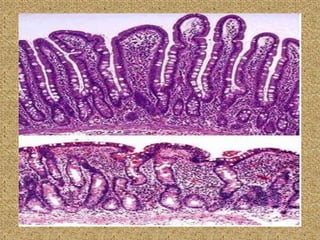
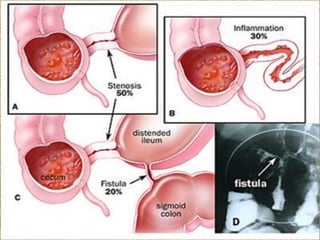
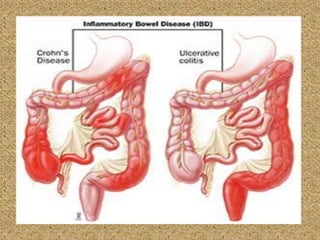
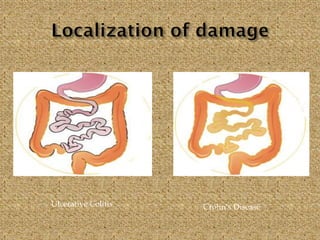
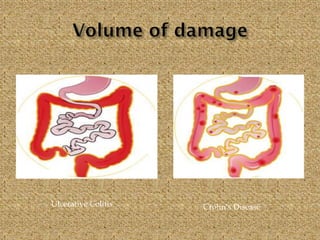
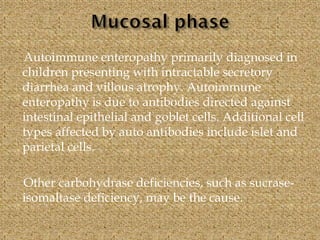
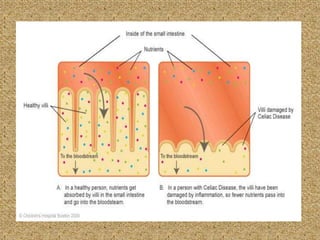
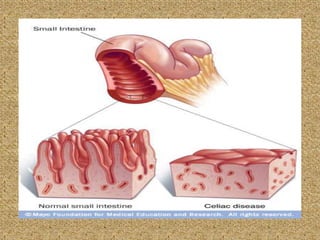
Celiac disease is an immune-mediated disorder caused by a permanent gluten intolerance that primarily involves the small intestine. It is characterized by chronic inflammation of the small intestine's mucosa and submucosa. Genetic factors like HLA-DQ2 and DQ8 increase risk, and it is associated with other autoimmune disorders like type 1 diabetes, thyroid disease, and rheumatoid arthritis. The triggers are immunogenic peptides in gluten that are resistant to digestion and cause an immune response and damage to the intestinal lining.


















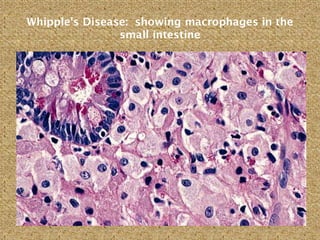
![ Obstruction of the lymphatic system, both
congenital (eg, intestinal lymphangiectasia,
Milroy disease) and acquired (eg, Whipple
disease, neoplasm [including lymphoma],
tuberculosis), impairs the absorption of
chylomicrons and lipoproteins and may cause
fat malabsorption or a protein-losing
enteropathy.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biology-140312170709-phpapp01/85/Malabsorption-Syndrome-20-320.jpg)






































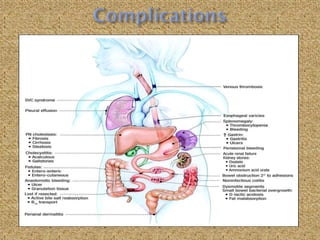
![ Osteopenia and osteoporosis (prevalence 1-
34%) might cause bone pain for several
reasons, including defective calcium transport
by the diseased small intestine, vitamin D
deficiency, and binding of luminal calcium and
magnesium to unabsorbed dietary fatty acids.
Neurologic symptoms (frequency 8-14%) that
result from hypocalcaemia include motor
weakness, paresthesias with sensory loss, and
ataxia. Seizures might develop because of
cerebral calcifications.[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biology-140312170709-phpapp01/85/Malabsorption-Syndrome-61-320.jpg)