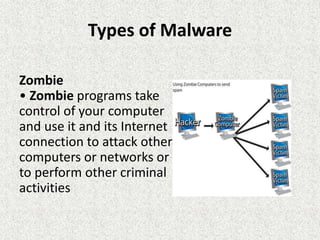
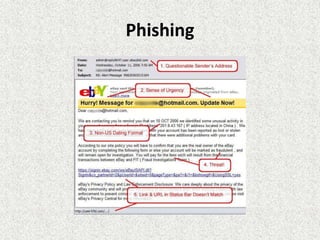
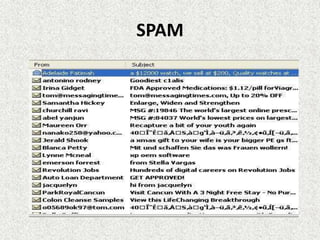
Malware comes in many forms and is used to disrupt computers or steal information. It can appear as viruses, Trojan horses, worms, spyware, or ransomware. Viruses replicate and spread while worms use networks to spread. Trojan horses masquerade as useful programs but compromise security. Spyware and ransomware collect users' private information or lock their devices until ransoms are paid. Malware is a serious threat that users must protect themselves from using anti-malware software.