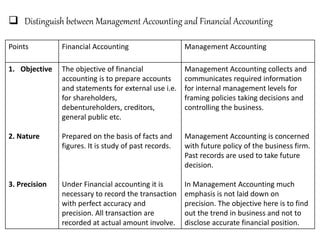
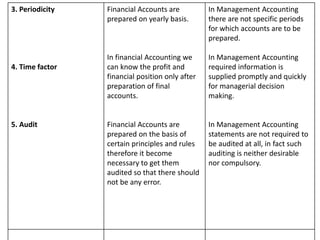
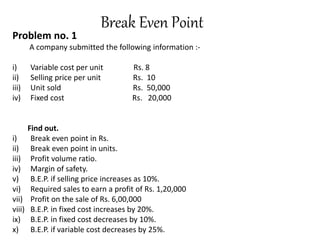
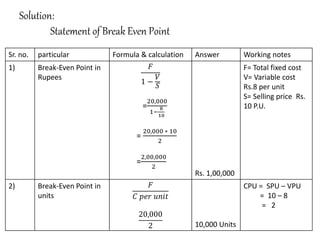
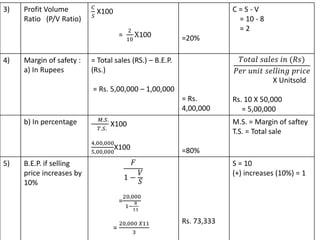
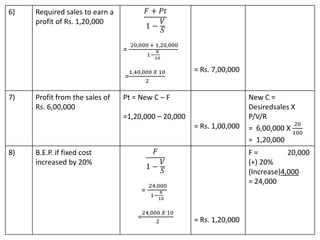
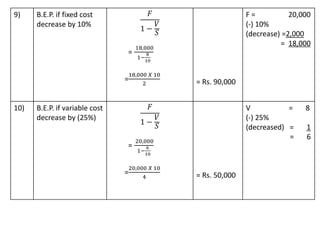
This document discusses management accounting and break-even analysis. It defines management accounting as accounting that enables efficient business operations through collecting and communicating internal information for management decision making. The document outlines the functions of management accounting as including data recording, interpretation, communication, planning, organizing, controlling, and decision making. It then provides an example break-even analysis problem calculating the break-even point in rupees and units, profit-volume ratio, margin of safety, and how these change with variations in selling price, fixed costs, and variable costs. The example problem is worked through in detail across 10 parts to demonstrate different aspects of break-even analysis.