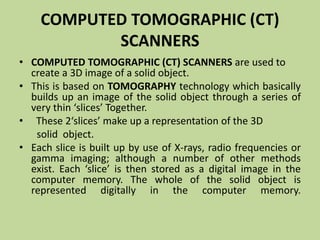
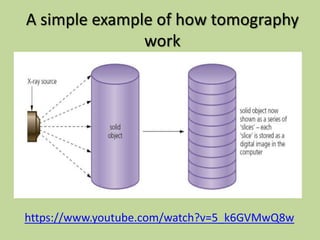
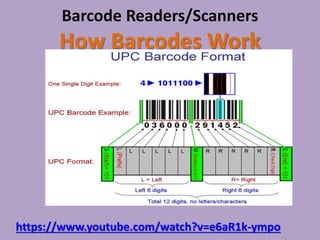
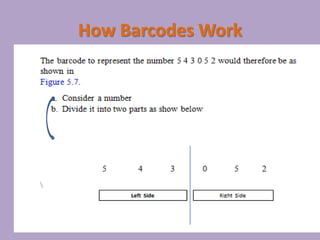
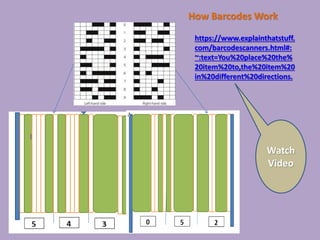
3D scanners scan solid objects and produce three-dimensional images by capturing x, y, and z coordinates of multiple points on the object's surface. These scans can be used in computer-aided design (CAD) programs for engineering and design work. 2D scanners are commonly used at airports to scan passports and capture traveler photos using optical character recognition and facial recognition technology. Computed tomography (CT) scanners build 3D images of solid objects through multiple thin "slices" captured using x-rays, radio frequencies, or other methods. Barcode scanners and readers use cameras and decoding software to interpret dark and light lines in barcodes as numeric data, allowing automatic identification and tracking of products and other