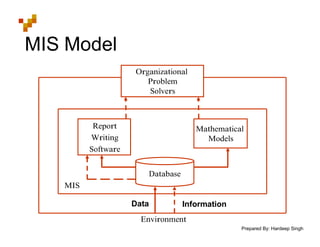
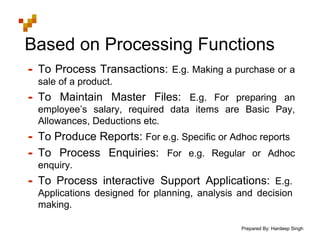
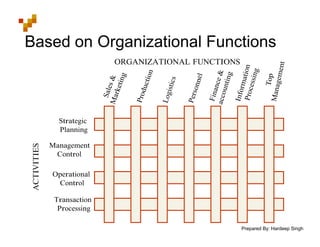
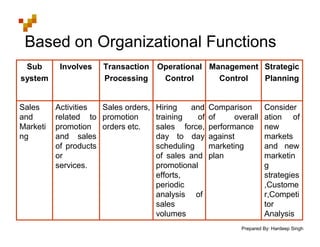
The document defines Management Information Systems and describes their key components and functions. MIS integrates computer hardware, software, databases, and users to provide information support to management functions like operations, analysis, and decision-making. It discusses the types of reports MIS provides managers, the inputs and outputs of MIS, and how MIS supports different levels and functions of management.