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. There are three levels of management - first-line, middle, and top. Managers require three types of skills: conceptual, human, and technical. The biggest challenges for management in a global environment include building competitive advantage, maintaining ethical standards, and managing a diverse workforce.