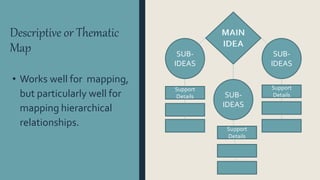
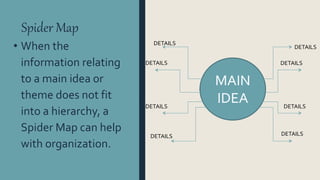
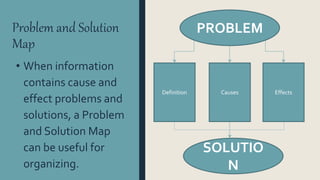
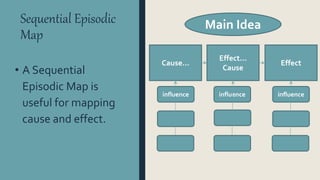
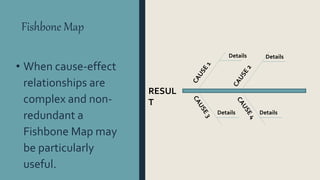
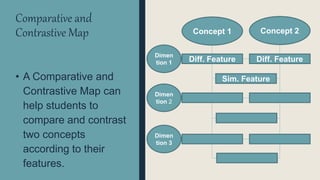
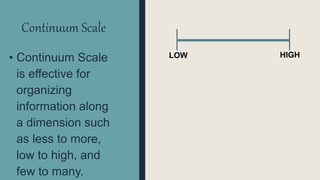
Graphic organizers are visual displays that show relationships between facts, ideas, and terms. They include knowledge maps, concept maps, story maps, cognitive organizers, advance organizers, and concept diagrams. Different types of graphic organizers are useful for different purposes. A sequential episodic map is useful for mapping cause and effect relationships. A continuum scale organizes information along a dimension from low to high. A descriptive or thematic map works well for hierarchical relationships. A spider map can help organize information that does not fit into a hierarchy relating to a main idea.