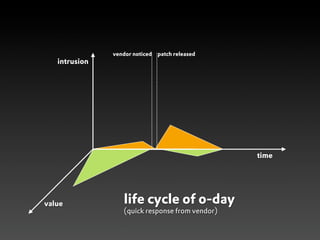
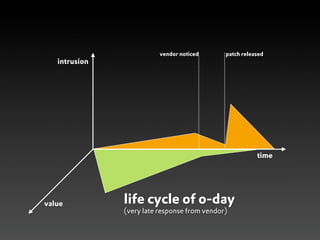
This document discusses zero-day vulnerabilities and the zero-day market. It describes what a zero-day is, how they are obtained and traded, various players in the zero-day industry, and programs that pay for the discovery and disclosure of zero-days. The document also notes that many security companies acquire startups to expand their solutions, and while companies invest in security, common issues still exist like weak passwords and misconfigurations.