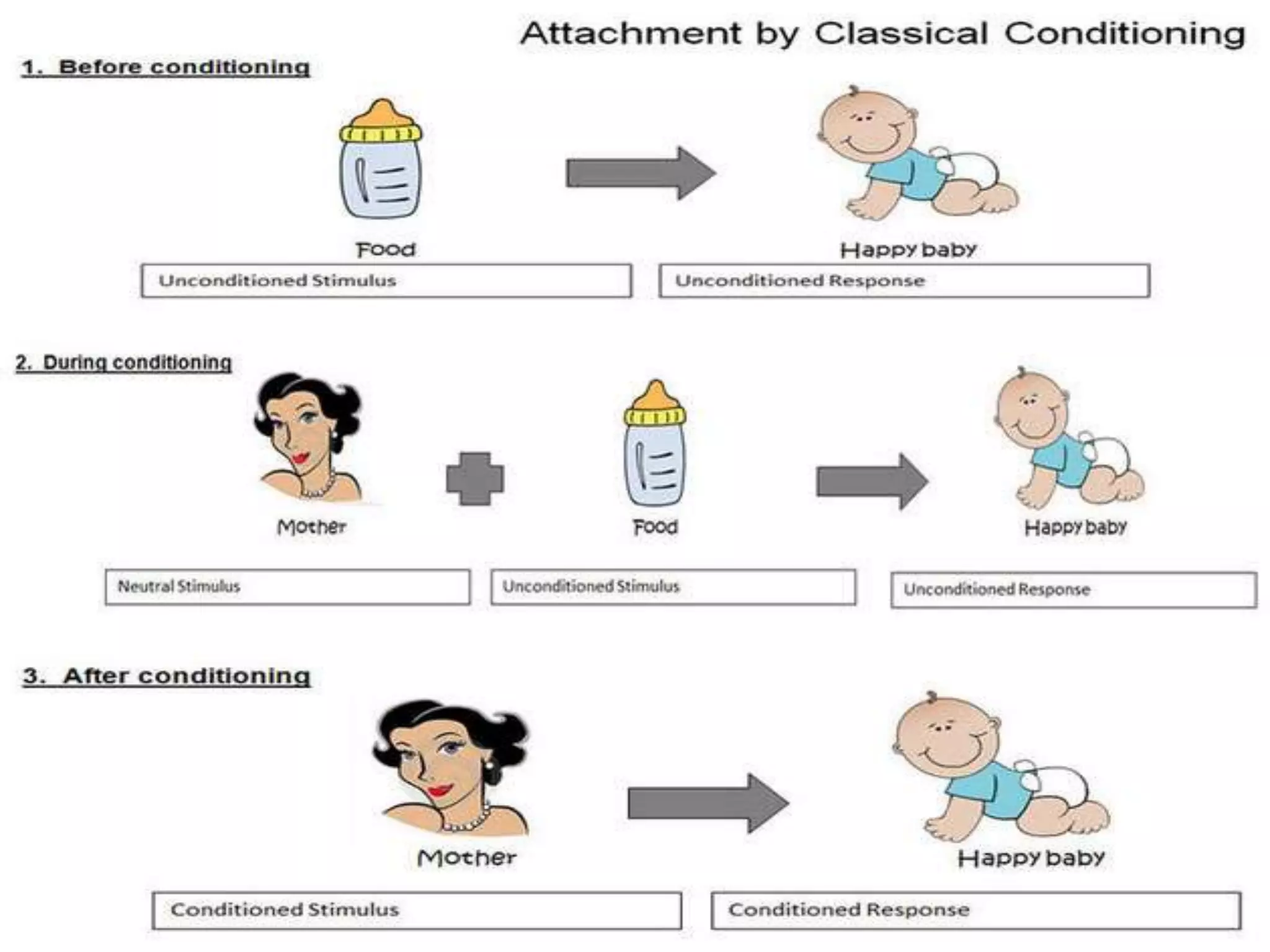
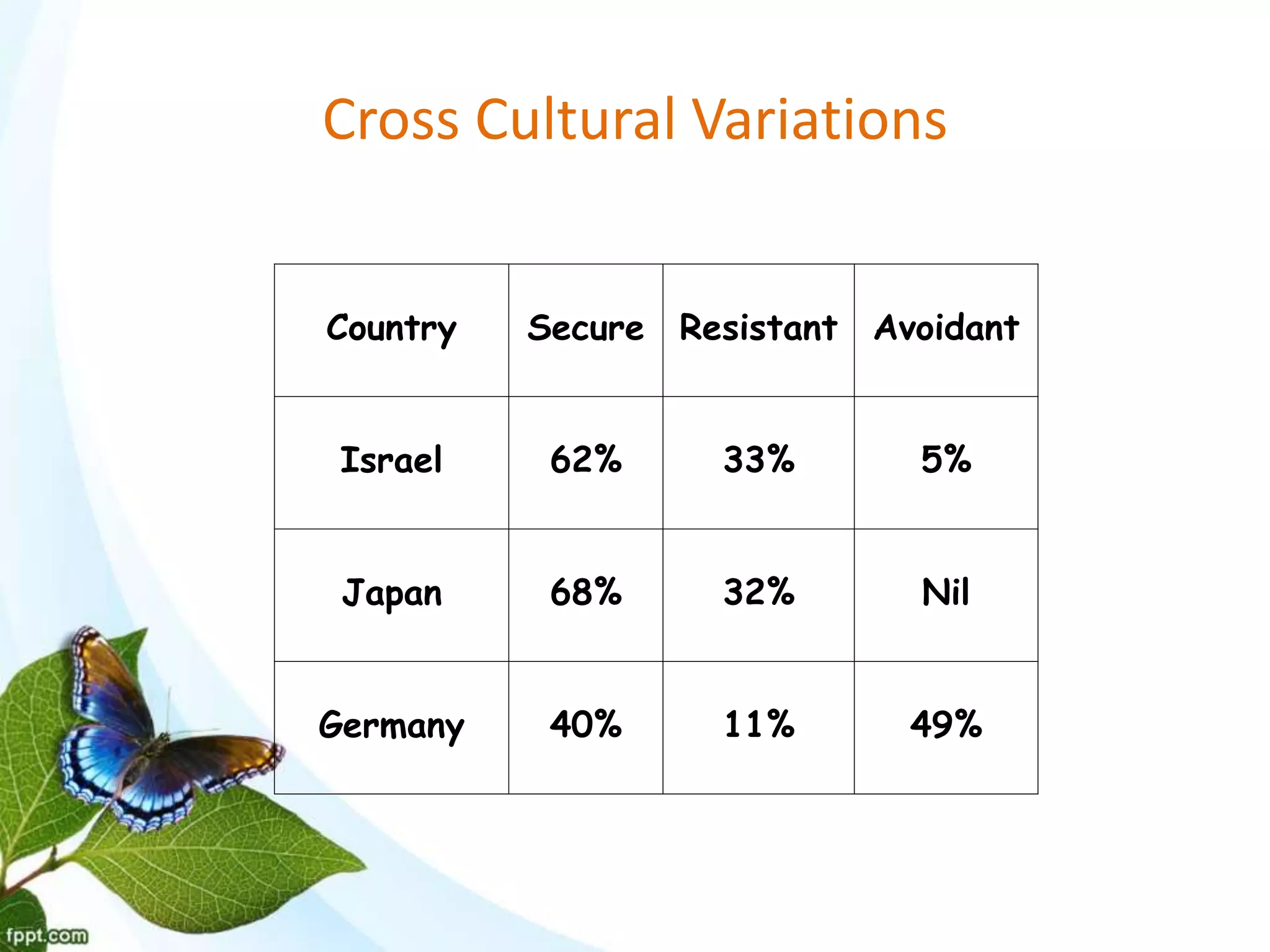
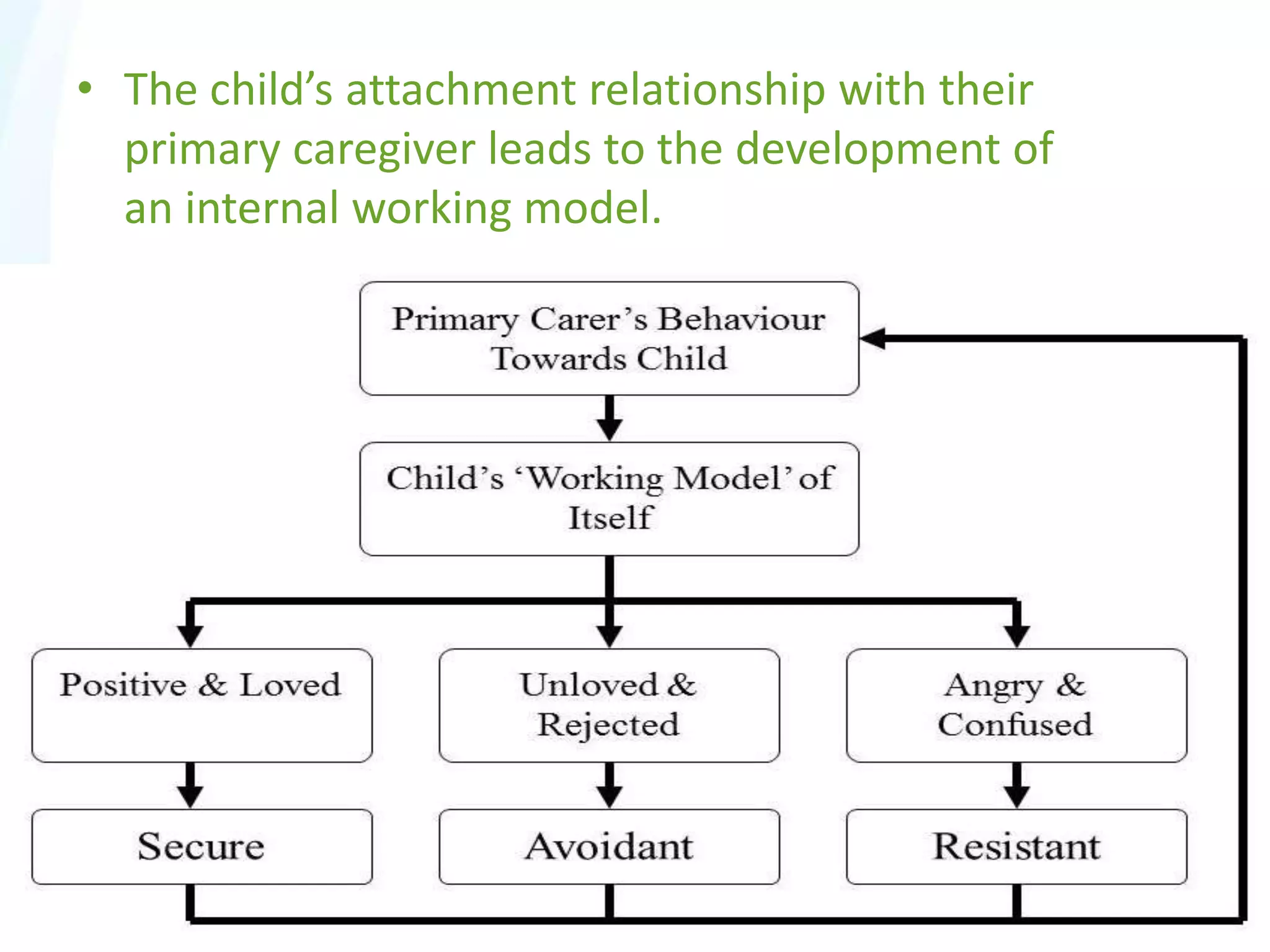
This document discusses maternal attachment and attachment theory. It defines attachment as a deep emotional bond between people that develops through caregiving behaviors and influences social and cognitive development. Attachment theory proposes that children have an innate need to attach to a primary caregiver, usually the mother, for security, exploration and emotional regulation. The quality of this early attachment relationship influences later relationships and development. Studies using the Strange Situation Procedure identified secure, avoidant and ambivalent attachment styles in children based on their behaviors when separated from and reunited with their mothers.